![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Enantiomer
|
1 of 2 stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other that are "non-superposable."
|
|
|
Diastereomer
|
When two or more stereoisomers have different configurations at one or more stereocenters & are not mirror images.
|
|
|
Meso Structure
|
Compound that is superposable on its mirror image.
|
|
|
Name the types of halides....
|
methyl halide
1° - primary alkyl halide 2° - secondary alkyl halide 3° - tertiary alkyl halide |
|
|
1° - primary alkyl halide...
|
1 alkyl group attached to head carbon
|
|
|
2° - secondary alkyl halide
|
2 alkyl group attached to head carbon
|
|
|
3° - tertiary alkyl halide
|
3 alkyl group attached to head carbon
|
|
|
A nucleophile is...
|
a compound that either is negatively charged or has a region of high electron density(lone pair/double bond).
|
|
|
A electrophile is...
|
a compound that either is + charged or has a region of low electron density.
|
|
|
SN1 means...
|
substitution nucleophile
unimolecular... |
|
|
SN2 means...
|
substitution nucleophile
bimolecular... |
|
|
SN1/SN2 reactions result in a racemix product mixture.
|
SN1
|
|
|
1st degree molecules undergo SN1/SN2.
|
SN2
|
|
|
3rd degree molecules undergo SN1/SN2.
|
SN1
|
|
|
1st degree molecules undergo SN1/SN2.
|
SN2
|
|
|
3rd degree molecules undergo SN1/SN2.
|
SN1
|
|
|
Does a strong nucleophile increases the reaction rate of an SN1 reaction?
|
No
|
|
|
Does a strong nucleophile increases the reaction rate of an SN2 reaction?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Strong nucleophiles favor SN*** reactions.
|
SN2
|
|
|
Polar aprotic solvents prefer SN*** reactions.
|
SN2
|
|
|
Strong nucleophiles prefer SN*** reactions.
|
SN2
|
|
|
Weak nucleophiles prefer SN*** reactions.
|
SN1
|
|
|
Name some alkane reactions...
|
halogenation
combustion cracking |
|
|
All Organic Reactions Fall into there categories
1) S*** 2) A*** 3) E*** 4) R*** |
1) Substitution
2) Addition 3) Elimination 4) Rearrangement |
|
|
*** State: Point on the reaction coordinate when the potential energy is maximum.
|
Transition
|
|
|
***: A potential energy minimum between two transition states.
|
Intermediate
|
|
|
Walden *** Reaction
|
Inversion
|
|
|
***: A species w/unshared electron pair seeking a *** charge.
|
Nucleophile
positive |
|
|
A good leaving group must be able to leave as a relatively stable, weakly *** molecule, or i***.
|
basic --- ion
|
|
|
The SN2 Reaction
• Reaction is with inversion at *** center • Follows *** order reaction kinetics |
reacting
second |
|
|
SN2?
|
S - substitution
N - nucleophilic 2 - bimolecular |
|
|
Alkyl halides are polarized at the *** bond, making the carbon ***.
|
carbon-halide
electrophilic |
|
|
The study of rates of reactions is called ***.
|
kinetics
|
|
|
SN# involves a transition state in which both reactants are together.
|
2
|
|
|
The transition state of an SN2 reaction has a *** arrangement of the carbon atom and the remaining three groups
|
planar
|
|
|
--- SN2 ---
There is/isn't a reaction at C=C (*** halides). *** halides are most reactive *** halides are unreactive by this path |
isn't --- vinyl
Methyl Tertiary |
|
|
No SN2 substitution of v*** halides
& a*** halides. |
vinyl
aryl |
|
|
Better nucleophiles are higher/lower in a column of the periodic table.
|
lower
|
|
|
What is a vinylic halide?
|
=CHX
|
|
|
*** (Latin = ***) refers to the relationship between 2 groups attached to the same atom.
|
Geminal
twins |
|
|
*** (Latin = ***) stands for any 2 groups bonded to two adjacent carbon atoms
|
Vicinal
neighbor |
|
|
--- t-butyl ---
1) The "t" signifies what? 2) Connected where? 3) Butyl? |
1) tertiary(3)
2) first carbon 3) 4 carbons |
|
|
--- sec-butyl ---
1) The "sec" signifies what? 2) Connected where? |
1) secondary
2) first carbon |
|
|
--- isobutyl ---
1) "iso" signifies what? 2) Connected where? |
1) equal
2) last carbon |
|
|
--- n-butyl ---
"n" signifies what? |
normal
|
|
|
C-X dipole moments are weird.
What is the strongest" F, Cl, I or Br? |
Cl
then F, Br, and I |
|
|
-C≡N is a *** group.
