![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
547 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the structural levels of organization?
|
Atoms~Molecules~Organelles~tissues~organs~systems
|
|
|
What are the 4 basic biomolecules
|
1- Carbohydrates 2 - Proteins 3 - Lipids 4 - Nucleic Acids
|
|
|
What is the difference between essential and nonessential amino acids
|
Essential - Need to be included in the diet; Nonessential - can be found or created in the body
|
|
|
What are the 3 polysaccharides (complex sugars)
|
1- Starch (plants) 2- Glycogen (liver) 3- Cellulose (cant eat)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How are carbs and proteins broken down
|
Proteins - Amino Acids Carbs - mono, di and poly saccharides
|
|
|
What bonds with Adenine
|
Thymine
|
|
|
What bonds with Cytosine
|
Guanine
|
|
|
Atomic #
|
# of protons in an atoms nucleus
|
|
|
amphipathic
|
both hydrophobic and hydrohilic
|
|
|
amino acid
|
20; elements of protein; building blocks of protein
|
|
|
peptide bond
|
Covalent bonds located between amino acids.
|
|
|
RNA
|
Nucleic acid found both in the nucleus and cytoplasm of cells! Inside and outside nucleus & in Ribosomes Functions in protein synthesis
|
|
|
DNA
|
– Genetic material carries “blueprint” of the body. responsible for chemical properties of genes! In chromosomes in cell nucleus
|
|
|
protein
|
Large molecules formed by linkage of amino acids by peptide bonds.
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the plasma membrane
|
Structure: lipid bilayer; proteins and cholesterol..... Function: Maintains boundary and cell structure
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the nucleus
|
Structure: surrounded by double layered nuclear envelope; Function: houses DNA which dictates cell function and protein synthesis
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Nucleolus?
|
Structure: dark oval structure inside nucleus; Function - synthesis of ribosomal RNA
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Cytosol
|
Structure: Gel like fluid; Structure - cell metabolism; storage; fluid
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Rough ER
|
Structure: continues with nuclear envelope flattened sacs with ribosomes; Function - protein synthesis and post translation processing
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Smooth ER
|
Structure: continues with rough er tubular structure with NO ribosomes; Function: lipid synthesis and post transitional pocessing of proteins; transport of molecules from ER To Golgi
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Golgi
|
Structure: series of flattened sacs near ER; Function: post transitional processing; packaging; sorting of proteins
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Mitochondria
|
Structure: oval shaped; folds called cristea that project into the matrix Function: ATP synthesis
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Lysosomes
|
Structure: granular; sac like; scattered through cytoplasm; Function: Break down of cellular and extracellular debris
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Ribosomes
|
Structure: granular; organelles composed of proteins and rRNA; located in cytosol or on surface of rough ER Function: Protein Synthesis
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the Centrioles
|
Structure: 2 cylinder bundles of protein filaments perpendicular to each other Function: direction of mitotic spindle; development during cell division
|
|
|
What is the function and structure of the cytoskeleton
|
Structure: Composed of protein filaments, including micro filaments intermediate filaments and micro tubules Function: Structural support of cell, cell movement and contraction
|
|
|
What are the main features of a prokaryotic cell
|
No nucleus; Bacteria; Small; Simple; No Membrane Bound Organelles
|
|
|
What are the main features of a eukaryotic cell
|
All other forms of life; plants - fungi- animals- protazoa
|
|
|
organelle
|
Any of many cell organs or organized structures. Example: ribosome or mitochondrion.
|
|
|
What is the atomic #
|
# of protons
|
|
|
What are the 4 elements that compose 96% of the body?
|
oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen
|
|
|
What are the special properties of water? (4)
|
1- Polarity 2 - High Specific Heat 3- High Heat of Vaporization 4- Cohesion/Adhesion
|
|
|
What is a compound
|
Composed of 2 or more DIFFERENT elements
|
|
|
What is a molecule
|
2 or more elements together
|
|
|
What is the difference between a cation and an anion
|
Cation is positive! Anion is negative!
|
|
|
What is the atomic weight
|
protons + neutrons in nucleus
|
|
|
If the Hydrogen + ions in a PH solution goes UP then it is
|
Acidic
|
|
|
If the Hydrogen ions decrease then it becomes
|
Alkaline
|
|
|
What is a Covalent Bond
|
Strongest; electrons are shared; (numerous)
|
|
|
What is a ionic bond
|
weak; steal or donate electrons and BECOME ions
|
|
|
What is a hydrogen bond
|
WEAKEST; slight + in hydrogen bc its polar covalent bond and it attracts other weak charges; easy to break; involves hydrogen
|
|
|
What is the difference between a polar and nonpolar covalent bond?
|
Polar - shares electrons UNEQUALLY ; Nonpolar - electrons are equally shared
|
|
|
What is a proton, neutron and electron
|
Proton - positive in nucleus; Electron - negative in orbit; Neutron uncharged in nucleus
|
|
|
pH
|
potential hydrogen; H+ ion concentration of a solution
|
|
|
Isotope
|
same # of protons DIFFERENT # of neutrons
|
|
|
buffer
|
Compound that combines with an acid or a base to form a weaker acid or base. Lessens the change in hydrogen ion concentration.
|
|
|
element
|
pure; Simple form of matter. A substance that cannot be broken down into two or more different substances.
|
|
|
anion
|
negative ion; GAINS electron
|
|
|
ionic bond
|
Formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
|
|
|
cation
|
positive ion; (LOST ELECTRON)
|
|
|
Solvent
|
liquid portion of solution
|
|
|
solute
|
substance that is being dissolved in solution
|
|
|
ion
|
charged particle; lost or gained electron
|
|
|
atom
|
Smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element; particles that combine to form molecules.
|
|
|
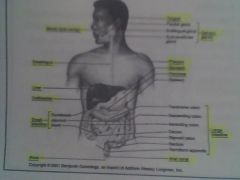
What is in the thoracic cavity
|
Right and Left Pleural Cavity (Lungs) and Mediastinum (Heart, trachea, R & L bronchi, esophagus, thymus gland, aortic arch and thoracic aorta, venae cavae, lymph nodes, thoracic duct)
|
|
|
What is in the abdominopelvic cavity
|
Abdominal Cavity - (liver, gall bladder, stomach, pancreas, intestines, spleen, kidneys, ureters) ~ Pelvic Cavity (urinary bladder, female repro, uterus, uterine tubes, ovaries, male repro, prostate, seminal vesicles, parts of vas def, part of large intestine, sigmoid colon and rectum
|
|
|
What is in the ventral cavity (front)
|
thoracic and abdominopelvic
|
|
|
What is in the dorsal cavity (back)
|
Cranial & Spinal
|
|
|
What is in the cranial cavity
|
Brain in skull
|
|
|
What is in the spinal cavity
|
Spinal column and houses the spinal cord
|
|
|
Anatomy
|
(structure) study of structure of an organism and the relationship of its parts
|
|
|
Physiology
|
(function) study of the functions of the living organism and its parts
|
|
|
Anterior
|
Front "in front of"
|
|
|
Ventral
|
Belly "toward the belly"
|
|
|
Posterior / Dorsal
|
Back or "in back of"
|
|
|
Superior / Cranial
|
towards the head "upper or above"
|
|
|
Inferior / Caudal
|
lower or below (caudal - back, tail)
|
|
|
Medial
|
toards the midline of the body;
|
|
|
Lateral
|
toward the side of the body or away from the midline
|
|
|
Prone position
|
body lying face down
|
|
|
Supine position
|
body lying face up
|
|
|
Anatomical Position
|
The body is in an erect, or standing, posture with the arms at the sides and palms turned forward. Head and feet are also pointing forward.
|
|
|
Proximal
|
Nearest “TOWARD” the trunk or origin (attachment to the body.)
|
|
|
distal
|
Furthest “AWAY” from the trunk or point of origin (attachment to the body.)
|
|
|
superficial / external
|
near the body surface
|
|
|
deep / internal
|
farther away from the body surface;
|
|
|
saggital plane
|
front to back; divides body into RIGHT and LEFT sides
|
|
|
frontal plane (coronal)
|
length side to side; anterior and posterior (front/back)
|
|
|
transverse/horizontal/cross sectional plane
|
divides the body (or any parts) into upper and lower parts.
|
|
|
parasaggittal
|
A cross section through the body (or any part) in the sagittal vertical plane parallel to the median plane. Sectioning in the sagittal plane results in a right and a left portion, an anatomical parasagittal section may be a two-dimensional view of the cut surface.
