![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
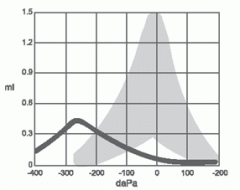
What type is this tympanogram and what does it indicate?
a. Type A - normal ear drum function b. Type B - negative middle ear pressure c. Type C - normal ear drum function d. Type C - negative middle ear pressure; Eustachian tube dysfunction |
The correct answer is D. This is a type C tympanogram and indicates negative middle ear pressure, Eustachian tube dysfunction, and/or conductive hearing loss
|
|
|
You get a client with a hearing loss of 65 dB. The client does not remember the severity level of the hearing loss and asks you for clarification. What is the correct response?
a. no loss, normal hearing b. mild-moderate c. moderate-severe d. severe-profound e. deaf |
The correct answer is c. Hearing losses of 56-70 dB indicate moderate-severe loss.
|
|
|
A retired construction worker comes into your clinic for a hearing test. The patient reports wearing hearing protection "most of the time". He reports he has developed ringing in his hear. He does not have a history of ear infections. The likely hearing loss will be:
a. conductive b. mixed c. sensorineural d. none |
The correct answer is c. Due to the prolonged exposure to noise and inconsistent use of hearing protection this patient likely damaged nerve cells. Also, the patient is experiencing tinnitus, a common accompanying condition of a noise induced sensorineural loss.
|
|
|
______ are from problems of the outer, middle, or inner ear; ______ are from problems of the transmission between the brainstem and the cerebrum and cause information to be received or processed incorrectly.
a. central auditory disorders; peripheral hearing disorders b. deafness; conductive hearing loss c. peripheral hearing disorders; deafness d. peripheral hearing disorders; central auditory disorders |
The correct answer is d. Peripheral hearing disorders are caused by problems in the outer, middle, or inner ear (not including CN VIII. Central auditory disorders involve processing of information between the brainstem and the cerebrum.
|
|
|
A patient presents with the following: unilateral high-frequency hearing loss, dizziness, tinnitus, off-balance, absent acoustic reflexes in the affected ear, pain in affected ear, normal PTA, and normal SRT in quiet. You suspect the following:
a. retrocochlear pathology b. CAPD c. Malingering d. Sensorineural loss |
The correct answer is a. Retrocochlear pathology includes all the listed symptoms.
|
|
|
An air-bone gap of 15 dB is noted on a patient's audiogram. What kind of hearing loss is indicated?
a. Conductive b. Sensorineural c. Mixed d. Deafness |
The correct answer is A. An air-bone gap is the difference between the bone-conduction hearing threshold and the air-conduction threshold for a frequency in the same ear. When the gap is +10 dB it indicates a conductive hearing loss.
|
|
|
A child experiences trauma at age 7 and becomes profoundly deaf. This is considered:
a. A congenital loss b. prelingual deafness c. postlingual deafness d. a conductive loss |
The correct answer is c. Since the loss occurred after age 5, the child is considered to have experienced postlingual deafness because it is after the acquisition of language.
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a prognostic indicator for speech and language development in children:
a. quality of intervention b. presence of blindness c. age when intervention begins d. extent of parent involvement e. none of the above |
The correct answer is e. Prognostic indicators include all of the listed choices.
|
|
|
People with hearing impairments often have trouble:
a. monitoring their own speech, language, and voice b. understanding spoken language c. with articulation d. with resonance e. all of the above |
The correct answer is E. People with hearing loss have difficulty with all the listed choices as well as difficulty with language, and fluency.
|
|
|
Which of the following is a common characteristic of language for a prelingual deaf speaker:
a. use of a variety of sentence types of increased length and complexity b. easily comprehending embedded sentences c. not providing background information to the listener d. acquiring grammatical markers at same rate as hearing speakers e. none of the above |
The correct answer is c. It is common for speakers who are prelingually deaf to not include sufficient background information to a listener.
|
|
|
Which is an expected voice characteristic of a person who is deaf:
a. hypernasal on non-nasal sounds b. abnormal flow of speech c. monotone speech d. restricted pitch range e. all of the above |
The correct answer is e. All of the listed characteristics are common in a speaker who is deaf. Also included is a too slow/fast rate, inappropriate pauses, voice quality differences, and abnormal stress patterns.
|
|
|
A parents reports their child has a marked long-term difficulty with localizing a sound source, following the melody in a song, following directions especially when it is noisy, and reading aloud. You suspect:
a. a conductive hearing loss b. a central auditory disorder c. a developmental language delay d. a developmental phonological delay |
The correct answer is b. A child with a central auditory disorder may also have difficulty understanding rapid speech, overall academic problems, poor auditory discrimination, auditory integration, auditory sequencing, auditory memory, auditory closure, and auditory memory.
