![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
pH gradient drives import of *** and ***.
|
pyruvate
phosphate |
|
|
|
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
1) Actin is *** wide. 2) Intermediate filaments are *** wide. 3) Microtubules are *** wide. |
1) 7 nm
2) 10 nm 3) 25 nm |
|
|
|
--- States of Actin Filaments ---
1) 2) 3) |
1) Nucleation
2) Elongation 3) Steady State |
|
|
|
NADH yields...
NADH2 yields... |
2 e-
3 e- |
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
Composed of # ***... |
13 protofilaments
|
|
|
|
1) A *** determines where mRNA is translated.
2) After translation it's cleaved by *** ***. |
1) 20-26 AA sequence
2) cleaved --- signal peptidase |
|
|
|
Eukaryotic cells contain these types of cytoskeletal filaments.
1) 2) 3) |
1) microfilaments
2) intermediate filaments 3) microtubules |
|
|
|
1) *** *** takes place in microtubules.
2) *** *** takes place in actin. |
1) Dynamic instability
2) Tread milling |
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
1) Accidental loss of *** *** causes rapid shrinkage and its gain causes rapid growth. |
1) GTP cap
|
|
|
|
Draw the flagellum.
|
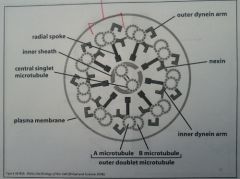
|
|
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
1) # outer *** microtubules. 2) # central *** microtubules. |
1) 9 --- doublet
2) 2 --- singlet |
|
|
|
--- G-Protein Linked Receptor ---
1) # transmembrane segments 2) AKA *** |
1) 7
2) serpentine |
|
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
Name Inner Parts... |
(2) Inner Sheath
(2) Central singlet microtubule |
|
|
|
Insulin is a ***
|
TKR
|
|
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
Name Outer Parts... inside to outside |
1) Radial Spoke
2/3) Inner/Outer dynein arm 4) Nexin 5/6) Outer doublet microtubule(complete A / incomplete B microtubule) |
|
|
|
--- G-Protein ---
1) *** with # subunits 2) called ***, ***, and ***. |
1) Trimeric --- 7
2) α, β, and γ |
|
|
|
1) ***: AA peptide on ***-terminus keeping proteins in ER(even Golgi)
2) Leave only if sequence is ***. |
1) KDEL --- N-Terminus
2) cleaved |
|
|
|
--- G-Protein ---
1) *** subunit decouples & pops da pup. 2) *** binds the first subunit which is ***. |
1) γ
2) GDP --- α |
|
|
|
GPCR?
|
G Protein-Coupled Receptor
|
|
|
|
--- Karyopherins ---
1) α su binds *** of imported protein. 2) β su helps complex to bind the *** *** ***. |
1) NLS of
2) nuclear pore complex. Nuclear Localization Signal/Sequence |
|
|
|
*** is a family of actin-binding proteins which disassembles actin filaments.
|
Cofilin
|
|
|
|
*** gets rid of old actin.
|
Cofilin
|
|
|
|
***: is used to mark proteins in Golgi for transport to ER.
|
KDEL
|
|
|
|
1) α-helical region in ***
2) then forms into coiled-coil *** 3) ***(adjective) ***mer of two coiled-coil dimers 4) # tetramers packed together end to end 5) # tetramers twisted into a rope-like *** |
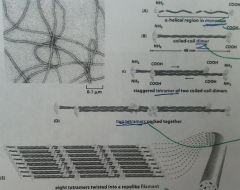
1) monomers
2) dimer 3) staggered tetramer 4) many 5) eight --- filament |
|
|
|
*** are made out of 13 protofilaments.
|
Microtubules
|
|
|
|
GPI? Spelled?
Anchors protein to cell membrane. Directs to ER > Golgi > ECM |
glycosylphosphatidylinositol
glycosyl - phosphatidyl - inositol |
|
|
|
1) ALS?
