![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
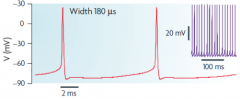
|
1. Purkinje fiber in cerebellum |
|
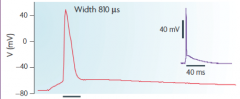
|
1. CA1 pyramidal nerve in cortex |
|

|
1. Substantia nigra |
|
|
What Na channels are targets for drug development? |
1. NaV 1.8 and 1.9 |
|
|
What Na channel is targeted by pufferfish toxin? |
1. NaV 1.7 |
|
|
What is the a1 subunit in Ca channels? |
1. Gatekeeper protein |
|
|
What are the B and a2 subunits in Ca channels? |
1. Auxiliary/modulatory subunits |
|
|
What is the excitatory NT in the CNS? |
1. Glutamate |
|
|
What is the function of acetylcholine? |
1. NM junction 2. SNS 3. ParaNS 4. CNS 5. EXCITATORY |
|
|
Where does glycine play a role? |
1. Spinal cord |
|
|
What will an excitatory NT do to the membrane potential? |
1. Drive it towards 0---- depolarization |
|
|
What will an inhibitory NT do to membrane potential? |
1. Hyperpolarize 2. GABA PRINCIPALLY |
|
|
How does glycine work with glutamate? |
1. Co-activator of NMDA receptors 2. Both glutamate and glycine required for activation |
|
|
Where does ketamine bind? |
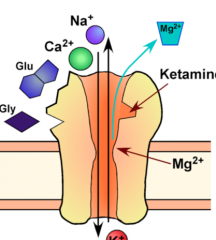
1. NMDA receptor
|
|
|
What is the state of NMDA receptors at rest? |
1. Blocked by Mg 2. AMPA receptors activated, depolarize membrane 3. Mg displaced from NMDA---- channel is activated |
|
|
In what process are NMDA receptors involved (one of many)? |
1. Learning |
|
|
What drugs target the NMDA receptor? |
1. Memantine--- Alzheimer's 2. Ketamine--- anesthesia |
|
|
What substances can bind to GABA receptors? |
1. Propofol 2. Sevoflurane 3. Ehtanol 4. Benzos 5. GABA 6. Barbiturates 7. Neurosteroids |
|
|
What is released from GABA receptors when they are stimulated? |
1. Cl |
|
|
What is the use of benzodiazepine? |
1. Anxiolytic 2. Sedative |
|
|
What is flumazenil? |
1. Benzodiazepine antagonist |
|
|
What is pentobarbital? |
1. Antiepileptic 2. Sedative |
|
|
What are propofol and sevoflurane? |
1. Hypnotic anesthetics |
|
|
What does capsaicin activate? |
1. TRPV1 channels--- nociception 2. Na ions enter cells |
|
|
Where are TRPV1 channels located? |
1. C fibers, A delta fibers in dorsal horn of spinal cord
|
|
|
What activates TRPV channels? |
1. Heat |
|
|
What activates TRPM? |
1. Cold---- menthol |
|
|
What induces TRPA? |
1. Pain 2. Garlic, mustard oil, tear gas |
|
|
What TRP channel has the highest activation temperature? |
1. TRPV2--- 55 C |
|
|
What is the MOA of 4-aminopyridine? |
1. KV blocking drug in demyelinated axons 2. Used to improve movement in MS patients |
|
|
What is the MOA of amiodarone? |
1. Block Kv11 |
|
|
What is the MOA of sevoflurane? |
1. Activation of K2P channels along with GABA channels |
|
|
What NTs lead to EPSPs? |
1. Ach 2. Glutamate |
|
|
What NTs lead to IPSPs? |
1. Glycine 2. GABA |
|
|
What is the primary non-NMDA channel activated by glutamate? |
1. AMPA |
|
|
What is the role of AMPA? |
1. Primary mediator of fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the CNS |
|
|
What blocks TRPA? |
1. Propofol |

