![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Types of pain |
Nociception - stimulus mediated (includes thermal, mechanical and chemical)
Neuropathic - burning pain from nerve damage or misfiring
Psychosomatic |
|
|
|
Mechanism of action of Mg in pre-eclampsia |
Competes with Ca in vascular sm m. to dec vascular tone and acts inside endothelial cells to increase nitric oxide and prostaglandin I2, both of which have vasodilator properties |
|
|
|
Methanol poisoning |
Converted to formaldehyde and formic acid by alcohol dehydrogenase
Vision changes, abd pain, pancreatitis, AMS, respiratory depression and bradycardia
Tx: support and treatment of acidosis, ethanol to prevent further conversion and HD in severe cases |
|
|
|
Haldane effect |
Shift of oxyhemoglobin curve - more O2 binding decreases hgb affinity for CO2 |
|
|
|
Effect of glucagon on body? On heart? |
inhibition of gastric motility, promotion of hepatic gluconeogenesis, and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi. In addition, glucagon also acts as a cardiac inotropic and chronotropic agent. It increases intracellular cAMP through a specific nonadrenergic receptor (D) and results in increased myocardial contractility |
|
|
|
Medications to be initiated after MI? |
beta-blocker, ACE-I, statin, and aspirin. Spironolactone should be given to patients with an ejection fraction of 35% of less. |
|
|
|
Which local anesthetic scan parcipitate with addition of HCO3? |
ropivacaine and levobupivacaine |
|
|
|
Cryoanalgesia |
- Using cold to kill nerves for post op pain - nerves regenerate in 1-3mo - good for intercostal nerves for thoracotomy - can have tactile hallucinations |
|
|
|
The the lung is divided into 3 regions. Describe the ventilation and perfusion in each |
I - apex, non-dependent, ventilation > perfusion, PA > Pa > Pc II - Pa > PA > Pc III - base, dependent ventilation, perfusion > ventilation, Pa > Pc > PA |
|
|
|
alveolar gas equation |
PAO2 = PiO2 − PACO2/R + [PACO2 * FiO2 * (1−R)/R]
Or
PAO2 = (FiO2*(760-47)) - PACO2/R Where R is 0.8 |
|
|
|
Diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia |
1) Widespread pain index (WPI - pain in certain areas) ≥ 7 and symptom severity (SS - 2 parts: fatigue and cognitive sxs + other sxs, i.e. IBS, dry mouth, itching) scale score ≥ 5 or WPI 3 - 6 and SS scale score ≥ 9. 2) Symptoms present for at least 3 months 3) No other disorder that would explain the pain |
|
|
|
Lusitropy |
Cardiac muscle relaxation |
|
|
|
What BP reading is the most accurate in an oscillating BP cuff? Least? |
MAP (maximal amplitude of oscillations corresponds to the mean arterial pressure); DBP |
|
|
|
Tumescent anesthesia |
injecting large amounts of tumescent solution composed of saline mixed with lidocaine (0.05%) and epinephrine (1:1,000,000) subcutaneously, seen with liposuction, max dose of lidocaine is 55mg/kg to prevent toxicity, 0.055mg/kg of epinephrine |
|
|
|
Drugs that slow CYP enzymes |
grapefruit juice, verapamil, diltiazem, amiodarone, and omeprazole |
|
|
|
Reflexes of the eye: Corneal Pupillary Oculocardiac |
Corneal: CNV --> VII Pupillary: CNII --> III Oculocardiac: CNV --> Vagus |
|
|
|
Conditions in which you should not use methylene blue with methemoglobinemia? |
G6PD deficiency - use as Corbin acid MAOI use, can cause serotonin syndrome |
|
|
|
Who needs abx prophylaxis for infective endocarditis? |
Prosthetic cardiac valves, previous infective endocarditis, special cases of CHD and valvular heart disease following cardiac transplantation WHEN undergo dental procedures with gingival manipulation or perforation of oral mucosa and respiratory tract procedures which involve incision or biopsy of mucosal tissue NOT abdominal procedure |
|
|
|
Heat loss during surgery |
Radiation, conduction, convection, and evaporation |
|
|
|
CYP 450 enzymes |
2D6: conversion of codeine to morphine
2C9: metabolism of most NSAIDs
3A4: increased by St. John's wary; metabolism of alfentanil, midazolam, lidocaine, and oral contraceptives |
|
|
|
Factor 5 Leiden |
hereditary pro-coagulant disorder characterized by resistance to activated protein C (APC). APC is a natural anticoagulant that works by cleaving and inactivating factors V and VIII. |
|
|
|
Glasgow Coma Scale |
