![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Visual Evoked Potentials
|
VEPs represent the activity of the visual pathway and can be used to assess the functional integrity of the
Optic nerves Optic chiasm Optic tracts Lateral geniculate body Geniculocalcarine tract Optic cortex |
|
|
Lateral geniculate body
Geniculocalcarine tract |
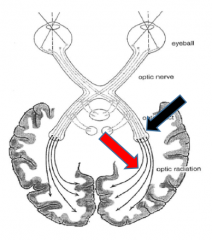
Black arrow= Lateral geniculate body
Red arrow = Geniculocalcarine tract |
|
|
VEP Collection
Stimulus |
Stimulus is “pattern reversal” checkerboard delivered at a rate of 1-5 Hz (delivered via a computer screen or through goggles
|
|
|
VEP Collection
Montage |
Montage:
Active (positive) electrode is O1 or O2 and inactive (negative) electrode is placed either or contralateral earlobe (A2 and A1) or using a common Cz |
|
|
VEP Collection
Time base is XXX msec |
Time base is 300 msec
|
|
|
VEP response
|
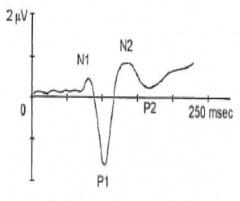
Primary response is the P100 which reflects activity of the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe
these are faceable, requires focused attention |
|
|
VEP Concerns
NOT routinely done in the OR because… |
Eyes roll back in the head when pt is asleep (due to oculomotor muscles being relaxed) which would result in the optic nerves not being stimulated (and thus no response)
VEP responses are highly sensitive to changes in metabolic factors and anesthesia, making them venerable to false positives |
|
|
ABR in IOM
Used to assess integrity of ... |
Used to assess integrity of CNVIII (primarily for AN resection) and brainstem
Primarily used for procedures involving the cerebello-pontine angle and with posterior fossa approach procedures |
|
|
ABR in IOM
How is it recorded? |
Recorded bilaterally (with masking in contralateral ear) so ear of concern can be compared to control ear
|
|
|
ABR in IOM
Primary interpretive function is ... |
Primary interpretive function is absolute and interpeak latenices (just like in clinic!)
and really important to get a baseline |
|
|
ABR Generators
|
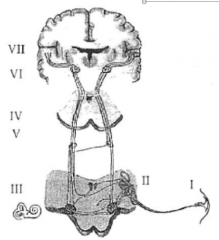
I
II III IV V VI VII |