2) AKA *** 3) Disease of the *** *** 4) Usually causes death in # ***. |
1) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
2) Lou Gehrig's disease 3) motor neurons 4) 3 years |
|
|
|
GAG?
|
GlycosAminoGlycans
|
|
|
|
1) *** is formed when highly glycosylated
2) glycoprotein is linked to a ***. |
1) proteoglycan
2) GAG Glycos Amino Glycan |
|
|
|
3 Pathways out of Golgi
1) 2) 3) |
1) lysosome
2) cell exterior 3) cell exterior (default no signal) |
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
1) Protofilaments are composed of these subunits... |
1) α-tubulin and β-tubulin
|
|
|
|
--- *** *** ---
Contains hyaluronan keratan sulfate chondroitin sulfate and link/core proteins. |
aggrecan aggregate
|
|
|
|
*** binds to importin complex releasing cargo...
|
Ran-GTP
|
|
|
|
--- Aggrecan Aggregate ---
1) *** fiber 2) Keratan *** 3) Chondroitin *** 4) L*** protein 5) C*** protein(aggrecan) |
1) Hyaluronan
2) sulfate 3) sulfate 4) Link 5) Core |
|
|
|
The core protein is also known as the ***.
|
aggrecan
|
|
|
|
--- Collagen Molecule ---
1) Structure is always *** ***. 2) Repeating units are... |
1) triple trimeric
2) glycine, x, y |
|
|
|
Cargo and *** bind to exportin. This becomes *** when it arrives in cytosol.
|
Ran-GTP
Ran-GDP |
|
|
|
1) *** molecule is always triple trimeric
2) w/repeating units of ***, x, and y . |
1) Collagen
2) glycine |
|
|
|
1) Vitamin C is required for the *** of lysine and of proline.
2) These two become *** and *** 3) and are necessary for proper *** cross-linking. |
1) hydroxylation
2) hydroxylysine and hydroxyproline 3) collagen |
|
|
|
--- Formation of Collagen Fiber ---
1) Synthesis of ***-*** *** 2) Hydroxylation of selected *** and *** 3) Glycosylation of selected *** 4) ***-*** of # pro-α chains 5) Procollagen t***-h*** formation 6) S*** 7) Cleavage of p*** 8) Self-assembly into *** *** 9) Aggregation of collagen *** to form a collagen *** |
1) pro-α chain
2) prolines --- lysines 3) hydroxyLysines 4) Self-assembly --- 3 5) triple-helix 6) Secretion 7) propeptides 8) collagen fibril 9) fibrils --- fiber |
|
|
|
--- Formation of Collagen Fiber ---
1) S*** of pro-α chain 2) *** of selected prolines and lysines 3) *** of selected hydroxyLysines 4) ***-*** of three pro-α chains 5) Procollagen triple-helix *** 6) *** 7) *** of propeptides 8) ***-*** into collagen fibril 9) *** of collagen fibrils to form a collagen *** |
1) Synthesis
2) Hydroxylation 3) Glycosylation 4) Self-assembly 5) formation 6) Secretion 7) Cleavage 8) Self-assembly 9) Aggregation --- fiber |
|
|
|
--- Formation of Collagen Fiber ---
1) Procollagen triple-helix is synthesized in the.... 2) It is composed of... |
1) ER/Golgi compartment
2) 3 pro-α chains |
|
|
|
--- Formation of Collagen Fiber ---
1) *** t***-*** is secreted in secretory vesicles into the ECM. |
1) Procollagen triple-helix
|
|
|
|
--- Formation of Collagen Fiber ---
1) Procollagen molecule is *** 2) by s*** p*** 3) into *** molecule 4) which form the c*** *** 5) which is # to # *** wide. |
1) cleaved
2) signal peptidase 3) collagen 4) collagen fibril 5) 10 - 300 nm |
|
|
|
--- Cell Cycle ---
1) Cell enters cell cycle by going into *** phase. 2) Before M/Mitosis phase is *** phase. |
1) S
2) G2 |
|
|
|
Name the three types of cell junctions.
1) *** junctions 2) *** junctions 3) *** junctions |
1) Occluding
2) Anchoring 3) Communicating |
|
|
|
1) M6P?
2) M6PR? |
1) mannose-6-phosphate
2) mannose-6-phosphate receptor |
|
|
|
--- Anchoring Junctions ---
Composed of... 1) I*** a** proteins 2) t*** a** proteins. |
1) Intracellular anchor
2) transmembrane adhesion |
|
|
|
--- Gap Junctions ---
1) *** Ca++ causes closure. 2) *** pH causes closure. 3) *** is an extracellular signals causing closure. |
1) Increased
2) Decreased 3) Dopamine |
|
|
|
1) *** form open channels between cells.
2) Composed of *** subunits. |
1) Connexons
2) six |
|
|
|
--- Gap Junction Channel ---
1) *** is an assembly of six 2) *** proteins forming open channel. |
1) Connexon
2) connexin |
|
|
|
POMC?
