![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acid-base homeostasis |
Acid producing, acid buffering, acid excretion |
|
|
Acid |
Substances that release hydrogen when dissolved in water Fats form fatty acids, proteins form amino acids |
|
|
Bases |
Substances that bind hydrogen ions when in water |
|
|
pH |
The measure of acidity or alkalinity due to the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in body fluid |
|
|
Alkaline solution |
Higher pH less amount of H+ ions |
|
|
Acid solution |
Lower the pH the greater amount of H+ |
|
|
Blood pH |
7.35-7.45 |
|
|
Urine pH |
4.6-8.0 |
|
|
Alkalosis |
Blood pH is >7.45 |
|
|
Acidosis |
Blood pH is <7.35 |
|
|
Bicarbonate buffer system (chemical regulator) |
-first line of defense against a change in pH -maintains the acid base balance 50% of the time -acts instantaneously but can’t maintain balance for long -acts with acids or bases to prevent significant changes in patients pH |
|
|
Bicarbonate in ECF & ICF |
-act primarily in ECF -common buffers -given IV during emergencies -acts instantaneously -normally bicarbonate base HCO3:: carbonic acid H2CO3 = 20::1 |
|
|
Phosphate buffers in ICF |
-control small fluctuations in pH -responds quickly |
|
|
Protein found in ICF (hemoglobin) and ECF (albumin) |
-responds quickly -most plentiful and most powerful of the buffer -act as acid or base as the occasion demand |
|
|
Respiratory regulation |
-second line of defense -reacts within minutes to hour to blood pH -come to the rescue when fluctuations are acute and chemical buffers are no longer doing -regulates carbonic level by altering rate and death of respiration’s *if excess acid= ^ resp. rate to blow off excess co2 and water vapor *if excess base= decreased resp rate to retain co2 which combines with water to form carbonic acid |
|
|
Renal regulatjon |
-third line of defense, most powerful mechanisms for regulating -takes a longer time to begin: slowest of the regulating systems (takes hours to days) -regulates by altering the rate of H+ or bicarb ion excretion -alkalosis: retains H+ excretes bicarb// acidosis: retains bicarbs, excretes H+ -eliminations metabolic acids (lactic acid), regulates PH+, forms ammonium salts -three major renal mechanisms; tubular kidney movement of bicarbonate, kidney tubule formation of acids, formation of ammonium from amino acid catabolism |
|
|
Arterial blood gas |
Blood gas measurements remain the major diagnostic tool for evaluating acid-base status |
|
|
pH value |
Acidosis <7.35-7.45>alkalosis Measures blood acidity, concentration of H+ ions, indicates acid base balance |
|
|
paCO2 value |
Alkalosis<35-45mmHg>acidosis Measures partial pressure of CO2 |
|
|
pa02 value |
Acidosis<80-100mmHg>alkalosis Measure partial pressure of O2 in arterial blood Indicates level of oxygenation of the cardiopulmonary systems |
|
|
HCO3 (bicarb) value |
Acidosis<22-26mEq/L>alkalosis Measures the amount of bicarbonate in the arterial blood Indicates level of kidney function Major factor in metabolic acid-base balance |
|
|
O2 saturation |
95% or higher The oxygen saturation of available Hemoglobin Not a reliable indicator, too many variables |
|
|
Nursing interventions for acid-base imbalances |
1. Monitor and assess patients for risks, s/sx and causes 2. Monitor ABG and lab results as ordered and report abnormalities 3. Monitor and assess vital signs, respiratory, cardiac and neurological status |
|
|
Respiratory acidosis |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Respiratory alkalosis |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Metabolic acidosis |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Metabolic alkalosis |
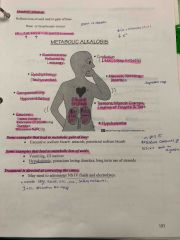
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Acid base imbalances |
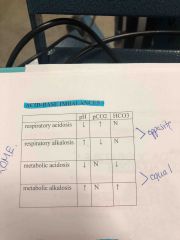
