![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1M solution = ***/***
|
1 mole/1L
|
|
|
1M of H2SO4 = 2M H+
Equivalence factor = *** 1M H2SO4 solution = *** normal |
equivalent factor...
0.5 2N |
|
|
1 molal solution = ***/***
|
1mol / 1000g of solvent
1mol / 1kg of solvent |
|
|
1mL of 50X + 24mL diluent
This is a *** dilution with the Dilution Factor being *** |
1/25
25 |
|
|
What is a Bronsted acid?
|
proton donor
|
|
|
What is a Bronsted base?
|
proton acceptor
|
|
|
What is autoionization?
|
spontaneous formation of ions
|
|
|
EQUATION for dissociation constant?
|
Keq=
[H+][OH-] ---------- [H2O] |
|
|
pH = pKa
[HA](***) concentration is *** [A-](***) concentration. |
acid - equal - base
|
|
|
pH > pKa
[HA](***) concentration is *** [A-](***) concentration. |
acid - less - base
|
|
|
pH < pKa
[HA](***) concentration is *** [A-](***) concentration. |
acid - greater - base
|
|
|
Buffers must be +/- *** pH from desired pH......
|
1 or 0.5
|
|
|
To make a buffer you need *** and ***.
|
weak acid(or weak base)
and its salt |
|
|
If x = b^y...
*** is the logarithm of *** to base *** Written... y=log***(***) |
y - x - b
logb(x) |
|
|
1000 = 10^3
log***(***) = *** |
log10(1000) = 3
|
|
|
What equation is used to find the pH of buffer solutions?
|
Henderson–Hasselbalch equation
|
|
|
Chromatography is a method for separating the components of a mixture by *** *** between a stationary phase and a mobile phase.
|
differential adsorption
|
|
|
All chromatographic systems have these common features...
*** phase *** phase *** mixture |
mobile
stationary component |
|
|
Partition coefficient: constant for a given *** with *** but varies w/***.
|
pair of solvents
a particular solute temp |
|
|
***: The ratio of concentrations of a compound in the two phases of a mixture of two *** solvents at equilibrium.
|
Partition coefficient
immiscible |
|
|
Chromatography: Cellulose w/acetone...
1) a neutral analyte travels w/*** 2) a polar analyte travels w/*** |
1) acetone - fast
2) thin layer of water on cellulose - slow |
|
|
Small molecules in gel filteration chromatography....
|
are retarded
|
|
|
***: Process by which the energy of a photon of electromagnetic radiation is taken up by another entity.
|
Absorption
|
|
|
A *** is used to measure absorbance.
|
spectrophotometer
|
|
|
Reagents *** or *** *** with a chemical of interest that doesn't absorb UV/visible wavelength.
|
react
form complexes |
|
|
Only use standard curves when absorbance values fall into the *** region.
|
linear
|
|
|
Sedimentation coefficient?
|
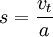
the ratio of a particle's sedimentation velocity to the acceleration that is applied to it (causing the sedimentation).
|
|
|
The sedimentation coefficient has the dimensions of a unit of time and is expressed in ***.
|
svedbergs
|
|
|
Bigger particles tend to sediment faster and thus have higher *** values.
|
svedberg
|
|
|
Two common types of centrifuge rotors...
1) 2) |
1) fixed angle
2) swing out |
|
|
*** law describes the rate of sedimentation of a sphere in a liquid and provides insight into purifying subcellular particles using centrifugation.
|
Stoke's
|
|
|
ρ(***) is commonly used as a unit for ***.
|
Rho - density
|
|
|
Rate zonal centrifugation is...
|
separation by size
|
|
|
Isopycnic centrifugation is...
|
separation by density
|
|
|
Enyzmes are measured in
|
M/L
g g/L katal |
|
|
The *** is the SI unit of catalytic activity.
|
katal(kat)
|
|
|
A *** *** can be used to estimate the initial rate of an enzyme.
|
progress curve
|
|
|
Plot of substrate (S) or product (P) against time is called a *** ***.
|
progress curve
|
|
|
Measure enzyme @ start & at a point on the linear phase to estimate ***.
|
initial rate/velocity
|
|
|
The ____ rate of the reaction increase as more substrate is added.
|
initial rate/velocity
|
|
|
Enzymes helps substrate reach its *** and does NOT alter the ***.
|
equilibrium
thermodynamics |