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a direct contributing factor to the increase of people having a hearing loss?
a. baby boomers are getting older b. use of personal music players and use of earbuds c. people living longer d. use of personal computers |
The correct answer is d. The use of personal computers is not a direct cause of the increase in hearing loss.
|
|
|
Which of the following would be not considered a risk factor for a hearing loss?
a. Cleft palate b. FAS c. pre-term birth d. Family hx of disfluencies e. mother contracted syphilis during pregnancy |
The correct answer is d. A positive family history of stuttering does not necessarily place a person at increased risk of hearing loss.
|
|
|
A person is considered deaf when the hearing loss is:
a. 45 dB b. 50 dB c. 60 dB d. greater than 75 dB |
The correct answer is d. A loss of greater than 75 dB would indicate deafness.
|
|
|
A child is born with a cleft palate and the ear canal is completely closed, you suspect the following:
a. retrocochlear pathology b. CAPD c. aural atresia and a conductive hearing loss d. normal hearing |
The correct answer is c. When the ear canal is closed it is called aural atresia and is commonly seen in children with cleft palate. Aural atresia will cause a conductive hearing loss.
|
|
|
______ occurs when a spongy growth develops on the footplate of the stapes causing the stapes to become rigid. Carhart's Notch is often seen on the audiogram.
a. otosclerosis b. Meniere's c. Malingering d. CAPD |
The correct answer is a. Otosclerosis is described here and often causes a conductive hearing loss.
|
|
|
STORCH stands for:
a. syphilis, toxoplasmosis, other, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes b. staff infection, tinnitus, other, retrocochlear, cystic fibrosis, herpes c. syphilis, tinnitus, other, rubella, colitis, heart disease d. SIDS, tinnitus,other, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes |
The correct answer is a. STORCH is the acronym that describes the major viral and bacterial causes of infant hearing loss.
|
|
|
_______ is a hearing impairment that is due to aging affecting the high frequencies causing people to have difficulty understanding speech in a noisy environment.
a. Meniere's b. CAPD c. ME Effusion d. presbycusis |
The correct answer is d. Presbycusis is hearing loss due to age and usually appears as sensorineural affecting the high frequencies.
|
|
|
A person with central auditory disorders has ______ ability to comprehend distorted speech when compared to a person with normal hearing.
a. less b. greater c. indifferent d. superior |
The correct answer is a. A person with central auditory disorder has great difficulty understanding distorted speech.
|
|
|
What is the common cause of a retrocochlear pathology?
a. FAS b. otosclerosis c. acoustic neuroma d. BPPV |
The correct answer is c. Acoustic neuroma is a tumor and is often found unilaterally.
|
|
|
Acoustic neuroma and Meniere's disease have similar presentations. What is used for differential diagnosis?
a. ABR b. PTA c. SRT d. CPA |
The correct answer is a.
|
|
|
_____ drugs are especially damaging to the cochlea and/or CN VIII fibers.
a. antibiotics b. vitamin D supplements c. ototoxic d. NSAIDS |
The correct answer is c. Ototoxic drugs can damage the cochlear or CN VIII fibers, especially antibiotics from the "mycin" family.
|
|
|
Middle ear problems can be caused by:
a. negative ME pressure b. increased mass of ME c. decreased stiffness of ME d. a and b only e. a, b, and c |
The correct answer is e. ME problems can also be caused by increased stiffness of the ME.
|
|
|
A patient has a hearing loss that comes and goes, dizziness, feeling full in the ear, tinnitus. You suspect:
a. Malingering b. Meniere's c. BPPV d. CAPD |
The correct answer is b. These are symptoms of Meniere's Disease.
|
|
|
Sources:
Roseberry-McKibbin, C., & Hegde, M. N. (2011). An advanced review of speech-language pathology. (3rd ed.). Austin, TX: Pro-Ed An International Publisher. |
Sources:
Roseberry-McKibbin, C., & Hegde, M. N. (2011). An advanced review of speech-language pathology. (3rd ed.). Austin, TX: Pro-Ed An International Publisher. |

