![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are sites called where two or more bones meet?
|
Joints or Articulations
|
|
|
Our ________ give our skeleton mobility and hold it together.
|
joints
|
|
|
In fibrous joints the bones are joined together by _______ tissue and lack a _______ cavity.
(structurally classified) |
fibrous; joint
|
|
|
In cartilaginous joints the bones are joined together by ________ and they lack a ________ cavity.
(structurally classifed) |
cartilage; joint
|
|
|
In ________ joints, the articulating bones are separated by a fluid-containing joint cavity.
(structurally classified) |
synovial
|
|
|
_________ are immovable joints.
(functionally classified) |
synarthroses
|
|
|
_________ are slightly movable joints.
(functionally classified) |
amphiarthroses
|
|
|
_________ are freely movable joints.
(functionally classified) |
diarthroses
|
|
|
How are bones held together at sutures?
|
they are held together with very short connective tissue fibers
|
|
|
Where do sutures occur?
|
between bones of the skull
|
|
|
In _________, the bones are connected by a ligament, which is a cord or band of fibrous tissue.
|
syndesmoses
|
|
|
Why are the joints of the skull considered synarthrotic?
|
because they are immovable
|
|
|
What are two ways joints are classified?
|
Structurally
Functionally |
|
|
What are the three structural classification of joints?
|
fibrous
cartilaginous synovial |
|
|
Epiphyseal plates are united by ___________.
|
Synchondroses
|
|
|
What is synchondroses?
|
involves a bar or plate of hyaline cartilage uniting the bones
|
|
|
Synovial Joints contain five distinguishing features.
2 out of 5 |
The joint(synovial) cavity is a space that is filled with synovial fluid.
|
|
|
What is symphyses?
|
amphiarthrotic joints composed of fibrocartilage that is compressible and resilient yet strong
|
|
|
Synovial Joints contain five distinguishing features.
1 out of 5 |
Articular cartilage covers the ends of the articulating bones.
|
|
|
Synovial Joints contain five distinguishing features.
3 out of 5 |
The two-layered articular capsule encloses the joint cavity.
|
|
|
Synovial Joints contain five distinguishing features.
4 out of 5 |
Synovial fluid is a viscous, slippery fluid that fills all free space within the joint cavity.
|
|
|
Synovial Joints contain five distinguishing features.
5 out of 5 |
Reinforcing ligaments cross synovial joints to strengthen the joint.
|
|
|
________ and _______ sheaths are bags of lubricant that reduce friction at synovial joints.
|
Bursae; tendon
|
|
|
The shapes of the articular surfaces of bones found at a synovial joint determine the movements that occur at the joint.
True or False |
True
Shape determines how it moves, but does not really play a role in stabilizing the joint. |
|
|
Ligaments help stabilize the joint.
True or False |
True
It does this by preventing excessive or unwanted movements. |
|
|
The greater the number of ligaments at the joint the greater the stability.
True or False |
True
|
|
|
What is the most important factor stabilizing joint?
|
The muscle tone keeps tendons that cross joints tight. .
|
|
|
What are the three types of movements that occur at synovial joints?
|
Gliding
Angular Rotation |
|
|
________ movements increase or decrease the angle between two bones.
|
Angular
|
|
|
Flexion
(7 types of angular movements at synovial joints) 1 out of 7 |
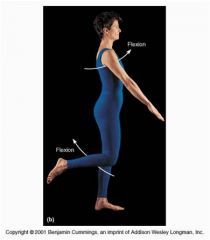
decreases the angle of the joint and brings the articulating bones closer together
|
|
|
Extension
(7 angular movements that occur at synovial joints) 2 out of 7 |
increases the angle between the articulating bones
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion
(7 angular movements that occur at synovial joints) 3 out of 7 |
decreases the angle between the top of the foot(dorsal surface) and the anterior surface of the tibia
|
|
|
Plantar Flexion
(7 angular movements that occur at synovial joints) 4 out of 7 |
decreases the angle between the sole of the foot(plantar surface) and the posterior side of the tibia
|
|
|
Abduction
(7 angular movements that occur at synovial joints) 5 out of 7 |
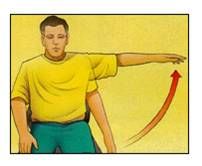
is the movement of a limb(or fingers) away from the midline body (or the hand)
(bring fingers apart) |
|
|
Adduction
(7 angular movements that occur at synovial joints) 6 out of 7 |
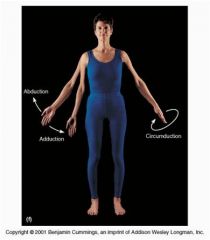
the movement of a limb (or fingers) toward the midline of the body (or the hand)
(bring fingers together) |
|
|
Circumduction
(7 angular movements that occur at synovial joints) 7 out of 7 |
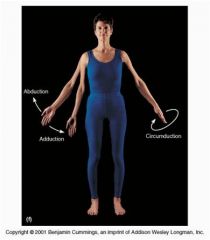
moving of a limb so that it describes a cone in the air
|
|
|
In _______ movements one flat, or nearly flat, bone surface glides or slips over another.