|
|
|
Name all the systems of the body
|
Integumentary~Skeletal~Muscular~Nervous~Encodrine~Cardiovascular~Lymphatic~Respiratory~Digestive~Urinary~Reproductive~Immune
|
|
|
What is the function of the integumentary system
|
skin ~ separates internal environment from external
|
|
|
What is the function of the skeletal system
|
supports, protects, and moves body
|
|
|
What is the function of muscular system
|
powers and directs skeletal movements
|
|
|
What is the function of the nervous system
|
regulatory system - senses changes, integrates and sends signals to effectors.
|
|
|
What is the function of the endocrine system
|
regulates internal enviroment by secreting hormones through blood to target area
|
|
|
What is the function of the lymphatic system
|
drains excess fluid from tissues, cleans it and returns it to the blood
|
|
|
What is the function of the respiratory system
|
exchanges O2 with CO2 between
|
|
|
What is the function of the digestive system
|
breaks down nutrients from the external environment and absorbs them into the internal environment.
|
|
|
What is the function of the urinary system
|
excretes excess water, salt and other substances
|
|
|
What is the function of the reproductive system
|
produces sex cells to form offspring
|
|
|
What is the function of the immune system
|
defends internal environment against injury from foreign cells and other irritants
|
|
|
What are the 3 monosaccharides (simple sugars)
|
1 - Glucose (G) 2- Fructose (F) 3 - Galactose (Ga)
|
|
|
What are the 3 disaccharides (double sugars)
|
1 - Sucrose (G+F) 2- Lactose (G+Ga) 3- Maltose (G&G)
|
|
|
lipid
|
Organic compounds including: fats, oils, and other substances.; water insoluble (fat) biomolecules; do not dissolve bc its nonpolar
|
|
|
nitrogenous bases
|
A molecule that contains purines and pyrimidines. Nitrogen based.
|
|
|
steroids
|
Lipids related to Sterols and forming reproductive and adrenal hormones.
|
|
|
nucleotide
|
5 carbon sugar, nitrogenous base, and phosphate group
|
|
|
carbohydrate
|
Organic compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in certain specific proportions; For example, sugars, starches, and cellulose.
|
|
|
triglyceride
|
Lipid that's synthesized from fatty acids & glycerol or excess glucose or amino acids. Stored mainly in adipose tissue cells.
|
|
|
phospholipid
|
Lipid made up of glycerol and fatty acids, with a phosphate group attached.
|
|
|
cholesterol
|
Steroid lipid found in many body tissues and in animal fats.
|
|
|
nucleic acid
|
Any organic compounds composed of nucleotides. RNA and DNA
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion
|
another molecule (like insulin) helps something (like glucose) move across a membrane PASSIVE
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
movement of H20 from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a semi-permeable membrane. Down gradient; PASSIVE
|
|
|
Active Transport
|
moves against gradient - PumP; ACTIVE
|
|
|
Exocytosis
|
bringing something out of the cell- (think unswallowing lol - reverse endocytosis)
|
|
|
Endocytosis
|
Bringing in something by surrounding it - swallowing
|
|
|
Phagocytosis
|
FOOD to eat;
|
|
|
Pinocytosis
|
cell DRINKING
|
|
|
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis
|
(activators) something must sit on receptor to start the process of surrounding it
|
|
|
Hypertonic
|
Cell has more liquid; sucks OUT of cell; Shrink - crenate
|
|
|
Hypotonic
|
cell less than the liquid; sucks INTO the cell from the osmostic pressure; swell- lyse
|
|
|
Isotonic
|
same pressure in cell and in the solution; no change in cell size
|
|
|
transcription
|
involves DNA in nucleus- gives message to mRNA to leave and GO into the CYTOSOL
|
|
|
translation
|
mRNA and tRNA putting the message together IN CYTOSOL
|
|
|
What 3 factors affect the rate of enzyme activity
|
temp, pH and inhibitors
|
|
|
composition of an enzyme and its special characteristics
|
proteins (amino acids) active site where substrate bonds; makes and breaks bonds
|
|

|
Hypertonic - it will crenate shrink
|
|

|
Hypotonic - swell lyse
|
|

|
Isotonic - no change
|
|
|
Describe the following action of an enzyme: E + S --> ES --> P + E
|
Enzyme + Substrate --> Enzyme Substrate Complex -->Product- & Release of Product
|
|
|
Where in the cell does glycolysis happen?
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
Where in the cell does the Kreb cycle happen? (TCA/Citric Acid cycles)
|
matrix of mitochondria
|
|
|
Where in the cell does Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phsophorylation take place?
|
accross inner mitochondrial membrane; (oxi - puts the phospate back on ATP)
|
|
|
Which biomolecules make ATP
|
proteins (amino acids), carbs (monos), fats (lipids, fatty acids)
|
|
|
What is the last electron acceptor in the electron transport chain
|
oxygen
|
|
|
What is a solvent and solute?
|
Solute – Dissolved particles in a solution.
Solvent – Liquid portion of a solution in which the solute is dissolved. |
|
|
Denature
|
enzyme no longer functional. To alter the shape of a protein by change in pH, heat, or another manner to change its chemical properties.
|
|
|
What is hydrophilic and hydrophobic?
|
Hydrophobic – Water-fearing.
Hydrophilic – Water-loving. |
|
|
Diffusion
|
Natural phenomenon caused by the tendency of small particles to spread out evenly within any given space. ?Diffusion – Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration;
|
|
|
Lyse
|
explode
|
|
|
crenate
|
shrink - shrivel
|
|
|
cytosol
|
gel like fluid outside of cell
|
|
|
Centromere
|
Bead-like structure that attaches one chromatid to another during the early stages of mitosis.
|
|
|
catalyst
|
Chemical that speeds up reactions without being changed itself
|
|
|
Nucleotide
|
5 Carbon sugar, phosphate base, nitrogen base
|
|
|
enzyme
|
proteins; chemical catylstt (speed up reaction), shape is key, makes or breaks a bond; reusable; specific
|
|
|
Ribosome
|
Organelle in the cytoplasm of the cells that synthesizes proteins.
|
|
|
mRNA –
|
Messenger RNA; single unfolded strand of nucleotides; serves as a working copy of one protein-coding gene. Template for protein synthesis; the form of RNA that carries information from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome sites.
|
|
|
tRNA
|
tRNA – Transfer RNA; single, folded strand of nucleotides; has an anticodon at one end and an amino acid-binding site at the other end; carries a specific amino acid to a specific codon of mRNA at the ribosome during translation.
|
|
|
rRNA
|
rRNA – Ribosomal RNA; single, folded strand of nucleotides; Component of the ribosome (along with proteins); attaches to mRNA and participates in translation.
|
|
|
anti codon
|
3 base seq in tRNA (binds to a corresponding codon in mRNA and designates a specific amino acid during protein synthesis)
|
|
|
codon
|
3 sequence base in mRNA; (determines the position of amino acid in a protein molecule during protein synthesis.)
|
|
|
triplet
|
3 base sequence DNA
|
|
|
simple diffusion
|
Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
|
|
|
Fibroblast
|
makes connective tissue (proper) ; When dormant it is a fibrocyte
|
|
|
Collagen Fibers
|
WHITE FIBERS; Thick fibers (tough and strong & give high tensile strength)
|
|
|
Chondroblast
|
(cartilage) A cell of growing cartilage tissue.
|
|
|
Elastic Fibers
|
( yellow fibers) bundles of proteins (elastin) of connective tissue (Stretch and Recoil-skin)
|
|
|
Reticular Fibers
|
Delicate fibers; made of collagen: reticulin; occur in small networks such as capillaries and nerve fibers.
|
|
|
Alopecia
|
Loss of hair; baldness.
|
|
|
macrophage
|
Phagocytic cell in the immune system; engulf foreign material (bacteria & dead cells) and their inner lysomes desolve it.
|
|
|
Lacunae
|
A space, gap, or a missing part.
|
|
|
Mast Cell
|
releases histamine & heparin; Immune system cell to which antibodies become attached in early stages of inflammation. (cx capillaries to become more leaky so WBC can fight infection)
|
|
|
Plasma Cell
|
formed from B Lymphocyte & secrete antibodies; immune system cell that produces antibodies against specific antigents.
|
|
|
Chondrocytes
|
Cartilage cell.
|
|
|
Keratin
|
Tough, fibrous protein substance in hair, nails, outer skin cells, and horny tissues.