*** makes this molecule functional |
preproopiomelanocorticotropin
pre pro opio melano cortico tropin proteolysis |
|
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
Composed of??????? 1) Complete A microtubule 2) Incomplete B microtubule |
--- Flagellum ---
Outer Doublet Microtubule 1) 13 protofilaments 2) 11 protofilaments |
|
|
|
1) F-actin uses *** protofilaments.
2) G-actin uses *** protofilaments. |
1) 11
2) 13 |
|
|
|
*** *** holds sugars being attached to *** during N-glycosylation.
|
dolichol bisphosphate
asparagine - N - Asn |
|
|
|
1) ***-actin uses 11 protofilaments.
2) ***-actin uses 13 protofilaments. |
1) F
2) G |
|
|
|
List 10-15 uses for ATP.
1) How many? 2) Group 1? |
1) 4
DNA Helicase DNA Gyrase DNA Clamp Spliceosome |
|
|
|
List 10-15 uses for ATP.
1) How many? 2) Group 2? |
1) 3
Myosin Kinesin Dynein |
|
|
|
List 10-15 uses for ATP.
1) How many? 2) Group 3? |
1) 2
Flippase Scramblase |
|
|
|
List 10-15 uses for ATP.
1) How many? 2) Group 4? |
1) 3
Proton pump Na+/K+ pump Nucleopore |
|
|
|
List 10-15 uses for ATP.
1) How many? 2) Group 5? |
1) 2
Chaperones (BiP) Chaperones (calnexin) |
|
|
|
List 10-15 uses for ATP.
How many? 1) Group 1? 2) Group 2? 3) Group 3? 4) Group 4? 5) Group 5? |
1) 4
2) 3 3) 2 4) 3 5) 2 |
|
|
|
***: Proteins transporting molecules from cytoplasm into nucleus.
|
Karyopherins
|
|
|
|
***-terminus end of protein contains # *** address tag.
|
N-terminus
4 AA |
|
|
|
Type of bonding...
Fatty acids Sugars Amino acids Nucleotides |
Fatty acids - ester bond
Sugars - glycosidic bond Amino acids - peptide bond Nucleotides - phosphodiester |
|
|
|
What are the acidic AA?
|
Glutamic Acid
Aspartic Acid |
|
|
|
Glycolysis products
|
2 [NADH]
2 [ATP] |
|
|
|
TCA/Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle
|
2 GTP
2 FADH2 6 NADH |
|
|
|
Nucleotides?
U - T - A - G - C |
Uracil
Thymine Adenine Guanine Cytosine |
|
|
|
AA that can be phosphorylated.
|
Ser-Serine
Tyr-Tyrosine Thr-Threonine |
|
|
|
Pyrimidine mnemonic?
Pyrimidines? |
--- CUT PYe ---
Cytosine Uracil Thymine |
|
|
|
Essential AA mnemonic?
1st SET? |
PVT TIM HALL
Phenylalanine Valine Threonine |
|
|
|
Essential AA mnemonic?
2nd SET? |
PVT TIM HALL
Tryptophan Isoleucine Methionine |
|
|
|
Essential AA mnemonic?
3rd SET? |
PVT TIM HALL
Histidine Arginine Lysine Leucine |
|
|
|
Acidic AA have a *** charge in pH 7.
|
negative
|
|
|
|
--- Endocytosis Vesicle---
1) E*** E*** 2) L*** E*** 3) E*** 4) L*** |
1) Early Endosome
2) Late Endosome 3) Endolysosome 4) Lysosome |
|
|
|
NLS typically has 1+ short sequences of *** charged AAs like *** or *** exposed on protein surface.
|
positively
lysine - K arginine - R |
|
|
|
Typically nuclear pore = *** wide.
W/ATP = *** wide. |
9nm
26nm |
|
|
|
Three subunits of nuclear pore.
1) 2) 3) |
1) annular subunit (circle)
2) column subunit 3) lumenal subunit |
|
|
|
--- Early Endosome ---
Pathways? 1) ***(back) 2) *** in lysosome 3) ***(new membrane) |
1) Recycling
2) Degradation 3) Transcytosis |
|
|
|
--- Endocytosis Vesicle---
1) *** *** 2) *** *** 3) *** 4) *** |
1) Early Endosome
2) Late Endosome 3) Endolysosome 4) Lysosome |
|
|
|
Proteins can't traverse nuclear pore alone...
