![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
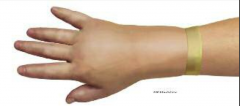
Site infection |
|
|
Infiltration |
|

|
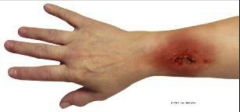
Phlebitis |
|
|

Extravasation |
|
|
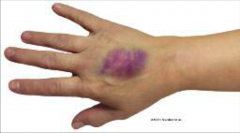
Hematoma |
|
|
Site Infection What are the SXS? What can it lead to if untreated? |
SXS: discharge, redness, warm, exudate at site Can lead to septicemia and shock Fever, chill,s headache, general malaise Potential for vascular collapse |
|
|
Infiltration What is it? What does it cause? SXS? Nursing implications? |
Leakage into extravascular tissues Causes swelling SXS: IV rate slows, edema/tight skin, blanching, coolness, burning, pain, IV can push against resistance and IV pump will say "occlusion" Nursing implications: discontinue IV, warm compress, elevate, restart IV |
|
|
Extravasation What is it? Causes? SXS: |
Leakage of vesicant drugs into surrounding tissue Severe local tissue damage, resulting in delayed healing, infection, tissue necrosis, disfigurement, loss of function, and even amputation. SXS: blanching, burning, or discomfort at the IV site, cool skin around IV site, swelling at or above the IV site |
|
|
Nursing implications of extravasation |
Stop IV and remove (unless needed to administer the antidote) Elevate arm Document document document: (appearance, solution, est amount, nursing actions, notification and name of MD, time) |
|
|
Hematoma What is it? Nursing implications? |
Ecchymosis Immediate swelling at site Leakage of blood at site Discontinue IV, apply pressure with sterile dressing, apply cool compress for 24 hours followed by warm compress, restart IV in opposite extremity |
|
|
Phlebitis What is it? Common causes? SXS? Nursing implications? |
Inflammation of a vein Common complication of peripheral IV therapy with acidic, alkaline, or high osomlarity solutions Redness or tenderness at the tip of the catheter, puffy area over vein, inflammation of vein, hard, cordlike, post infusion Stop infusion, warm compress to relieve pain, rest, elevate |
|
|
Thrombophlebitis |
Traumatic venipuncture, multiple attempts, catheter size, slowed, stopped infusion, swollen, tender, red Stop IV, do not milk tubing, warm compress, elevate, restart IV in opposite extremity |
|
|
Air embolism SXS? Nursing implications? |
Air enters central venous system Absence of vesicular breath sounds, murmur, chest pain, dyspnea, anxiety, tachycardia, hypotension Clamp, left side/trendelenberg, O2, ABG, EKG |