|
|
|
Melanin
|
Brown pigment primarily in skin and hair.
|
|
|
Ceruminous Gland
|
Gland that produces earwax. (waxy substance called cerumen)
|
|
|
Eccrine Sweat Gland
|
MOST ABUNDANT; palms, soles of feet, and forehead; Ducts empty on SURFACE;
|
|
|
Apocrine Sweat Gland
|
Sweat glands located in axillae (armpit) & genital regions; begin to function at puberty; Ducts empty into HAIR FOLLICE
|
|
|
Sensible Perspiration
|
The perspiration excreted in large quantity; appears as moisture on the skin.
|
|
|
Insensible Perspiration
|
the loss of body fluid by evaporation. (B4 perceived as moisture on skin)
|
|
|
1) List four major types of tissue:
|
Epithelial, Connective, Musclar, and Nervous
|
|
|
2) Features of the epithelial tissue
|
Close together and covers linings.
|
|
|
3) What is the function of cillia and microvilli? And what type of tissue and location can each be found in?
|
Cilia – Found in Pseudo columbnar– (trachea)Function: Extracellular movement
Microvilli – Found in Simple Columnar (intestine)– Function: Absorbtion |
|
|
4) two basic classification of epithelial tissue:
|
shape and layers
|
|
|
6) What are the general features of connective tissue:
|
1) Ground Substance 2) Fibers 3) Cells
|
|
|
8- 2 ways fluid is lost through intact skin
|
Sensible & insensible Perspiration
|
|
|
8) Know six general functions of the skin:
|
Protection
Temperature Regulation Excretion Metabolic Function Sensation Blood Reserve (Please Take Every Movie Subject Back) |
|
|
9) Know the general functions of the dermis: (Ask Instructor what she wants us to know
|
Blood Supply, support, protection and sensory
|
|
|
Simple Squamous Epithelial (L&F)
|
–Location: alveoli (lung) – Function: Diffusion
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial
|
Location: kidney tubules; glands – Function: Secretion & Absorption
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelial
|
Location: small intestine – Function: Secretion & Absorption ( can have microvilli or cillia)
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial–
|
Location: trachea – Function: Secretion & Propulsion of mucus with cilia
|
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelial
|
Location: Esophogus, mouth, vagina– Function: Protection
|
|
|
Fibrous (Connective Tissue Proper)
|
Location: Dermis – Function: Support
|
|
|
Bone Tissue F&L
|
Bone – Location: Skeleton (outer shell of bones) – Function: Support
|
|
|
Cartilage tissue F&L
|
Location: Part of the nasal septum – Function: Firm, flexible support
|
|
|
Blood F&L
|
Location: In the blood vessels – Function: Transportation & Protection
|
|
|
Areolar
|
F: Cushions organs & support/protection; L- around (packaging organs) & under epidermis
MOST ABUNDANT CONNECTIVE TISSUE |
|
|
Adipose Tissue F&L
|
L: under skin, eyeballs, breast F: reserve food fuel
|
|
|
Dense regular conn. Tissue
|
L: tendons & ligaments F: Muscle to Bone; Bone to Bone
|
|
|
Dense irregular
|
L dermis of skin F protection/ strength in all directions
|
|
|
Hyline (cartilage)
|
F: supports and reinforces L: costal cartilage of rubs; embryonic skeleton
|
|
|
Axial
|
central skeleton; skull - auditory ossicles - hyoid bone - ribs - sternum- vertebral column; 80 Bones
|
|
|
Appendicular
|
bones of the upper and lower extremities and they connect to the axial (126 bones)
|
|
|
osteoprogenitor
|
(osteogenic) unspecialized; mitotic potential; differentiate into osteoblasts; (embryonic connective tissue)
|
|
|
osteoblasts
|
(bone generators) bone forming; NO mitotic potential; associated with bone formation; (secretes collagen fibers)
|
|
|
osteocyte
|
(mature bone cell) main cells in bone tissue; NO mitotic potential;
|
|
|
osteoclast
|
(bone breakers) has mitotic potential; breaks down bone
|
|
|
Diaphysis
|
shaft of long bone
|
|
|
Endosteum (of diaphysis in long bone)
|
(with in the bone) thin connective tissue covers internal bone surface; contains osteoblast and osteoclast
|
|
|
Periosteum (of diaphysis in long bone)
|
(around the bone) 2 layers; vascular and has nerves; contains osteoblasts, osteocytes
|
|
|
Epiphyseal plate (of diaphysis in long bone)
|
Cartilage plate b/t diaphysis & epiphyses; upper portion of bone in length by hyline cartilage (18 female 21male)
|
|
|
medullary cavity
|
hollow in diaphysis (marrow cavity) - made of conn. fat tissue = yellow marrow
|
|
|
canaliculi
|
channels where osteocytes meet to exchange waste, O2 and nutrients
|
|
|
epiphyses
|
both ends of the long bone
|
|
|
calcitonin
|
hormone secreted by thyroid; decrease blood calcium
|
|
|
parahormone
|
hormone by parathyroid; increase blood calcium
|
|
|
resorption
|
bone is being broken down by osteoclasts
|
|
|
What are the differences between intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification.
|
Intra- (skull, clavicle) tough membrane
Endo - rest of bones - hyline cartilage - more common. |
|
|
Compact Bone
|
Dense bone
|
|
|
Spongy Bone
|
Thin, cancellous bone with red marrow.
|
|
|
Osteogenesis
|
Action of osteoblasts & osteoclasts to mold bones into adult shape.
|
|
|
2) Describe the classifications and functions of bones:
|
By shapes: Long bones, Short bones, Flat bones, Irregular bones, and Sesamoid bones.
Functions: Support, Protection, Movement, Mineral storage, Hematopoiesis |
|
|
epimysium
|
surrounds entire muscle organ
|
|
|
perimysium
|
surrounds fascile (bundle) of muscle fibers
|
|
|
endomysium
|
surrounds an individual muscle fiber
|
|
|
sarcolemma
|
muscle cell membrane
|
|
|
sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
myofibrils
|
Bundles of very fine fibers found in skeletal muscle cells.
|
|
|
sarcomere
|
area of muscle cell that contracts
|
|
|
sarcoplasm
|
cytoplasm of muscle cell
|
|
|
myosin heads (cross bridges)
|
(golf clubs) double heads twisted together, active site for ATP during contraction
|
|
|
What are the 3 muscle types? Functions? Location? Are they voluntary? # of nuclei? Striated/Not
|
1- Skeletal - voluntary - multi nuclei - striated
2- Cardiac - involuntary - not multi-nuclei - striated 3 - Smooth - involuntary - not multi-nuclei - NOT striated |
|
|
What is origin and insertion
|
Origin is: broader - proximal and less movable end Insertion is: narrow & distal; connects to something else.
|
|
|
What is the composition of muscle? How many are in the body?
|
75% H2O 20% Protein 5% (Carbs, lipids, inorganic salts) There are more than 600 muscles
|
|
|
How are muscles named?
|
1. Location 2. Shape 3. Relative Size of the muscle 4. Direction of muscle 5. # of origins 6. Location of attachment 7. Action _Locate the shape, and size of the direction; dont forget the origin attachment and action
|
|
|
General Important Features of Muscle Tissue
|
1. Movement 2. Maintain Posture 3. Heat Production 4. Stabilize Joints
|
|
|
Functional Characteristics of Muscle
|
1. Excitability 2. Contractility 3. Extensibility 4. Elasticity
|
|
|
6 Steps of Muscle Contration
|
1. Action potential is generated along the sarcolemma and down the T tubules 2. Action potential triggers CA+ release from the SR 3. Calcium ions bind to tropin- (which then changes its shape removing the blocking action of trpomysin) Actin active site is exposed 4. Contraction; Myosin cross bridges, attach to actin and detach (by pulling the actin filamanets toward the center of the sarcomere); Then it releases energy ATP (hydrolysis) 5. Removal of CA by active transport (pump) into the SR after the action potential ends 6. Tropomyosin blockage restored - blocking actin active site ok; contration ends and muscle fiber relaxes
|
|
|
Tropomyosin
|
Long protein molecule that covers the active site of myosin.
|
|
|
Acetylcholine (ACh)
|
Neurotransmitter at junctions used to stimulate muscle contraction.
|
|
|
Thick (myosin) filament
|
Made up of myosin molecules.
|
|
|
Troponin
|
Protein molecules; small portions attach to G actin and tropomyosin.
|
|
|
G Actin
|
Protein molecule w/an active site that binds to the head of myosin.