|
gliding
|
|
|
_______ is the turning of a bone along its own long axis.
|
Rotation
|
|
|
Pointing the toes is an example of _________.
|

plantar flexion
|
|
|
Neck Flexion
|
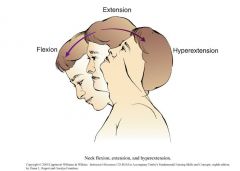
looking towards the ground
(leaning head foward) |
|
|
Neck Extension
|
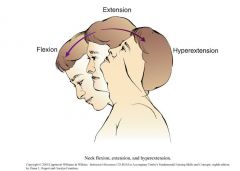
looking straight ahead
(keeping head straight) |
|
|
Neck hyperextension
|
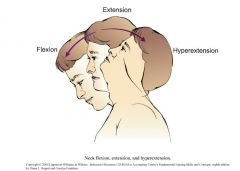
looking up
(leaning head back) |
|
|
What is a strain?
|
a pulled muscle
|
|
|
What is a sprain?
|
a pulled ligament
|
|
|
What is supination?
|
rotating the forearm laterally so that the palm faces anteriorly or superiorly
|
|
|
What is pronation?
|
rotation the arm medially so that the palm faces posteriorly or inferiorly
|
|
|
What is inversion?
(pertains just to feet) |
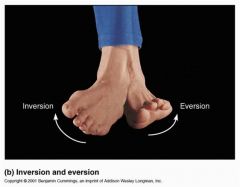
turns the sole of the foot so that it faces medially
|
|
|
What is eversion?
|
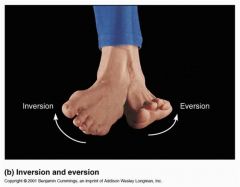
turns the sole of the foot so that it faces laterally
|
|
|
6 types of Synovial Joints
|
Plane Joints
Hinge Joints Pivot Joints Condyloid or Ellipsoid Joints Saddle Joints Ball and Socket Joints |
|
|
Plane Joints
|
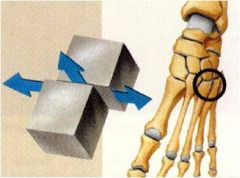
have a flat articular surface and allow gliding and transitional movements
|
|
|
Hinge Joints
|

consist of a cylindrical projection that nests in trough-shaped structures, and allow movement along a single plane
|
|
|
Condyloid or Ellipsoid Joints
|
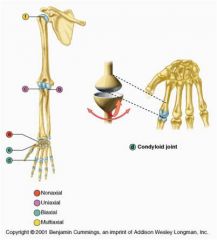
consist of an oval articular surface that nests in a complementary depression and permit all angular movements
|
|
|
Saddle Joints
|
consist of each articular surface bearing complementary concave and convex areas, and allow more freedom of movement than condyloid joints
|
|
|
Ball and Socket Joints
|
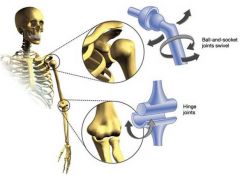
consist of a spherical or hemispherical structure that articulates with a cuplike structure.
|
|
|
__________ are the most freely moving joints and allow ________ movements.
|
Ball and Socket Joints ; multiaxial
|
|
|
Example of Hinge Joint
|
Elbow
Knee |
|
|
Example of pivot joint
|
atlantoaxial joint
|
|
|
Example of condyloid joint
|
radiocarpal joint
|
|
|
Example of Ball and Socket Joint
|
shoulder and hips
|
|
|
Which of the synovial joints are considered biaxial joints?
|
Condyloid
Saddle |
|
|
What is bursitis?
|
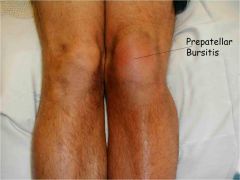
-an inflammation of the bursa
-usually caused by a blow or friction |
|
|
What is arthritis?
|
-decribes many inflammatory or degenerative diseases that damage the joints
|
|
|
What dsease results in pain, stiffness, and swelling of the joint?
|
arthritis
|