Motor: 6 points No response Extends in response to pain Flexes in response to pain Withdraws from pain Localized pain Follows commands
Verbal: 5 points No response Incomprehensible Inappropriate Confused Appropriate
Eyes: 4 points No response Opens to painful stimuli Opens to voice Opens spontaneously
Severe is <8 |
|
|
|
Anatomy of epidural (median vs paramedian approach) |
Median: skin, subcutaneous tissue, supraspinous ligament, interspinous ligament, and then ligamentum flavum
Papamedian: skin, subcutaneous tissue, and then ligamentum flavum |

|
|
|
Innervation of the leg |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Innervation of pharynx and larynx |
Pharynx: sensory (gag reflex) = CN9, motor = CN X - except stylopharyngeal --> CN9
Larynx: sensory at and above vocal cords = superior laryngeal internal branch of laryngeal; sensory below vocal cords and all motor = recurrent laryngeal - expect cricothyroid --> superior laryngeal, external branch |
|
|
|
Amount of receptor binding by NDMB for 1-4 twitches |
1 palpated twitch indicates >90% suppression. 2 palpated twitches indicate 80-90% suppression. 3 palpated twitches indicate 70-80% suppression. 4 palpated twitches indicate up to 65-75% suppression. |
|
|
|
Storage of blood products |
Store platelets at room temperature. PRBCs are preferably kept refrigerated, but can be kept at room temperature in the operating room for up to 6 hours. |
|
|
|
Risks of post-op renal failure |
age ≥59, BMI ≥32, chronic liver disease, COPD requiring chronic bronchodilator use, Peripheral vascular occlusive disease, High risk surgery, Emergency surgery. |
|
|
|
Blood products |
Cryopercipitate - 200mg fibrinogen/unit, factor V and VIII, von Willebrand -- vW disease, hemophilia A
FFP - all coagulation factors |
|
|
|
Goal temperature of hypothermic following cardiac arrest? Fastest method of cooling? |
1. 32-34oF for 12-24hrs 2. Endovascular cooling (coil placed in femoral a) |
|
|
|
Goal temperature of hypothermic following cardiac arrest? Fastest method of cooling? |
1. 32-34oF for 12-24hrs 2. Endovascular cooling (coil placed in femoral a) |
|
|
|
Mechanism of action of meperidine |
Opioid agonist, main use today is for rigors |
|
|
|
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome |
- Associated with small cell lung cancer - Abs causing destruction of the PREsynaptic voltage-gated Ca channels in the NMJ - improvement with use! - depressed or absent DTRs - decreased doses of Sux and N-D NMB |
|
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis |
- middle age women with ocular sxs - associated with thymomas - Ab to Ach receptor at post-synaptic junction - worse with use - normal DTRs - resistant to sux --> dec dose - sensitive to Non-depolarizing NMB --> inc dose |
|
|
|
Nerve damaged in lithotomy |
COMPRESSION Injury for inguinal ligament: lateral femoral cutaneous (LFCN) - anterior lateral thigh femoral obturator - medial thigh
Sciatic - stretch injury --> lateral leg and foot (sural n) |
|
|
|
Complications of retrobulbar blocks |
1. Pressure or retraction of the eye leads to ciliary and gasserian ganglia stimulation (trigeminal nerve, afferent limb) followed by vagal stimulation (efferent limb) --> bradycardia, heart block 2. Retrobulbar hemorrhage -- inc IOP 3. Central retinal artery occlusion -- painless vision loss 4. puncture of the posterior globe -- painful vision loss |
|
|
|
How to calculate MELD and Child-Pugh scores? |
MELD: "I Crush Beer Daily" - INR, Creatinine, Bilirubin, Dialysis
Child-Pugh: "Pour Another Beer At Eleven" - PT, Ascites, Bilirubin, Albumin, Encephalopathy |
|
|
|
How to calculate MELD and Child-Pugh scores? |
MELD: "I Crush Beer Daily" - INR, Creatinine, Bilirubin, Dialysis
Child-Pugh: "Pour Another Beer At Eleven" - PT, Ascites, Bilirubin, Albumin, Encephalopathy |
|
|
|
Effect of electrolyte abnormalities on EKG |

HyPeR = PR prolongation! |
|
|
|
What muscle returns from paralysis first? |
corrugator supercilii muscle (eyebrow twitch), supplied by the facial nerve
--> can be good indicator of good intimating conditions due to correlation to laryngeal adductors |
|
|
|
autonomic hyperreflexia Sxs |
Same as Cushing brain injury --> hypertension, bradycardia |
|
|
|
Mechanism of action of amiloride Amiodarone Atropine Adenosine |