|
|
|
Thin (actin) filament
|
Twisted: made up of three proteins (Actin, Troponin, & Tropomyosin.)
|
|
|
What are the structural classifications of joints?
|
Fibrous ~ Cartilaginous ~ Synovial
|
|
|
What are the functional classifications?
|
Synarthroses (immovable) ~ Amphiarthroses (slightly movable) ~Diarthroses
|
|
|
What are the 3 FIBROUS joints
|
Sutures ~ Syndesmoses ~ Gomphoses
|
|
|
What are 2 CARTLAGINOUS joints
|
Synchondroses & Symphyses
|
|
|
What are the Synovial joints
|
Plane/Gliding ~ Hinge ~ Pivot ~ Condyloid ~ Saddle ~ Ball & Socket
|
|
|
Sutures
|
Fibrous; skull; synarthroses
|
|
|
Syndesmoses
|
Fibrous; tibia & fibia; synarthroses
|
|
|
Gomphoses
|
Fibrous; roots of teeth; synarthroses
|
|
|
Synchondroses
|
Cartilaginous; epiphyseal plate (hyline); synarthroses
|
|
|
Symphyses
|
Cartilaginous; invertebral discs, amphiarthroses
|
|
|
How many types of Fibrous joints
|
3
|
|
|
How many types of Cartilaginous joints
|
2
|
|
|
How many Synovial joints
|
6
|
|
|
Plane / Gliding
|
Synovial; betwween carpal bones; Nonaxial
|
|
|
Hinge
|
synovial; Elbow or knee; uniaxial;
|
|
|
Pivot
|
synovial; atlas & axis; uniaxial
|
|
|
condyloid
|
synovial; knuckes; biaxial
|
|
|
saddle
|
synovial; trapezium; biaxial
|
|
|
ball and socket
|
synovial; shoulder/hip; multiaxial
|
|
|
Which tissue lines the trachea and upper respiratory tract?
|
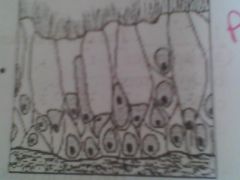
pseudo columbnar
|
|
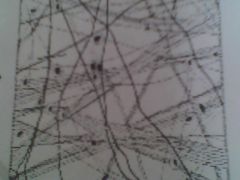
|
Areolar tissue (tic tac toe lines with dots)
|
|

What does this tissue connect to? What type of tissue is it?
|
Dense Regular; (ligaments/tendons); Bone to Bone or Muscle to Bone; Connective (wavey looking)
|
|
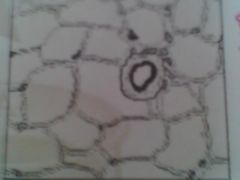
What is this? What type of tissue is it?
|
Adipose tissue; Connective (hypodermis, around kidneys and eyeballs, within the abdomen and breast
|
|
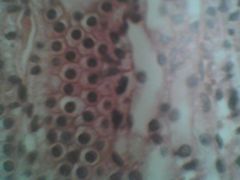
What is this? What type of tissue is it?
|
Simple Cuboidal; Epithelium tissue
|
|
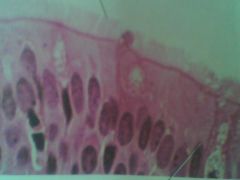
What is this
|
Pseudo Stratified Columbnar
|
|
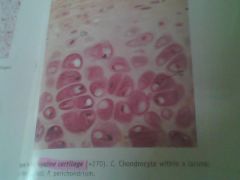
|
Hyline; chondrocytes; lacunae in the spaces between chondros
|
|
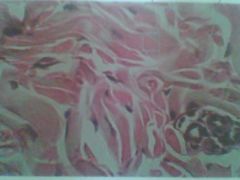
|
Dense IRREGULAR connective tissue; looks petals on a flower
|
|
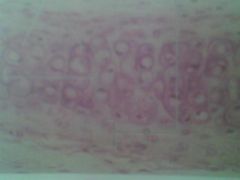
|
Hyline Cartilage
|
|
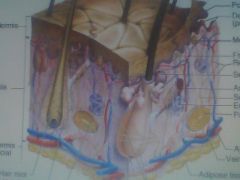
ID- Hair follicle, Meissnar's Corpuscle, Dermal Papilla, Sebaceous Gland, Pacinian Corpuscle, hypodermis, sudoriferous gland, dermis, erector pili muscle
|
Meissnars Corpususcle- Tiny at top left yellow - under papila layer
Pacinian Corpuslce- Onion looking at bottom Sebacous (oil gland)- attached at hair follicle Sudor???? |
|
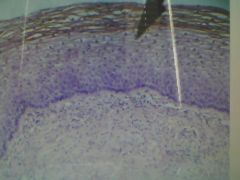
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium - protection :mouth, esophagus
|
|

|
Reticular Fibers- snake like, outline pebble looking structures
|
|
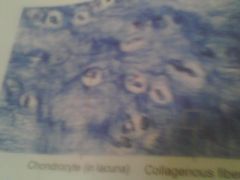
|
Collagen Fibers (scape looking) chondrocyte in lacuna
|
|
|
Collagen Fibers
|
White
|
|
|
Elastic Fibers
|
Yellow
|
|
|
Reticular Fibers?
|
?
|
|
|
Electrocardiogram
|
record of the heart’s electrical activity (conduction of impulses)
|
|
|
Fibrous Pericardium
|
– Tough, loose fitting sac around the heart.
|
|
|
Serous Pericardium (Epicardium)
|
– Consists of two layers: Parietal layer (lining inside the fibrous pericardium) and Visceral layer (Outer layer of the heart wall.)
|
|
|
Pericardial Cavity
|
– Space between visceral & parietal layer that contains fluid for lubrication.
|
|
|
Vasodilation
|
– Increase in vessel diameter caused by relaxation of vascular muscles.
|
|
|
Vasoconstriction
|
- narrowing (constriction) of blood vessels.
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis
|
hardening of the arteries by fatty deposits;cx blockage or weakening of arteries.
|
|
|
Arteriosclerosis
|
– Hardening of the arteries; calcium deposits form
|
|
|
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
|
– (Heart Attack) Death of cardiac muscle cells from low blood supply.
|
|
|
Antibody
|
– Plasma protein produced by B-lymphcytes that destroys a specific substance that has entered the body.
|
|
|
Antigens
|
Substance (toxin or protein fragment) that stimulates an immune response to the body; causes production of antibodies.surface RBC -
|
|
|
SA Node
|
The heart’s pacemaker; where the impulse conduction of the heart starts; 70-80 bpm; creates action potential
|
|
|
AV Node
|
atrioventricular node; which conducts the normal electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles
|
|
|
Myocardium
|
Heart muscle.
|
|
|
Diastole
|
Relaxation of the heart when it fills with blood.
|
|
|
Systole
|
Contraction of the heart muscle; when blood is driven to the aorta.
|
|
|
Hypertension
|
High blood pressure.
|
|
|
Autorhythmicity - ?
|
Autorhythmicity - ?
|
|
|
Endocardium
|
Endocardium – Thin layer of very smooth tissue lining each chamber within the heart.
|
|
|
Ventricular Tachycardia - (V-tach)
|
Abnormal, rapid heart rate originating from an area of the ventricle.
|
|
|
Ventricular Fibrillation
|
ventricles contract in rapid and unsynchronized rhythms and cannot pump blood into the body
|
|
|
Tachycardia
|
abnormally rapid heartbeat (over 100 beats per minute)
|
|
|
Bradycardia
|
Abnormally slow heartbeat (under 60 beats per minute)
|
|
|
Bundle of His
|
Specialized cells that transmit electrical impulses from the AV node in the heart to the muscle cells of the heart wall, which produce the heart beat.
|
|
|
Myogenic
|
Rhythmic activity generated by muscles.
|
|
|
Neurogenic -
|
Neurogenic -
|
|
|
Trace the flow of the Heart
|
1. Right Atrium
via - Inferior or Superior Vena Cava or Coronary Sinus 2. Tricuspid Valve 3. Right Ventricle 4. Pulmonary Semilunar Valve 5. Pulmonary Trunk 6. R&L Pulmonary Arteries 7. Lungs 8. R&L Pulmonary Veins 9. Left Atrium 10. Mitral/Bicuspid Valve 11. Left Ventricle 12. Aortic Semilunar Valve 13. R & L Coronary Arteries 14. Ascending Aorta 15. Systemic - through out body |
|
|
What is pulmonary & systemic circuits
|
Pulmonary - Right side of heart - pumps blood to lungs
Systemic - Left side of heart - pumps blood to get to cells in the body |
|
|
5 functions of cardiovascular
|
1. Transport & distribute gases (O2 & Co2) to and from cells
2. Transport and distribute nutrients, hormones and waste to and from cells 3. Regulate temp 4. Protect against blood loss with clotting factors 5. Protect against pathogens with its immune cells |
|
|
Structural and Functional properties of cardiac muscle and how it differs from skeletal muscle
|
Cardiac ----> Skeletal
1 nuclei -----> Multi Dependent ---> Independent s & f Mitrochondria 25% for making more ATP and resisting fatigue ---> 2% |
|
|
Components of the conduction system of the heart & trace the conduction pathway
|
SA Node - pace maker 70-80 bpm starts action potential
AV Node - 40-50 bpm Atrioventricular Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje Fibers Located them on Diagram???? |
|
|
how to take a bp reading and what systolic and diastolic #s mean
|
Systolic - top - ventricle ???
