![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chain termination DNA Sequencing---
Q1) DNA sequence is read from ----.(***) Q2) Bottom bands are the *** fragments. |
Q1) bottom of the gel upward(AFTER primer)
Q2) shortest |
|
|
*** EXPLAIN ***
Chain termination DNA Sequencing 1) dsDNA > ??? 2) Add ??? to reaction tubes .............. |
1) ssDNA
2) ssDNA - A, T, G, C |
|
|
*** EXPLAIN ***
Chain termination DNA Sequencing 3) heat to *** & *** according to size by ---. 4) Analyze with ***/*** film OR ***/gel ***. |
3) denature & separate - gel electrophoresis
4) autoradiography/x-ray film UV light/gel image |
|
|
FIVE CELL TERMS
3/5 - Outside To Inside |
Apical plasma membrane
Lateral plasma membrane Basal plasma membrane |
|
|
FIVE CELL TERMS
2/5 - Outside To Inside |
tight junction
basal lamina |
|
|
Epithelial cells have two surface compositions called *** & ***.
|
basolateral membrane
apical membrane |
|
|
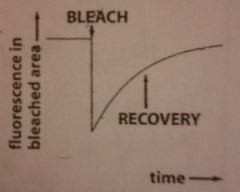
FRAP?
|
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching
|
|
|
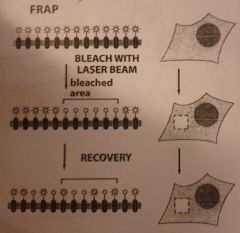
How does FRAP work?
1) small *** is --- 2) t---... 3) b--- d--- |
1) Small area is bleached
2) Time... 3) Bleached dissipates |
|
|
DRAW FRAP diagram
|
|
|
|
Tight junctions AKA ***.
|
zonula occluden
|
|
|
Name the four ways lipids move around?
1) Common 2) 3) 4) Rare |
Lateral diffusion
Flexion - break a pencil Rotation - spinning Flip-flop |
|
|
Hybridoma experiment.
1) - & - cell 2) form ---- |
1) Mouse & human cell
2) Form heterocaryon |
|
|
Hybridoma experiment.
3) components |
3) mouse Ig w/ fluorescein
human Ig w/ rhodamine |
|
|
Hybridoma experiment.
4) results |
0 minutes = 50/50 split
40 minutes = complete diffusion |
|
|
--- Ion Concentration gradients INSIDE cell ---
Higher? Lower? |
Higher - K+
Lower - Na+, Ca++, Cl- |
|
|
Glucose uptake in intestinal epithelial cells is driven by this common mechanism...
--- --- --- of *** ***. |
Potential energy gradient of second molecule
|
|
|
First glucose uptake protein? ***
Second? *** This helps too... *** |
Na+ driven glucose symport - Na+/Glucose IN
passive glucose transporter - Glucose out Na+/K+ pump - Na+ out and K+ in |
|
|
ABC-transporter?
|
ATP-binding cassette transporter
|
|
|
***(***) is the prototype and most extensively-studied ***.
|
Pgp (P-glycoprotein)
ABC transporter |
|
|
Pgp is a problem in *** because it transports drugs like...
*** |
chemotherapeutic treatment
adriamycin |
|
|
MDR?
|
Multidrug resistance
|
|
|
1) What is the problem with MultiDrug Transporter?
--- *** of *** *** w/*** *** 2) Why does it occur? --- *** *** a*** h*** s*** |
1) efflux of xenobiotic compounds w/broad specificity
2) defense mechanism against harmful substances. |
|
|
***: chemical present but not normally produced by the body.
Greek? |
Xenobiotic
xenos = foreigner bios = life -ic = adjective |
|
|
***: word/phrase naming an attribute.
|
adjective
|
|
|
Draw FRAP process....
|
|
|
|
***: a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface.
|
DNA microarray
|
|
|
DNA microarray is used to measure...
|
gene expression
|
|
|
DNA microarray steps...
1) --- & --- tagging 2) --- & wash 3) analyze w/--- |
1) red & green fluorescent tagging
2) hybridize & wash 3) fluorescence microscope |
|
|
Microarrays use strands of *** to ***.
|
DNA to complement mRNA
|
|
|
1) Three parts of cholesterol.
4) How long? |
1) polar head group
2) rigid steroid ring structure 3) nonpolar hydrocarbon tail 4) 2nm |
|
|
*** is a drug that utilizes lysosomes.
|
Doxorubicin
|
|
|
---CELL MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY---
?3? - hydrophobic molecules |
O2 - N2 - steroid horomones
highly |
|
|
---CELL MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY---
?3? - small uncharged polar molecules |
h2o - urea - glycerol
occasionally |
|
|
---CELL MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY---
?2? - large uncharged polar molecules |
glucose - sucrose
rare |
|
|
---CELL MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY---
?5? - ions molecules |
H+ - Na+ - K+ - Cl- - HCO3-
never |
|
|
***: Glial cells of the CNS.
|
Oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters bind to *** on *** and cause an inrush of Ca++.
|
transmitter-gated ion channels
dendrites |
|
|
*** is a good endonuclease restriction enzyme.
|
HpaI
I=roman numberal Haemophilus parainfluenzae |
|
|
Lipid bilayer is *** thick.
|
5nm
|
|
|
1) PE?
2) PS? |
Phosphatidyl-
1) ethanolamine 2) serine |
|
|
NANA is also known as ***. It is known for...
|
Sialic acid
net negative charge in ECM |
|
|
*** charge in cytosol... *** on outside.
|
-
+ |
|
|
The *** is what is duplicated in bacteria during molecular cloning.
|
recombinant plasmid
|
|
|
BAC?
|
Bacterial artificial chromosome
|
|
|
Only the creation of a *** library uses restriction nuclease ***.
|
genomic DNA
digestion |
|
|
Bacteria used in Genomic DNA Libraries have a *** for identification.
|
selectable marker
|
|
|
Membrane protein that uses...
mutiple alpha helixes |
multipass transmembrane protein
|
|
|
Membrane protein that uses...
covalent bonds on outer monolayer |
partial anchoring protein
|
|
|
(S)*** are found in the cytosol.
|
sulfhydryl groups
|
|
|
Transmembrane proteins can be limited to regions through a --- and ---.
|
membrane 'skeleton' and associated proteins
|
|
|
Channels control by these means...
|
1) voltage-gated
2) ligand-gated(extra/extracellular ligand) 3) mechanically gated |
|
|
States of Na+ channels...
|
Closed
Inactivated Open |
|
|
***: action potential of myelinated axons....
***: action potential of nonmyelinated axons.... |
Saltatory conduction
action potential conduction |