amiloride - K sparing diuretic Amiodarone - antiarrhythmic: Class I (Na ch blocker), II (antisympathetics), III (K ch blocker) Atropine - anticholinergic/antimuscarinic Adenosine - tx of SVT by slowing conduction through AV node |
|
|
|
Pralidoxime vs Phyostigmine |
Pralidoxime - oxime that reverses the inactivation of achetylcholinesterase inhibition from organophosphate poisoning, poor BBB crossing
Phyostigmine - activation of N and M Ach Rs, crosses BBB, used in atropine toxicity |
|
|
|
Hungry bone syndrome |
Rapid absorption of Ca into bone following parathyroid removal |
|
|
|
MEN (cancer) syndromes |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Metabolic Changes Associated With TPN |
Can also get hepatic steatosis
- Hypophosphatemia - Hyperglycemia - Hypercarbia - Hypokalemia - Hypomagnesemia - Hyperinsulinemia |
|
|
|
Addiction vs dependence vs tolerance |
Addiction: continued use despite adverse consequences
Dependence: withdrawal sxs with stopping
Tolerance: requiring higher doses to achieve same effect |
|
|
|
Hemolysis lab results |
- low haptoglobin - elevated bilirubin - hematuria - positive Coombs test |
|
|
|
Requirements for PACU d/c |
BP O2 sats Alertness Activity Respirations
**do NOT need to void if low retention risk |
|
|
|
Requirements for PACU d/c |
BP O2 sats Alertness Activity Respirations
**do NOT need to void if low retention risk |
|
|
|
Side effects of amiodarone |
LFTs PFTs TFTs (thyroid function - hypo w/ risk of thyroid storm)
bradycardia, hypotension, prolonged QT |
|
|
|
What absorbent is used in anesthesia machines? |
Soda lime: Ca(OH)2 + H2O + NaOH |
|
|
|
Kounis syndrome |
AKA allergic angina, coronary events associated with hypersensitivity reactions |
|
|
|
Pierre-Robin sequence (PRS) Klippel-Feil syndrome Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome |
1. presence of micrognathia (small mandible), glossoptosis (posteriorly placed tongue), and airway obstruction
**tongue obstruction causes biggest intubation problem --> awake supraglotic airway 1st! +/- cleft palate - Can have severe sxs with failure to thrive from difficulty swallowing - Can see with FAS, Treacher-Collins (small bones in face don't develop)
2. Congenital fusion of cervical spine and low hairline, may have strabismus, scoliosis, scapular defects
3. Hypoglycem from organomegaly, macroglossia, associated with omphalocele |
|
|
|
Most effective way to prevent contrast induced nephropathy? |
IV fluid hydration, N-acetylcysteine not as effective alone |
|
|
|
Hyperkalemic vs Hypokalemic periodic paralysis syndromes |
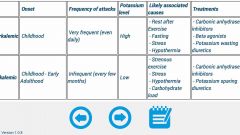
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Factors that increase MAC |
hyperthermia, hypernatremia, chronic ethanol abuse, and increased central neurotransmitter levels ex. MAOIs (A), acute amphetamine use, cocaine, ephedrine, and levodopa |
|
|
|
Effect of anesthesia on EEG? Perioperative monitors of? |
decrease in frequency and increase in amplitude
-BIS: process the EEG signal into a numerical representation of depth of anesthesia -Entropy: measures degree of disorder in the EEG signal -Patient state analyzer: analyzes the temporal and spatial gradients of the power distribution between different frequency bands during induction and emergence of anesthesia |
|
|
|
Post-reperfusion syndrome after transplant |
HypoTN with plum HTN, inc vascular permeability due to Na/K pump failure from dec glycogen stores |
|
|
|
What receptors inc hepatic blood flow (note: most drugs dec!)? |
Glucagon, dopaminergic D1, and adrenergic beta2 |
|
|
|
Volume of gas at which N2O pressure will start to dec? |
<400L Until then will read 745psi |
|
|
|
CI/SEs of each ND NMB |
Atracurium/cisatricurium: histamine release (hypoTN), bronchospasm, laudanosine metabolite causes seizures
Pancuronium: HTN, inc HR from vagal blockade, arrythmias from inc catecholamine release, inc dose in cirrhosis
Rocuronium: prolonged duration in liver failure and pregnancy |
|
|
|
Muscarinic receptor agonists |
Methacholine - asthma Bethanecol - bladder atony |
|
|
|
Opioid receptors |
Mu: resp depression, m rigidity, dependence Kappa: sedation, spinal analgesia Delta: analgesia, epileptogenic Omega: dysphonia, hallucinations |
|
|
|