Diastolic -bottom - ???? 120/80 |
|
|
average adult pulse rate is
|
70-80 bpm & has an average of 5 liters of blood
|
|
|
difference between fetal cardiovascular structures and a babies
|
Fetus -----> Baby/Adult
Ductus Arteriosus ---> Ligamentum Arteriosum Foramen Ovale ----> Fossa Ovalis Ductus Venosus ---> Ligament Venosum Umbilical Vein ---> Round Ligament Umbilical Arteries ---> Umbilical Ligaments |
|
|
which blood type is the most common.... which is the rarest.... occurance of RH+ and RH - in the US
|
Common - O
Rarest - AB 85% RH + 15% RH - RH+ Male and RH - Mom = baby 1 ok; mom makes RH antibodies - then when 2 baby comes it attacks and lyses the babys blood cells. Tx: Rogain |
|
|
know each blood types antigens on the surface of RBCs and the antibodies in the plamsa
|
Type = Erythrocytes RBCs = Antibodies Plasma
A - A antigens on RBCs - Antibodies in plasma B B - B RBC surface - Anti A in plamsa AB - A & B on RBC surface; Neither A or B in plamsa O - Neither A or B on RBCs; Anti A & b in plasma In plasma - is the anti- cant have have |
|
|
autorhythmic cells
|
like pace maker and do not contract but start action potential
|
|
|
contractile cells
|
91% muscle - mechanical pump of heart- do not initiate their own action potential
|
|
|
SA Node
|
pacemaker ~ Fast Depolarization rate ~Creates action potential 70-80 times /min
|
|
|
P wave
QRS Complex T Wave |
P - atrial depolarization
QRS- ventricular depolarization (ventricles contract) T- ventricular repolarization |
|
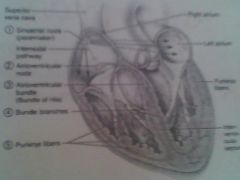
j
|
k
|
|
|
Hydrochloric Acid
|
Hydrochloric Acid – A strong acid produced in the wall of the stomach; forms pepsin and destroys bad organisms
|
|
|
Parotid Gland
|
Parotid Gland – Largest; saliva enters mouth through parotid duct near molars
|
|
|
Submandibular Glands
|
Submandibular Glands – Compound glands that contain enzyme & mucus producing elements.
|
|
|
Salivary Amylase
|
Enzyme that starts the breaks down (digests) carbs.
|
|
|
4 Primary Modifications for digestion and absorption
|
1. Circular Folds
2. Villi 3. Microvilli 4. Enzymes |
|
|
Microvilli
|
Microvilli – Brush-like border made up of epithelial cell on each villi.
|
|
|
Cardia ~ Fundus
|
Cardia – Small collar-like section of the stomach near the junction of the esophagus.
Fundus – Enlarged portion near the opening of the esophagus to the stomach. |
|
|
Pepsinogen
|
converted to pepsin by hydrochloric acid; inactive form of pepsin
|
|
|
Bile
|
Bile – emulsifies fat for digestion;
produced by the liver and released into the digestive tract. |
|
|
Emulsification
|
Emulsification – Disperse fats into very small droplets for digestion.
|
|
|
Rugae
|
Rugae – Ridges of epithelial lining in stomach is folded; when stomach is empty the mucosa and submucosa fold inward... when the stomach extended folds flatten and allow stomach to expand.
|
|
|
Exocrine Gland
|
Exocrine Gland – Secretes outside; secretes mucus, oils via a duct onto the body’s surface.
|
|
|
Disaccharide
|
Disaccharide – Double sugars; Sucrose, Lactose, & Maltose.
|
|
|
Polysacchride
|
Polysacchride – Complex sugars; starch, glycogen, & cellulose.
|
|
|
Monosacchride
|
Monosacchride – Simple sugars; glucose, fructose, & gulactose.
|
|
|
Where does digestion of:
Starch Proteins Lipids begin? |
Starch - Mouth - with salivary amylace
Proteins - Stomach - Pepsin Lipids - Small Intestine - pancreatic lipase & bile |
|
|
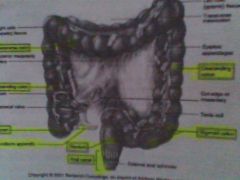
List all the structures food passes through
|
Alimentary Canal/ GI Tract
Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach (Carda, Fundus, Body, Pylorus) Small Intestine (Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum) Large Intestine (cecum) Colon (Ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon) Rectum Anal Canal Anus |
|
|
Main digestive functions of the
LIVER GALLBLADDER PANCREAS |
Liver- produce bile and release into duodenum
Pancreas- endo & exo gland; secrete hormones and digestive enzymes (pancreatic juice) Gallbladder - stores bile??? |
|
|
What is the difference b/t HDL & LDL's in compostiotion?
|
HDL - more protein less cholesterol
DOES NOT pick up garbage & does not lay down flat LDL - more cholesterol less protein formed by VLDL; removes stuff and lay down flat Formed in liver |
|
|
Where and how does chylomicrons are formed and how they differ from high and low density lipoproteins
|
Chylo- over 80% triglyceride from the diet... Formed -?
Differs-? |
|
|
Blood Values
|
Total Blood Cholesterol <200 mg/dl
LDL <135 mg/dl HDL >35 mg/dl |
|
|
What form does Proteins, Carbs and lipids enter the blood stream or lyphatic system
|
Proteins - amino acids - small intestine - blood stream
Carbs - monos - small intestine to blood stream Lipids - monoglycerides & fatty acids - small intestine - chylomicrons into lacteals (lympatic) |
|
|
How many kcals per gram
proteins carbs lipids |
proteins - 4
carbs - 4 lipids - 9 |
|
|
Bile is made by the BLANK stored in the BLANK and released in the BLANK
|
Bile is made in the LIVER, stored in the GALLBLADDER, and released in the DUODENUM.
|
|
|
deglutition
|
swallowing
|
|
|
mastication
|
chewing
|
|
|
bolus
|
food that has been swallowed
|
|
|
sodium bicarbonate
|
brings pH back up; so duodenum doesnt get ulcer
|
|
f
|
ff
|
|
k
|
dsdfa
|
|
|
Hypoglycemia
|
Low blood glucose
|
|
|
Hyperglycemia
|
High blood glucose
|
|
|
Hyposecretion
|
Too little secretion.
|
|
|
hypersecretion
|
Too much secretion.
|
|
|
What is the difference between endocrine glands & exocrine glands
|
Endocrine - (within) - Ductless; Secretes Hormones into surrounding tissues that travel through the blood system.
