![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cycle of homelessness |
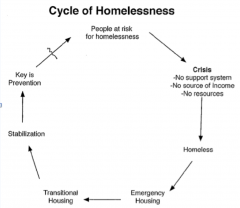
|
|
|
What is homelessness? |
Anyone who lacks a fixed, regular, safe, and adequate shelter, resources, and community ties. (Stewart B. McKinney act)
living in a shelter, temporary housing, or with family could all be considered homeless. |
|
|
Definition of Poverty |
the extent at which an individual does with out resources (bridges out of poverty, 2001) |
|
|
Who is at risk for homelessness? |
everyone who lacks resources, disabled, mental health issues, undocumented immigrants, single moms, runaways, lower education levels, unemployed |
|
|
Characteristics of Homeless population. |
28% domestic violence 25% chronic substance abuse 50% incarceration (more men) 20% mental illness 13% are employed 9% of homeless men are vets
|
|
|
Race of Homeless population |
49% African American 35% caucasian 13% Latinos 2% native americans 1% asians |
|
|
What is the fastest growing population of homeless |
families with children 44% |
|
|
How does a decline in public assistance affect poverty and homelessness. |
since 2001, there is a 40% increase in people participating in food stamps and other assistance programs |
|
|
% of income that should be going to housing? |
33%
severely burdened households are paying more than 33% of their income on housing |
|
|
What issues do children have when they are hungry? |
They don't learn as well, have fatigue, weight loss, more colds, difficulty concentrating, anemia |
|
|
Why are people homeless? |
lack of affordable housing, money, work mental illness, physical disability, substance abuse. |
|
|
Three types of homeless: |
Temporary homeless Episodically homeless Chronically homeless |
|
|
Temporary homeless |
fire, flood victims, relocating
*only happens one time |
|
|
Episodically homeless |
evicted, unstable employment, violence, welfare, interrupted support.
in and out of homelessness |
|
|
Chronically homeless |
mentally ill, substance abuse,
homeless for extended periods of time. |
|
|
Issues for homeless population |
-illness, lice, bedbugs, diarrhea, viral illness, HepA, TB, -immunizations behind -speech behind in children -vision issues - may be overweight (not healthy food options)
|
|
|
Stewart b McKinney Homeless Assistance Act 1987 |
children have a right! facilitate need for: health care housing, education labor
|