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Oxygenation |
Delivery of oxygen from lungs, to heart, and rest of the body Delivery of deoxygenated blood from body to heart and pulmonary circulation Function of both respiratory/CV systems to supply body’s oxygen demand |
|
|
Ventilation |
Process of moving gases into and out of the lungs |
|
|
Tissue perfusion |
Ability to the cardiovascular system to pump oxygenated blood to the issues and returned deoxygenated blood to the lungs |
|
|
Diffusjon |
The spreading of something widely |
|
|
Diffusion |
The spreading of something widely |
|
|
Inspiration |
ACTIVE process, stimulated by chemical receptors |
|
|
Expiratjon |
PASSIVE process that depends on the elastic recoil properties of lungs, requiring little to no muscle work |
|
|
Surfactant |
Chemical produced in the lungs to maintain the surface tension of the alveoli and keep from collapsing |
|
|
Atelctasis |
Collapsed lung |
|
|
Accessory muscles |
Increased lung volume during inspiration |
|
|
Compliance |
Ability of the lungs to distend or expand in response to increased intra-alveolar pressure |
|
|
Airway resistance |
Increased in pressure that occurs as the diameter of the airways decrease from mouth/nose to alveoli |
|
|
Tidal volume |
Amount of air exhaled following a normal inspiration |
|
|
Residual volume |
Amount of air left in the alveoli after a full expiration |
|
|
Forced vital capacity |
Maximum amount of air that can be removed from the lungs during forced expiratjon |
|
|
Oxygen transport |
Consists of the lungs and cardiovascular |
|
|
Regulation of respiration |
Ensures sufficient O2 intake and CO2 elimination to meet the demands of the body Neural/chemical regulators control the process of respiration |
|
|
Hypovolemia |
Extracellular fluid loss and reduced circulating blood volume - shock and severe dehydration |
|
|
Decreased inspired oxygen concenration |
Decline of the concentration of inspired O2 and the O2 carrying capacity of the blood decreases |
|
|
Increased metabolic rate |
IncreasesO2 demand |
|
|
Conditions affecting chest wall movement -Pregnancy- |
As the fetus grows, the enlarging uterus pushes abdomen contents up against the diaphragm |
|
|
Obesity |
Have reduced lung volumes from the heavy lower thorax/abdomen mostly in recumbent and supine positions |
|
|
MS abnormalities |
Impaired the thoracic region reducing O2 ex: kyphosis, poor posture/body alignment |
|
|
Trauma |
Unstable chest wall allows the lung under injury to contract on inspiration and bulge on expiration=hypoxia |
|
|
Neuromuscular/diseases |
Affect tissue oxygenation by decreasing a patients ability to expand/contract the chest wall |
|
|
CNS alterations |
Any disease medulla/spinal cord results in impaired respiration ex: narcos, sedatives, anti anxirty |
|
|
Risk factors for infants/toddlers |
^ risk for ^ respiration infections, immature system, second hand smoke and aspiration with small toys |
|
|
Risk factors young and middle adults |
Exposed to unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, over the counter and prescription drugs, smoking |
|
|
Risk factors for older adults |
Cardiac/respiration systems change, calcification of heart valves, SA node, and coastal cartilage, decreased alveoli, cough reflex, airway reflexes, mobility and lunch expansion |
|
|
Lifestyle factors- nutrition |
Amount of protein and fluid intake Malnourished- low hemoglobin, iron and protein |
|
|
Lifestyle factors- exeecise |
Active or sedated- Less able to respond to stressors |
|
|
Lifestyle factors- smoking |
Decreased or paralyzed cilia, increased sputum and risk for bronchi spasms, 10x risk for cancer |
|
|
Substance anuse |
Alcohol decreased depressed respiratory efforts, risk for aspiration with vomiting |
|
|
Lifestyle factors- stress |
Depression decreases everything, anxiety increases everything |

