![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
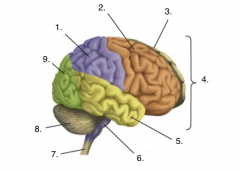
Label the picture
|
1. Parietal lobe
2. Frontal lobe 3. Left hemisphere 4. Cerebrum 5. Temporal lobe 6. Brain stem 7. Spinal cord 8. Cerebellum 9. Occipital lobe |
|
|
3 layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord
|
1. Dura mater 2. Arachnoid mater 3. Pia mater
|
|
|
What is the thickest and outer most layer surrounding the brain and spinal cord?
|
Dura mater
|
|
|
What is the middle layer that looks like spider webs and surrounds the brain and spinal cord?
|
Arachnoid mater
|
|
|
What is the inner most layer that hugs the brain and spinal cord closely and is thin / clear?
|
Pia mater
|
|
|
What is the function of the Olfactory bulbs?
|
-function in smell
|
|
|
What is the function of the Optic nerve?
|
-transmission of vision impulses
|
|
|
What is the Optic chiasma?
|
-site where visual pathways switch
|
|
|
What is the Pons and where is it located?
|
–between the midbrain and medulla oblongata that forms a bridge between the two
|
|
|
What role does the Pituitary gland have in the brain?
|
–role in releasing many hormones
|
|
|
What is the Medulla oblongata?
|
–most inferior part of brain stem that blends into spinal cord
|
|
|
What are gyri?
|
-Elevated ridges
|
|
|
What are sulci?
|
-shallow grooves
|
|
|
What is the significance of the longitudinal fissure?
|
-Separates cerebral hemispheres
|
|
|
What is the significance of the transverse cerebral fissure?
|
-separates cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum
|
|
|
What is the Corpus callosum?
|
-connects right and left cerebral hemispheres
|
|
|
What are Ventricles in the brain?
|
-spaces in the brain that house and circulate cerebral spinal fluid
|
|
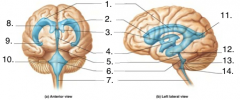
Label the image
|
1. Lateral Horn
2. Anterior Horn 3. Interventricular foramen 4. Third Ventricle 5. Cerebral Aqueduct 6. Fourth Ventricle 7. Central Canal 8. Septum Pellucidum 9. Inferior Horn 10. Lateral Aperture 11. Posterior Horn 12. Inferior Horn 13. Median Aperture 14. Lateral Aperture |
|
|
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
|
-To increase the conduction/speed of the impulses
|
|
|
What cell type is responsible for the myelin sheath in a peripheral nerve? In a CNS nerve?
|
-PNS: Schwann cell / -CNS: oligodendrocyte
|
|
|
Where do we commonly find multipolar neurons?
|
-Throughout the body, common in the CNS
|
|
|
Where do we commonly find bipolar neurons?
|
-in sensory organs such as eye, ear, olfactory mucosa
|
|
|
Where do we commonly find unipolar neurons?
|
-In the PNS: bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglia for spinal nerves.
-For cranial nerves/ bodies are located in the sensory ganglia. |
|
|
What type of material composes the gray matter of the spinal cord?
|
-Mostly cell bodies, unmyelinated fibers, glial cells
|
|
|
What type of material composes the white matter of the spinal cord?
|
-Myelinated axons
|
|
|
What is the location and function of the dorsal root ganglion?
|
-Dorsal root ganglion is located bilaterally, flanking the posterior aspect of the spinal cord.
-The DRG contains the bodies of the sensory/afferent neurons. |
|
|
What are the three meningeal layers that cover the brain and spinal cord?
|
-Dura mater
-Arachnoid mater -Pia mater |
|
|
What is a sulcus?
|
-The groove formed by the convolutions of the external brain. The “valley” between the hills
|
|
|
What is a gyri?
|
-The protrusion formed by the convolutions. The “hills”
|
|
|
Which 3 regions make up the diencephalon?
|
-Thalamus
-Epithalamus -Hypothalamus |
|
|
What function does the thalamus have?
|
-Acts as a relay station for the nerves entering the brain
|
|
|
Where is the choroid plexus found and what does it do?
|
-Located in the epithalamus
-functions to produce CSF |
|
|
In the medulla, what are the pyramids?
|
-Ridges located on the ventral surface of the medulla. They are composed of the motor neurons leaving the CNS. They cross or decussate, and the fibers from the right brain run to the left side of the body.
|
|
|
What is the optic chiasma?
|
-The region in which the optic nerve crossed from one side of the brain to the other. Not all fibers cross so we perceive visual information in both sides of the brain.
|
|
|
What are the ventricles? How many are there?
|
-The ventricles are spaces in the brain that house and circulate CSF.
-There are four ventricles |
|
|
What is the function of the corpus callosum?
|
-The corpus callosum connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres
|
|
|
How do Monosynaptic reflexes work?
|
-impulse only crosses one synapse / Forms a reflex arc to stimulate motor fibers Does not involve the brain / ex: (patellar reflex: causes extension of the leg)
|
|
|
Would the fiber that runs from a Pacinian corpuscle be afferent or efferent?
|
-afferent
|
|
|
Do the ST and DCML tracts decussate in the same location? Which one decussates where?
|
No = ST: in spinal cord / DCML: in the pyramids of Medulla oblongata
|
|
|
Since the Plantar response test is looking for a response to pain in which ascending column would this pathway run?
|
-(lateral) Spinothalamic tract
|
|
|
What structures make up the tenecephalon?
|
-Cerebrum: cortex, white matter, and basal nuclei
|
|
|
What structure makes up the mesencephalon?
|
-Brain stem/ midbrain
|
|
|
What structure makes up the metenphalon?
|
-pons
|