Exocrine - (outside) DO NOT secrete hormones; sweet, oil, mucus, pancreatic juices; Via a duct onto the body surface |
|
|
Know the 3 ways endocrine glands are stimulated to manufacture and release their hormones?
|
HUMORAL
NEURAL HORMONAL |
|
|
What are the chemical classifications of hormones
|
1- Amino Acid hormones (MOST)
a. amines b. Proteins & Peptides 2. Steroids |
|
|
Amino Acid Hormones: Amines
|
- modified from acid tyrosine; Small & water soluble
|
|
|
2. Steroids
|
derived from cholesterol and lipid soluble
|
|
|
Amino Acid Hormones: Proteins & Peptides
|
chains of amino acids & water soluble
|
|
|
amniocentesis
|
Aminotic fluid is removed to produce a karyotype.
|
|
|
gonads
|
Sex gland with reproductive cells; Ovary for women – Testis for men.
|
|
|
karyotype
|
The characterization of the chromosomal complement, including number, form, and size of the chromosomes. (Ex: tests done from amniocentesis); chromosome pair
|
|
|
STD
|
Sexually transmitted disease.
|
|
|
endometrium
|
Mucus membrane lining of the uterus; if pregnancy does not occur, this layer is shed during menstruation.
|
|
|
perimetrium
|
External layer of the serous membrane of the uterus
|
|
|
myometrium
|
Thick, middle muscle layer of the uterine wall.
|
|
|
1. What are the functions of the male and female repro?
|
Male: 1. Produce Sperm 2. Secrete Hormones 3. Deliver sperm into female so fertilization can take place
Female: Reproduce organisms |
|
|
urethra
|
carry urine and semen
|
|
|
vas ductus deferens
|
carry sperm from testis to ejac. duct
|
|
|
penis
|
contains urethra - for urinary & reproductive tracts
|
|
|
prostate gland
|
1/3 total vol of semen; slightly acidic; citrate and PSA.
|
|
|
spermatic cord
|
made of nerves and arteries formed by the vas deferens
|
|
|
bulbourethral (cowpers) gland
|
neutralizes and lubes urethra prior to ejaculation with an alkaline
|
|
|
testis
|
Male sex gland
|
|
|
seminal vesicles
|
60% sperm; semen is alkaline, fructose, ascn, prostagladins and coagulating enzymes
|
|
|
ejaculatory ducts
|
where semen passes through
|
|
|
glans penis
|
sensitive part of penis on underside
|
|
|
corpus cavernosum
|
specialized tissue that engorges with blood
|
|
|
epididymis
|
store mature sperm
|
|
|
scrotum
|
holds testis outside of body
|
|
|
seminiferous tubules
|
where sperm are developed
|
|
|
ovaries
|
where egg and progesterone & estrogen are produced
|
|
|
Where does fertilization take place? When does implantation occur?
|
1/3 way down fallopian tube; 6-7 days after fertilization
|
|
|
estrogen
|
Female steroid sex hormone secreted by the ovary.
|
|
|
testosterone
|
Male sex hormone that stimulates sperm production, growth, and maintainence.
|
|
|
progesterone
|
Produced by ovary & placenta
Maintains proper conditions for pregnancy. |
|
|
What are the 3 phases of the uterine clycle?
|
Phase 1 - Menstrual Phase (1-5 Dyas Phase 2 Proliferative Phase (6-14 days) Phase 3 - Secretory Phase (day 15-28)
|
|
|
Tropic Hormone
|
Hormone that stimulates another endocrine gland to secrete its hormone
|
|
|
Nontropic Hormone
|
Hormones that directly stimulate target cells to induce effects.
|
|
|
Target cell
|
Cell that has receptors that a hormone can bind to.
|
|
|
alpha cell
|
Pancreatic islet cell that secretes Glucogon; increase blood sugar
|
|
|
Beta cells
|
Pancreatic islet cell that secretes Insulin; lowers blood sugar
|
|
|
What does the thyroid secrete?
|
Thyroid Hormone & Clacitonin
|
|
|
What does the adrenal glands secrete
|
Corticosteroid & Catecholamine
|
|
|
What does the pancreas secrete
|
insulin & glucagon
|
|
|
What does the parathyroid secrete
|
parathyroid hormone
|
|
|
HUMORAL
|
(glucose) change in blood stream levels of ions and nutrients triggers release
|
|
|
HORMONAL
|
(all anterior pituitary) hormone released by other hormones
|
|
|
NEURAL
|
( adrenal & epinephrine) nerve fibers on gland stimulate its own release
|
|
|
corpus luteum
|
~Secretes: Progesterone & estrogen;
~Maintains Endometrium ~!Pregnant increases Not decreases |
|
|
LH
|
Lutenizing hormone;
Cx: ovulation rupture of follicle : develops & stimulates corpeus leutem; |
|
|
FSH
|
Development of Ovarian Follicle & Estrogen secretion
Males: production of sperm |
|
|
HCG
|
-->Stimulates estrogen & progesterone during pregnancy
-->Keeps corpus luteum active -->Produced by the EMBRYO & placenta after 10 days fertilization |
|
|
Phase 1 Menstrual Phase 1-5 days
|
Phase 1 Menstrual 1-5
• Sheds all but the deepest layer of endometrium • Bloody discharge 3-5 days • Hormones are @ lowest • FSH (pituitary) begins to rise • Day 5 the ovary starts to produce more estrogen |
|
|
Phase 2 Proliferation 6-14
|
Phase 2 Proliferative Phase 6-14
• Endometrial lining begins to rebuild from the rising estrogen • Estrogen prepares endometrial receptors for pregosterone • Day 14 – ovulation (from LH) cx rupture of follicle turn into corpus leutum |
|
|
Phase 3 Secretory Phase (days 15-28)
|
Phase 3 Secretory Phase 15-28
• Endometrium prepares for implantation with aid of increased progesterone • Develops more arteries thick vascular secretory mucosa |
|
|
What are the 7 effects hormones have on the body?
|
1. Controls chemicals composition and volume internal fluid
2. Energy balance & Metabolism 3. Contraction of cardiac & smooth muscle & glands/secretions 4. Respond to change in environment and copes 5. Regulate immune system 6. Growth and development 7. Reproduction – gamete – fertilization – fetus - delivery |
|
|
What does the pituitary secrete?
|
ANTERIOR:
1. Growth Hormone (GH) 2. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) 3. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) 4. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) 5. Luteinizing Hormone (LH) 6. Prolactin (PRL) POSTERIOR: 7. Oxytocin 8. Antidiuretic Hormone or Vasopressin (ADH) |
|
|
epineurium
|
– Fibrous coat; surrounds a bundle of nerve fibers.
|
|
|
endoneurium
|
thin, fibrous tissue that surrounds each axon in a nerve
|
|
|
synpase
|
– Nerve information is transmitted from one neuron to another
|
|
|
synaptic terminals ASK KRISTEN
|
Small gap which the neurotransmitters travel & adjacent membrane of an axon or dendrite with the receptors for picking up the neurotransmitters.
|
|
|
12 Cranial Nerves
|
Olfactory
Optic Oculmotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abcucens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Accessory Hypoglossal |
|
|
What happens when their is a great increase in sodium
|
depolarization (more positive inside)
|
|
|
Which part of the adrenal gland secretes epinepherine and norepoinepherine
|
Medulla (neurally stimulated)
|
|
|
Which hormones are released from posterior pituitary gland
|
ADH & Oxytocin
|
|
|
Thyroid stimulating hormone
|
stimulates to secrete t3 and t4
|
|
|
Neural
|
medulla - adrenal - epinepherine and norepinepherine
|
|
|
ANTERIOR Pituitary
|
GH (growth)
TSH (thyroid stimulating) ACTH (adenocorticotropic) FSH (ovary & testes - ovary follicle & estrogen) LH (cx ovulation) PRL (prolactin) |
|
|
Posterior Pituitary
|
Oxytocin & ADH (antidiuretic/Vasopressing) kidney reabsorbition of water
|
|
|
Adrenal
|
corticosteroids (cortex)
catecholamine (medulla) |
|
|
Ohms Law
|
I = E/R
I - current E - voltage R - resistence |
|
|
What is the mV of resting state
|
-70
|
|
|
What is threshold? What is the peak?
|
-55 ; +30mV
|
|
|
What is the sodium potasium pump ratio
|
3:2
3 Na out 2 K in |
|
|
Somatic Nervous System
|
voluntary - ex. skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Autonomic ANS
|
involuntary - ex. heart and smooth muscle
|
|
|
What 2 systems are off of the ANS
|
Sympathetic - fight/flight emergency
Parasympathetic - brings back to normal - non emergency |
|
|
Nerve
|
A collection of motor axons & sensory axons in the PNS
|
|
|
Neuron
|
Nerve cell
|
|
|
Interneuron
|
Nerve cell that conducts impulses from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron
|
|
|
Axon
|
Transmits impulses AWAY from the cell body; travels down
|
|
|
Voltage
|
Measured potential between two points; potential difference; (measure of potential)
|
|
|
Perineurium
|
surrounds a bundle of nerve fibers in a nerve cell.
|
|
|
Myelin
|
Lipoprotein substance that contributes to high-speed productivity of impulses
|
|
|
Nerve Cell Body
|
nucleus & cell organs; Largest part of a nerve cell; surrounding the nucleus
|
|
|
motor (efferent) neurons
|
Transmit nerve impulses AWAY from CNS to PNS.