1) *** is required 2) Serving as either *** or ***. |
1) karyopherin
2) importin --- exportin |
|
|
|
--- KDEL ---
K? D? E? L? |
K--Lys--Lysine
D--Asp--Aspartic acid E--Glu--Glutamic acid L--Leu--Leucine |
|
|
|
--- Karyopherins ---
β su helps dock importin ***-bound protein to the nuclear pore complex. |
heterodimer
|
|
|
|
Proteins with an *** can form a heterotrimeric complex with an exportin.
|
nuclear export sequence (NES)
|
|
|
|
N-linked glycosylation begin with addition of a *** precursor through the *** enzyme.
|
14-sugar
oligosaccharyltransferase oligo saccharyl transferase |
|
|
|
Transfers 14-sugar to protein.
|
oligosaccharyl transferase
|
|
|
|
β su uses the *** repeat of *** as a ladder into the nucleus.
|
FG (phenylalanine—glycine)
nucleoporins |
|
|
|
1) ***: Chaperone ensuring only properly folded/assembled proteins proceed thru secretory pathway.
2) Protein is given *** chances to be sent to ***. |
1) Calnexin
2) 3 --- golgi |
|
|
|
1) N-linked glycosylation of *** in ***.
2) O-linked glycosylation of *** in ***. |
1) Nitrogen --- ER
2) Oxygen of hydroxyl --- Golgi apparatus |
|
|
|
The islets of Langerhans are the regions of the *** that contain its endocrine cells.
|
pancreas
|
|
|
|
--- O-linked Glycosylation ---
1) Oxygen of these AA(3 forms) 2) When followed by... |
1) (Ser)ine, (Thr)eonine, (tYr)osine
2) (asp)aragiNe |
|
|
|
Kinetochores(on centromeres) link chromosome and *** *** through ***.
|
mitotic spindle
microtubules |
|
|
|
--- N-linked Glycosylation ---
1) Nitrogen of AA *** 2) Followed by AA ***... |
1) asparagiNe - Asn
2) (aRg)inine |
|
|
|
Primer attaches to the *** end of its complementary strand..
|
3'
|
|
|
|
--- VTC(*** *** ***) ---
Compartment trafficking between ER & Golgi carried on ***. |
VTC(Vesicular tubular cluster)
microtubules |
|
|
|
Nucleosomes contain about ** bp of DNA.
|
200
|
|
|
|
--- Histone Mods ---
1) M 2) P 3) A 4) U?? |
1) methylation
2) phosphorylation 3) acetylation 4) ubiquitylation |
|
|
|
--- Insulin Mechanism ---
1) *** Bi*** 2) ***tion 3) C*** c*** 4) T****** of t*** |
1) Ligand Binding
2) Dimerization 3) Conformation Change 4) Transphosphorylation of Tyrosines |
|
|
|
1) *** forms coated vesicles.
2) *** shaped with # heavy chains 3) and # light chains. |
1) Clathrin
2) triskelion --- 3 3) 3 |
|
|
|
NLS is *** AA long containing *** charged AAs...
1) 2) |
8-10 --- positively
1) lysine - Lys - K 2) aRginine - Arg - R |
|
|
|
--- Cholesterol Import ---
1) E*** 2) U*** 3) Fusion With *** 4) Budding Off Of *** *** 5) Return of *** *** to *** |
1) Endocytosis
2) Uncoating 3) Fusion With Endosome 4) Budding Off Of Transport Vesicles 5) Return of LDL Receptors to PM |
|
|
|
--- *** ---
In inner mitochondrial membrane. Essential for energy metabolism. |
Cardiolipin
|
|
|
|
Lysosomal enzymes are tagged w/***--***-*** and sent to lysosome.
|
mannose-6-phosphate
|
|
|
|
1) Ubiquitin ***, has *** subunits
2) attaches ubiquitin to the *** AA 3) via an *** bond. |
ligase --- three
lysine isopeptide |
|
|
|
--- Cholesterol Import Verbs ---
1) E*** 2) U*** 3) F*** 4) *** O*** 5) Return |
1) Endocytosis
2) Uncoating 3) Fusion 4) Budding Off |
|
|
|
-- rRNA locations?!?! ---
1) *** rRNA not from nucleolus 2) *** rRNA from nucleolus |
1) 5S
2) 45S |
|
|
|
The *** *** *** are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine cells.
|
islets of Langerhans
|
|
|
|
***: AA sequence used for nuclear import.
|
NLS (Nuclear localization signal/sequence)
|
|
|
|
1) There's # way out of ER...
2) goes through the *** 3) Another method is through *** contact sites. |
1) one
2) golgi 3) membrane |
|
|
|
Strand newly synthesized started at its *** end.
|
5'
|
|
|
|
What AA is important in glycosylation?
What type and where? |
asparagiNe - Asn
O-linked - 1st of 2... N-linked - 1st of 1... |
|

