![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does sustainable development differently? |
- Usual Progression of Legal Concept: Domestic to International
- Sustainability as Reverse Progression: from International toDomestic - Sustainability as a Legal Tool (a.k.a. “cause of action“) inGermany, UK, India, USA and South Africa |
|
|
History ofLegal Concept of Sustainability |
- 1987 WCED (UN World Commission on Environment and Development)names environmental goal of “sustainable development” (only political, notlegal) Why?? - 1992 UNCED (Conference on Environment and Development) signs 5legal documents: Agenda 21, Rio Declaration, Statement of Forest Principles,UNFCCC, UN Convention on Biological Diversity - 2002 Johannesburg: Declaration on Sustainable Development - 2005 New York: Three Pillars: env. protection, social dev. andecon. dev. |
|
|
Definitions:Compliance,Enforcement |
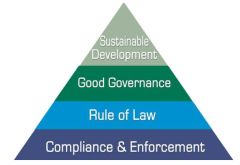
Environmental compliance and enforcement are the foundation for therule of law, good governance, and sustainable development. Compliance when an actor does what the rule oflaw says to do, regardless of motivation. Enforcement actions states or others take tocompel or induce compliance |
|
|
How does one know that “sustainable development” or “sustainability” isa custom? |
ICJCases |
|
|
WHO Sustainable Development Goals |
· Replaces the Millennium Development Goals of2000 – 2015. · Note that SD is now used as the major concept ofworldwide WHO development |
|
|
What would you bundle together as asource of law so you can pin down a state? |
- Trail smelter arbitration - State responsibility principle → if company hurts people in another state, a state has to reactlike they are their citizens |
|
|
Challenges for Transgovernmental Networks |
- Behavioral Change (Economic incentives, Socialnorms) - Trilemma: need for global rules withoutcentralized power but with political accountability |
|
|
Example to Meet theChallenges of Transgovernmental Networks |
- Behavioral Change (Economic incentives, Socialnorms) - Trilemma: need for global rules withoutcentralized power but with political accountability |
|
|
GeneralPrinciples of Law |
- AbsoluteTerritorial Sovereignty (Harmon Doctrine 1896) - Communityof Interests (1929—RiverOder Case) - AbsoluteTerritorial Integrity (TrailSmelter Case 1941) - LimitedTerritorial Sovereignty (the prevailing theory today) |
|
|
River Oder Case(1929) |
- principleof Community of Interests - principleof freedom ofnavigation - generalprinciples of international river law |
|
|
Trail SmelterCase (1941) |
- Noharm principle - AbsoluteTerritorial Integrity |
|
|
The Lake LanouxArbitration (1958) |
- AbsoluteTerritorial Integrity· principleof Community of Interests - “therule that states may utilize the hydraulic power of international water cannotbe established as a custom, even less as a general principle of law“ |
|
|
Czechoslovakia against Hungary (1997) |
Hungaryuses custom and cites Lac Lanoux and River Oder cases in its application. |
|
|
Nuclear Test Cases (1995) |
Australiaargued that the 1963 Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (France not a member) also formed“emergent rule of customary international law.“ |
|
|
International adjudications canoccur through: |
- ICJ - Commissions - Arbitrationpanels - Even whenno official result is reached, the act of taking a claim before one of theabove can be effective to achieve desired result. |