Locals in decreasing order of toxicity |
Lidocaine = tetracaine > bupivicaine > ropivicaine |
|
|
|
How does propofol differ from volatiles in regard to pulm affects? |
Dec TV and RR, volatiles dec TV with inc RR |
|
|
|
Complication of long term propofol infusion |
Inc triglycerides, rhabdomyolysis, metabolic acidosis, renal failure |
|
|
|
What drugs can stimulate a porphyria crisis? |
Thiopental or methohexital |
|
|
|
Antidote for benzos? |
Flumazenil - benzo R antagonist |
|
|
|
Affects of chemo drugs |
Doxorubicin- cardiomyopathy Bleomycin - pneumonitis, especially with increased O2 conc Vincristine & vinblastine - neuropathies |
|
|
|
Affects of chemo drugs |
Doxorubicin- cardiomyopathy Bleomycin - pneumonitis, especially with increased O2 conc Vincristine & vinblastine - neuropathies |
|
|
|
Propfol infusion syndrome |
Rhabdomyolysis, lipidemia, metabolic acidosis, renal failure
Seen more is kids and neurosurg pts |
|
|
|
Hemodynamics affects of acidosis |
Dec SVR, dec contractility, QT abnormality |
|
|
|
Risk factors for difficult airway in all? In obese? |
All: male, inc age, TMJ, abnormal upper teeth
Obese: large neck, OSA, short Mallumpati III or IV |
|
|
|
Changes in geriatric population |
- dec central vol of distribution - dec clearance - Dec VC with inc RV and FRV - inc closing capacity - dec DBP - inc catecholamines with desensitization --> poor exercise response - dec dyastolic fund from dec LV relaxation - normal systolic func |
|
|
|
Obesity changes |
- inc MV - dec FRC - pulm HTN - inc CO - polycythemia - hypercoaguable due to inc fibrinogen, VII, VIII and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
|
|
|
Things that affect spinal duration |
Dose Type Height of spinal (higher = dec duration) adrenergic use Protein binding |
|
|
|
Universal donor? Recipient? |
O- AB |
|
|
|
Cause of transfusion fever |
Recipient antibodies to DONOR leukocytes To: leukoreduced RBCs |
|
|
|
Factors in FFP vs cryo |
FFP - II, V, VII, IX, X, protein c and s, anti thrombin 3 Cryo - vWF, I, VIII, XIII, fibronectin |
|
|
|
Thrombin inhibitors |
Dabigatran Agatroban |
|
|
|
Xa inhibitors |
Apixaban |
|
|
|
How a pulse ox works |
Deox hemoglobin absorbs red light (660) > infrared (940)
Remember: wavelength Radio > micro >infrared >visible > ultraviolet > X-ray > gamma ray |
|
|
|
Effects of parathyroid adenomas |
Inc Ca Dec Ph Inc Cl Dec HCO3 w/ dec pH |
|
|
|
Treatment of serotonin syndrome |
Cyproheptadine - serotonin R antagonist |
|
|
|
Drugs that release histamine |
Morphine Atracurium Sux Thiopental |
|
|
|
Syndrome X |
Insulin resistance without hypoglycemia - also see dec HDL and HTN, associated with CAD |
|
|
|
Bayes thereom |
Probability of an event given certain conditions. Used to formulate pre-test algorithms |
|
|
|
Bland-Altman Kaplan-Meier Wilcox-Mann |
B-A: scatter plot to look as agreement between 2 groups K-M: tests survival or events W-M: ranks or ordinal data (think Chi or logistic regression!) |
|
|
|
Type I vs II error |
1. Incorrectly accept there IS a difference (alternate hypothesis), alpha - false positive 2. Incorrectly accept iS NOT (Null hypothesis), beta - false negative |
|
|
|
Electrolyte changes in CKD |
Dec Ca, inc K Can have anorexia |
|
|
|
Strong ion difference |
(Na + K + Ca + Mg) - (Cl + lactate) Normal = 40 |
|
|
|
Anion gap |
Na - (Cl + HCO3) Normal = 8-16 |
|
|
|
Adverse effects of TURP |
Dec Na from hypotonic solution - hypoTN, inc QRS, seizure |
|
|
|
ANP BNP |
ANP: inc GFR with dec Na resorption BNP: vasodilation, diuresis from dec R-A-A system |
|
|
|
Hemofiltration vs hemodialysis |
Filtration uses P gradient Dialysis uses concentration |
|
|
|
Nestiride |
Recombinant BNP |
|
|
|
Electrolyte change in chronic alcoholism |
Inc urea Dec K, Mg, Na Respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
|
Mendelson Syndrome |
Chemical pneumonitis following aspiration RF: pH<2.5, vol>25cc Sxs: tachycardia, tachypnea, pulm congestion and hypoxia |
|
|
|
Eye complications |
Retinal hemorrhage - painful, inc IOP Corneal abrasion - painful, most common cause of eye pain Globe penetration - painful, vision loss Ischemia neuropathy - painLESS, sluggish pupil |
|
|
|
Meralgia paresthetica |
Entrapment of LFCN often after prolonged labor - biting pain |
|