AKA anion CN− |
cyanide
|
|
|
Nitrogen has *** valence electrons available for bonding.
|
five
|
|
|
F- is a strong/weak nucleophile.
|
weak
|
|
|
Boron and Aluminum need *** valence protons to satisfy their happiness.
|
three
|
|
|
Factor favorable for nucleophilicity but NOT basicity.
|
polarizability
|
|
|
DMF is a nonpolar/polar aprotic/protic solvent w/high BP.
|
polar aprotic
Di - methyl - formamide |
|
|
***: special type of SN or E reaction where the nucleophile is also the solvent.
|
Solvolysis
|
|
|
Arrange in order of increasing reactivity w/ethanol solvolysis:
t-butyl bromide t-butyl iodide isopropyl chloride methyl iodide |
methyl iodide <
isopropyl chloride < t-butyl bromide < t-butyl iodide |
|
|
List in order of increasing reactivity as substrates in SN1 reactions:
PhBr PhCH2Br PhCH(CH3)Br |
PhBr <
PhCH2Br < PhCH(CH3)Br |
|
|
SN1 reactions usually proceed with:
A) equal inversion/retention B) slightly more inversion than retention C) slightly more retention then inversion D) complete inversion E) complete retention |
B) slightly more inversion than retention
|
|
|
When steric configuration doesn't change during a reaction it's said to occur with __________ of its stereochemistry.
|
retention
|
|
|
Which describe E1 reactions of alkyl halides (RX)?
I. Rate = k[base] II. Rate = k[base][RX] III. Rate = k[RX] IV. Reactions occur in 2 or more distinct steps. V. Rearrangements are sometimes seen. |
III
IV V |
|
|
Q: Why does CH2=CH-CHBr-CH3 undergo solvolysis more rapidly than 2-bromobutane?
A: The i*** carbocation is stabilized by r***. |
intermediate
resonance |
|
|
Dehydration of 1-butanol w/acid @ 140°C results in mainly trans-2-butene.... via E# w/a *** shift.
|
E1
hydride |
|
|
2) Which of the following is classified as a vinylic halide?
A) CH3CH=CHOH B) CH3CH=CHCl C) CH3CH=CHCH2Cl D) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br E) BrCH2CH=CH2 |
B) CH3CH=CHCl
|
|
|
23) Which of the following compounds will undergo an SN2 reaction most readily?
A) (CH3)3CCH2I B) (CH3)3CCl C) (CH3)2CHI D) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH2I E) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH2Cl |
D) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH2I
|
|
|
40) Which of the following alkyl bromides undergoes solvolysis in aqueous methanol most rapidly?
A) PhCHBrCH3 B) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br C) (CH3)2CHCH2CHBrCH3 D) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br E) PhBr |
A) PhCHBrCH3
|
|
|
44) List the following bromides in order of their increasing reactivity as substrates in SN1 reactions: 2-chlorobutane, 2-iodobutane, and 1-iodobutane.
|
Answer: 1-iodobutane < 2-chlorobutane < 2-iodobutane
|
|
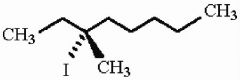
How many distinct alkene products are possible when the alkyl iodide below undergoes E2 elimination?
|
5
|
|
|
When two diastereoisomers differ from each other at only one stereocenter they are ***.
|
epimers
|
|
|
--- H1 NMR Signals ---
The *** of the signals shows how shielded or deshielded the proton is. |
location
|
|
|
--- H1 NMR Signals ---
The *** of the signal shows the number of protons of that type. |
intensity
|
|
|
--- H1 NMR Signals ---
Signal *** shows the number of protons on adjacent atoms. |
splitting
|
|
|
The more shielded methyl protons appear toward the *** of the spectrum (*** field)
|
right
higher |
|
|
2,130hz/300,000,000 = # ppm
|
7.10
|
|
|
More electronegative atoms deshield more and give *** shift values.
|
larger
|
|
|
1 delta = 1 ***
|
ppm
(same over all frequency NMRs) |
|
|
The chemical shift of an NMR absorption in DELTA units is ***, regardless of the operation frequency of the spectrometer.
|
constant
|
|
|
DEPT-NMR allows us to determine...
|
# of H attached to each C.
|
|
|
Coupling constants are independent/dependent of field strength.
|
independent
|
|
|
The coupling constant is the *** between the peaks of a m*** (in Hz).
|
distance
multiplet |
|
|
***topic groups in a chemical compound are equivalent groups.
|
Homo
|
|
|
Descriptions of *** are used to describe the stereochemical relationships between substituents... hetero, homo, enantio, or diastereo -topic.
|
Topicity
|
|
|
*** H+ are chemically & electronically equivalent... but replacement causes chirality.
|
Enantiotopic
|
|
|
*** H+ are not chemically & electronically equivalent.
|
Diastereotopic
|
|
|
Less shielded H+ need *** energy for resonance and are found on the *** of the NMR chart.
|
less
left |
|
|
More shielded H+ need *** energy for resonance and are found on the *** of the NMR chart.
|
more
right |
|
|
Suffix
-oate? |
Carboxylate
or Ester |
|
|
--- NMR ---
Integrating is used to... |
determine RATIO of H+
|
|
|
--- NMR ---
Spin-spin splitting is used to... |
determine # of H+ is ADJACENT carbons
Triplet = 2 adjacent H+ |
|
|
Septet?
|
7
|
|
|
*** is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation.
|
Irradiation
|
|
|
Name one factor that is favorable for nucleophilicity but not for basicity.
|
polarizability
|