|
|
|
Node of Ranvier
|
Space in the myelin sheath between adjacent Schwann cells.
|
|
|
sensory (affterent) neurosn
|
Transmit nerve impulses from pns TO (CNS) spinal cord or brain.
|
|
|
synpatic cleft
|
Space between synaptic knob & plasma membrane of a postsynaptic neuron.
|
|
|
repolarization
|
Membrance potential changes from maxium degree of depolarization to resting state.
|
|
|
dendrite
|
Transmits impulses TOWARD the cell body; receiving end of all neurons (branching structures)
|
|
|
Classify neurons structurally & functionally
|
Structural: (by # of their extensions fro cell body)
Multipolar- one axon many dendrites Bipolar- 1 axon 2 branching dendrites Unipolar- cell body? Functional: Afferent neurons, Efferent neurons, & Interneurons P2 Function 1- Sense information in the internal environment 2. to integrate the sensory information 3. respond to stimuli by activating muscles and or glands |
|
|
What is the organization of the nervous system?
|
CNS - central - brain and spinal cord! PNS - peripheral
Motor efferent & senspory afferent Autonomic nervous system (involuntary_ sympathetic - fight or glight and parasypathetic - brings back into balance |
|
|
How is a nerve impulse conducted fro one neuron to another?
|
z
|
|
|
What is the difference between a myelinated neuron and unmyelinated?
|
Myelinated are: faster & jump (saltitory conduction ); dont have to depolarize every section; nerve fibers with many Schwann cells that form: thick myelin sheath (white fibers.)
Unmyelinated neurons are when several nerve fibers are held by a single Schwann cell with no sheath (also known as gray fibers.) ; |
|
|
What is the general anatomy of a neuron?
|
Cell body - nucleus and cell organelles
Dendrites - receiving end Axon - impulse travels down Axonal Terminal - release neurotransmitter |
|
|
What is released bc of low blood sugar? And how
|
glucagon - humorally
|
|
|
What 2 hormones regulate blood calcium
|
parathyroid & calcitonin
|
|
|
What causes the endometrial lining to slouff off
|
decreased progesterone and estrogen
|
|
|
What is cut in a vasectomy
|
vas deferens
|
|
|
Their are many more
|
proteins & amines than steroids
|
|
|
Once initiating an action potential it
|
continues at the same strength & speed & must reach threshold -55mV
|
|
|
LH causes
|
ovulation & comes from pituitary
|
|
|
Seminal vesicles
|
60% semen & alkaline
|
|
|
prostate gland
|
1/3 semen & slightly acidic
|
|
|
bulbo gland thingie ma-bop- er
|
pre ejac secretions
|
|
|
Humoral
|
glucose
|
|
|
Hormonal
|
all anterior pitutary
|
|
|
Thryoid
|
TH (Thyroid) T3 & T4
Calcitoning (decrease blood calcium) |
|
|
Parathyroid
|
increases blood calcium
|
|
|
Functions of the kidneys
|
to help keep the body in homeostasis by controlling the composition and volume of blood
|
|
|
The differences between cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons
|
Cortical Nephrons - 85% of kidney nephrons; located in the cortex of kidney except the small parts of their loops of Henle that dip into the outer medulla
Juxtamedulallry Nephrons 15% located very close to the cortex medulla junction, The loop of Henle of juxtamedullary nephrons are much longer than those of cortical nephrons and consist of a very long thin segment. This thin segment is primarily responsible for water absorption (water movement from the tubules back to the blood) |
|
|
Tissue types
PCT, Loop (thin/thick), DCT, collecting |
PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULES
walls of lumen = simple cuboidal epithelium with Microvilli (secretion & reabsorption) LOOP OF HENLE (thin & thick) Thin - Simple squamous epithelium conductive of water reabsorption Thick - simple cuboidal epithelium DISTAL CONVOLUTED TUBULES & COLLECTING DUCT simple cuboidal epithelium LESS microvilli |
|
|
Glomerular Filtration
|
Urine formation begins;
Blood flows into the afferent arteriole, then to glomerular capillaries where certain components of blood plasma are forced through the filtration membrane of the glomerular capillaries into the Bowman's (glomerular) capsule. The filtrate consists of all the materials present in blood except for proteins (that are too large to pass through) |
|
|
Tubular Reabsorption
|
2nd step. 99% of the filtrate is returned to the blood with in the peritubular capillaries
Glucose and amino acids to be reabsorbed into the blood but the reabsportion of water are adjusted to the bodies needs |
|
|
Tubular Secretion
|
3rd - substances such as hydrogen, potassium etc move from the blood in the peritubular capillaries into the tubules, then excreted from the body in urine
|
|
|
If you have low blood pH what will happen
|
It will NOT reabsorb H+
secrete H+ |
|
|
If the blood pH is high it will
|
Bring in H+
or reabsorb it back into the blood. |
|
|
more H+
|
lower the pH (14)
|
|
|
less H+
|
higher the pH (0)
|
|
|
nephron
|
consists of 2 primary parts - renal corpuscle that filters the blood, renal tubule through which the filtrate travels and becomes modified in the formation of urine
|
|
|
ureter
|
Carries urine from the kidney to the bladder (2)
|
|
|
Urethra
|
Passageway from the bladder to exterior; eliminates urine.
|
|
|
retroperitoneal
|
position in superior lumbar region - kidneys lie in position between the dorsal body wall and the parietal peritoneum
|
|
|
renal hilus
|
The ureter, renal veins & arteries EXIT each kidney along the medial surface where it is concaved
|
|
|
major calyx
|
large funnel shaped renal pelvis which is the central collecting area for each kidney
|
|
|
minor calyx
|
CUP like region that flows into the major calyx
|
|
|
afferent arteriole
|
brings blood to the glomerulus and is larger and shorter than the efferent.
|
|
|
efferent arteriole
|
carries blood away from the glomerulus and into the peritubular capillaries
|
|
|
renal corpuscle
|
Bowmans capsule + glomerulus together = renal corpuscle YEY!!!
|
|
|
filtrate
|
urine (Substance remaining in a liquid after passing through a filter)
|
|
|
Peritubular Capillary
|
Capillaries around the tubules in the kidney.
|
|
|
Podocyte
|
Makes up the visceral layer of the bowman capsule
|
|
|
3 Functions (Goals) of Respiratory System
|
1. Receive O2 & eliminate CO2 (Primary Goal)
2. Sense of Smell 3. Vocalization |
|
|
4 Major Processes of Respiration
|
1. Pulmonary Ventilation
2. External Respiration 3. Transport of Respiratory Gases 4. Internal Respiration |
|
|
2 Functional Divisions of the respiratory system
|
1. Respiratory Zone - actual site of gas exchange in the lungs (resp bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli)
2. Conducting Zone - way that gases reach the site of exchange (includes structures to aid in: warming, filtering, and humidifying air) |
|
|
3 Regions of the Pharynx
|
1. Nasopharynx
2. Oropharynx 3. Laryngopharynx |
|
|
epiglottis
|
flap that covers the opening of the larynx
|
|
|
Vocal Folds
|
(true vocal cords) vibrate when air from the lungs pass
|
|
|
Vestibular Folds
|
(false vocal cords) superior to the vocal folds; DO NOT play any role in voice production
|
|
|
Glottis
|
opening of the larynx
|
|
|
Epiglottis
|
covers glottis; when food passes into the laryngopharynx and down the esophagus
|
|
|
Carina
|
Last tracheal cartilage has a ridge on the internal surface; marks division of trachea into primary bronchi
|
|
|
Alveoli
|
Off the tiny respiratory Bronchioles;
Tuny cluster of air sacs, each made of 1 layer of epithelium (simple. sq. epi) |
|
|
Cricoid
|
Only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea.
|
|
|
Bronchioles
|
Small airways of the lung extending from the bronchi to the aveoli.
|
|
|
Heterozygous
|
Bb
capital and lower |
|
|
Homozygous recessive and dominant
|
bb & BB
the same |
|
|
Ex of Incomplete dominance in red and white flower
|
Rr Pink flower
|
|
|
Sex linked
Male and Female |
Male Xy
Female XX |
|
|
Color Blindness in WOMAN
|
XX - Normal
X c X - Normal X c X c Colorblind |
|
|
Color Blindness in MEN
|
XY Normal
X c Y Color Blind |
|
|
Blood Pheno Type
|
Type O, A , B, AB
|
|
|
Genotype Multiple alleles in blood
|
AA / Ai
BB / Bi AB ii |
|
|
What are the phases of mitosis?
