![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

male
|
meiosis
|
|

|

|
|
|
gland that produces estrogen and progesterone
in back of model oval and yellowish |
ovaries
|
|
|
inner surface of the uterus
closest to cavity produces menstrual flow |
endometrium
|
|
|
smooth muscle that surrounds endometrium and forms most of the wall of the uterus
|
myometrium
|
|
|
opening for urethra
|
urethral orifice
|
|
|
opening for vagina
|
vaginal orifice
|
|
|
sperm can be stored in the
|
ampulla
|
|
|
within the spermatic cord
|
vas deferens
|
|
|
erectile tissue that surrounds urethra
|
corpus spongiosum
|
|
|
erectile tissue on posterior and lateral aspects of the penis
*on posterior only when erect |
corpora cavernosa
|
|
|
glands that produce energy for sperm via fructose
|
seminal vesicles
|
|
|
gives antibacterial agents to secretions to aid in procreation
|
prostate gland
|
|
|
cleans and lubricates the urethra from the urine
|
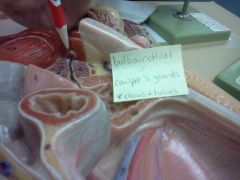
bulbourethral or Cowper's glands
|
|
|
space where testis drop through to go to outside of body
|
inguinal canal
|
|
|
where sperm mature
|
epididymis
|
|
|
site of sperm production
inside testis |
seminiferous tubules
tubes go in testis |
|
|
oven where baby develops
|
uterus
|
|
|
funnel shaped area of fallopian tubes
|
infundibulum
|
|
|
superior portion of uterus
|
fundus
|
|
|
central region of uterus
|
body
|
|
|
inferior end fo uterus...muscular opening
|
cervix
|
|
|
all outside female reproductive features
|
vulva
|
|
|
tube transporting sperm from production site to delivery area
|
vas deferens
|
|
|
tissue covering the gans at birth
|
prepuce or foreskin
|
|
|
male reproductive organ that produces hormones
|
testis
|
|
|
folds near the urethral and vaginal orifices
|
labia minora
|
|
|
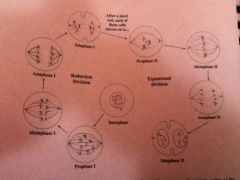
part of meiosis where cross over occurs
|
prophase 1
|
|
|
part of meiosis where pairs line up in middle
|
metaphase 1
|
|
|
part of meiosis where pairs separate
|
anaphase 1
|
|
|
part of meiosis where we have 2 new cells
|
telophase 1
|
|
|
part of meiosis where nuclear envelope disappears
|
prophase 2
|
|
|
part of meiosis where chromosomes line up single file
|
metaphase 2
|
|
|
part of meiosis where chromatids separate
|
anaphase 2
|
|
|
part of meiosis where there are 4 new cells
|
telophase 2
|
|
|
Oogenesis
primary oocyte primordial follicles primary follicle secondary follicle Graafian follicle then.... |
if not fertilized to become an ovum then it will just get ovulated
|
|
|
the ouchie on model
ovarian blood clot |
corpus hemorrhagicum
|
|
|
scar on model
ovarian scar white puffy on right |
ccorpus albicans
|
|
|
cell of the female which is ovulated
|
secondary oocyte
|
|
|
stays if pregnant and doesn't continue on with repair
|
corpus luteum
|
|
|
fluid filled ovarian structure
|
antrum
|
|
|
process in which the egg is released from the Graafian follicle
|
ovulation
|
|
|
cell produced at the end of telophase 2 in the male
|
spermatids
|
|
|
DNA replication occurs during
|
interphase
|
|
|
formation of polar bodies occurs when
|
telephase 1 and 2
|
|
|
phase that begins with a diploid cell
|
prophase 1
|
|
|
phase that ends the reduction division
|
telephase 1
|