|
1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase
|
|
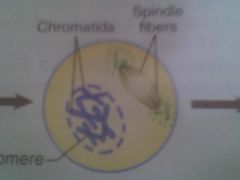
Prophase
|
Nuclear membrane is going away (gone); centrioles divide
|
|
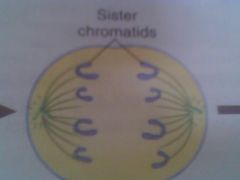
Anaphase
|
Spindle seperates chromosomes and pulls to each opposite side of cell
|
|
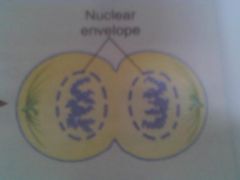
Telophase
|
cell membrane pinches in; nuclear envelope reforms; spindle unwinds and disappears;
|
|
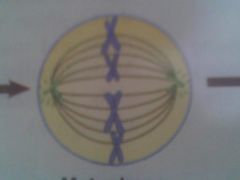
Metaphase
|
chromosomes line up in the middle of cell
|
|
|
Juxtamedulallry Nephrons
|
15% located by cortex medulla junction,
~The loop of Henle juxtamedullary nephrons are longer than cortical nephrons and have a long thin segment (for water absorbtion) ~ (water movement from the tubules back to blood) |
|
|
Cortical Nephrons
|
85% of kidney nephrons;
located in the cortex of kidney except the small parts of their loops of Henle that dip into the outer medulla |
|
|
Tissue types
proximal convoluted tubule |
PCT
walls of lumen = simple cuboidal epithelium with Microvilli (secretion & reabsorption) |
|
|
Tissue types
Loop of Henle (thin/thick) |
LOOP OF HENLE
Thin - Simple squamous epithelium conductive of water reabsorption Thick - simple cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
Tissue types
Distal Convoluted Tubule & Collecting Duct |
DCT & Collecting Duct
simple cuboidal epithelium LESS microvilli |
|
|
Glomerular Filtration
|
--->Urine formation begins;
Blood flows into the afferent arteriole, then to glomerular capillaries where blood plasma go through filtration into the Bowman's (glomerular) capsule. The filtrate consists of all that are too large to pass through (proteins) |
|
|
Tubular Reabsorption
|
2nd step
99% of the filtrate is returned to the blood by the peritubular capillaries Glucose and amino acids to be reabsorbed into the blood reabsportion of water depends on bodies needs |
|
|
Tubular Secretion
|
3rd - hydrogen, potassium etc move from the blood in the peritubular capillaries into the tubules, then excreted from the body in urine
|
|
|
2 Functional Divisions of the respiratory system
Name the 1st one!!!! |
1. Respiratory Zone - actual site of gas exchange in the lungs (resp bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli)
|
|
|
2 Functional Divisions of the respiratory system
Name the 2nd one!!!! |
2. Conducting Zone - way that gases reach the site of exchange (includes structures to aid in: warming, filtering, and humidifying air)
|
|
|
Nasopharynx
|
starts at the back of the nasal cavity and ends just above the soft palate
*** AIR PASSAGE ONLY*** ~Pharyngeal tonsils ~Adenoids ~Eustachian tube |
|
|
Oropharynx
|
begins posterior to the oral cavity and extends to the epiglottis, which is at the level of the hyoid
~Palatine tonsils ~Lingual tonsils ***BOTH Food and Air Pass*** |
|
|
Laryngopharynx
|
posterior to the larynx and opens into the esophagus and larynx
***BOTH food and air pass*** |
|
|
homologous chromosomes
|
pair during meiosis; one inherited from each parent.
|
|
|
Chromatid
|
2 DNA strands joined by a centromere after DNA has replicated (before cell division.)
|
|
|
Trait
|
constitutes the physical, biochemical & physiological make up of every cell in the body
|
|
|
Phenotype
|
what you can see or measure (appearance)
Type A Type O etc |
|
|
Genotype
|
specific alleles that an individual inherits from their parents
AA ii Bi etc |
|
|
crossing over
|
Pairs of homologous chromosomes exchange during meiosis. prophase 1
|
|
|
synapsis
|
The pairing of homologous chromosomes during the meiotic phase of cell division
|
|
|
Chromatid
|
2 DNA strands joined by a centromere after DNA has replicated (before cell division.)
|
|
|
Pulmonary Ventilation
|
the movement of air into and out of the lungs (breathing/ventilation)
|
|
|
External Respiration
|
gas exchange (o2 & carbon dioxide)
|
|
|
Transport of Respiratory Gases
|
transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide from the lungs to the cells of the body
|
|
|
Internal Respiration
|
gas exchange between the blood and the cells
|
|
|
Nasopharynx
|
starts at the back of the nasal cavity and ends just above the soft palate. AIR PASSAGE ONLY;
~Pharyngeal tonsils ~Adenoids ~Eustachian tube |
|
|
Oropharynx
|
begins posterior to the oral cavity and extends to the epiglottis, which is at the level of the hyoid;
~Palatine tonsils ~Lingual tonsils BOTH Food and Air Pass |
|
|
Laryngopharynx
|
posterior to the larynx and opens into the esophagus and larynx
BOTH food and air pass |
|
|
3 functions of the Larynx
|
1. Provides an open airway
2. Acts as a switching mechanism to route food and air into the proper channels 3. Responsible for voice production |
|
|
Trace Air molecule
|
1. Vestibule
2. Nasal Cavity 3. Superior, Middle & Inferior Concha 4. Nasopharynx 5. Pharyngeal Tonsils 6. Opening of Pharyngotympanic tube (=s pressure) 7. Oropharynx 8. Palatine Tonsils 9. Lingual Tonsils 10. Epiglottis 11. Laryngopharynx 12. Larynx 13. Glottis 14. Vestibular Folds (false vocal cords) 15. Vocal Folds (true vocal cords) 16. Trachea 17. Carina 18. R & L Primary Bronchi (right caught) 19. Bronchioles 20. Terminal Bronchioles 21. Respiratory Bronchioles 22. Alveoli 23. Blood Capillary |
|
|
during which phase a sister chomatids together
|
metaphase
|
|
|
centromere
|
hold chromatids together
|
|
|
gametes
|
sex cells; sperm and egg
|
|
|
microtubules
|
– Thick cell fiber that moves substances within the cell.
|
|
|
homologous chromosomes
|
One pair of chromosomes that pair during meiosis; one inherited from each parent.
|
|
|
histones
|
j
|
|
|
sister chromatids
|
Two identical strands joined by a centromere from a chromosome that duplicated during the S phase.
|
|
|
meiosis
|
– Cell division; number of chromosomes is reduced in half; produces gametes.
|
|
|
Which cells undergo meiosis? How many cells are produced during the process? How many chromosomes will be in each human cell?
|
Sex Cells ; 4 cells are produced; 23 chromosomes in each new cell
|
|
|
Differences between mitosis and meiosis
|
Mitosis -
1 cell divides into 2 cells 2N end 2N 1 set of divisions Somatic Cells genetically identical No synapsis or crossing over MEIOSIS 1 cell divides into 4 cells 2N becomes 1N 2 Sets of divisions (I &II) Sex Cells Genetically different Synapsis & crossing over |
|
|
What info can be gathered from a karyotype?
|
Sex
# of chromosomes chromosome abnormalities Down Syndrome Edwards Syndrome Missing chromatid leg |
|
|
G1
|
increased enzymes needed BEFORE dna synthesis; cells that dont divide stay here
|
|
|
S
|
DNA & Centrioles divide; chromosomes duplicate
|
|
|
G2
|
Measurable increase in protein synthesis; cell prepares to divide
|
|
|
Diploid 2N
|
Somatic cell that contains two sets of chromosomes (46 chromosomes.)
|
|
|
Haploid 1N
|
23 chromosomes found in mature sex cells, or gametes.
|
|
|
Karyotype
|
The entire chromosomal complement of an individual or cell, which may be observed during mitotic metaphase (such as the shape, type, number, etc. of chromosomes).
|
|
|
somatic cell
|
body cell
|
|
|
Centrioles
|
Two cylindrical bundles of protein filaments that are perpendicular to each other
|
|
|
Interphase
|
(G1, S, G2) Mitotic phase b4 (prophase-mitosis) b4 visible condensation of the chromosomes
|

