![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
protiens are the most
|
The most versatile macromolecules in living systems
|
|
|
they Function as: what (4)
|
Function as: catalysts,
transporters, mechanical support, immune protection |
|
|
what do protiens control
|
They also control movement, growth and development and they transmit nerve impulses
|
|
|
protiens are...
|
Linear polymers built from monomer units called amino acids
|
|
|
contain a wide range of
|
Contain a wide range of functional groups
|
|
|
can interact with...
|
Can interact with one another and with other biological molecules to form complex assemblies
|
|
|
what type of strucutres can they have
|
Can have very rigid structures or can display flexibility
|
|
|
Amino acids can exist as either....
|
Amino acids can exist as either L- or D- isomers, however only the L-form is found in proteins
|
|
|
draw Ionization state as a function of pH of protiens
|
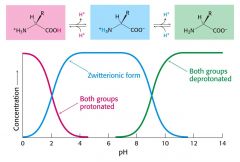
|
|
|
draw the structures of glycine and alanine
|
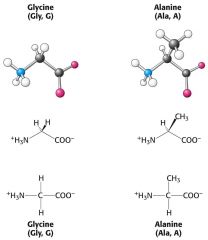
|
|
|
list all the amino acids with aliphatic side chains
|
valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine
|
|
|
which amino acid has a cyclic strucutre
|
proline
|
|
|
which amino acids have aromatic side chains
|
phenylalanine
tyrosine tryptophan |
|
|
what are the basic amino acids
|
lysine, arginine, histidine
|
|
|
what do pka values represent
|
pKa values represent the pH at which 50% of the molecules are ionised and 50% are not
|
|
|
what do pka values depend on
|
ionic strength, temperature, and the micro environment of the ionisable group
|
|
|
what does protein primary structure consist of
|
-carboxyl group of one amino acid joined to the -amino group of another
A series of amino acids joined by peptide bonds form a polypeptide chain |
|
|
why does a polypeptide chain have polarity
|
A polypeptide chain has polarity because its ends are different
|
|
|
what is taken as the beginning of a polypeptide chain
|
By convention the amino end is taken as the beginning of a polypeptide chain
|
|
|
The linking of two amino acids is accompanied by
|
the loss of a molecule of water. The reaction requires the input of free energy
|
|
|
draw a diagram for peptide bond formation
|
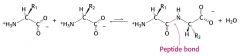
|
|
|
what doe polypeptide chains consist of
|
Polypeptide chain consists of a constant backbone and variable side chains
|
|
|
draw thes structure of a polypeptide chain
|
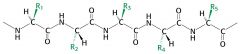
|
|
|
Proteins have unique amino acid sequences that are specified by
|
genes
|
|
|
The formation of a disulphide bond from two cysteine residues is an
|
oxidation reaction
|
|
|
show the formation of a disulphide bond between 2 cysteine residues
|
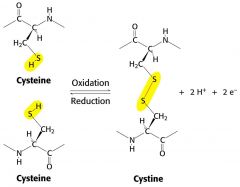
|
|
|
disulphide bonds can either be
|
The disulphide bonds can be either inter- or intra-chain
|
|
|
The peptide bond has considerable double –bond character, which prevents
|
prevents rotation about this bond
|
|
|
peptide bonds are what shape
|
planar
|
|
|
how are some polypeptide chains flexible
|
Some of the bonds in the polypeptide backbone are capable of rotation
This freedom of rotation allows proteins to fold in many different ways |
|
|
which bonds in polypeptides have freedom of rotation
|
Bonds between the amino group and the -carbon atom and between the -carbon atom and the carbonyl group are single bonds and have freedom of rotation
|
|
|
The structure of each amino acid in a polypeptide can be adjusted by
|
the rotation about 2 single bonds
|
|
|
what is phi and what is psi
|
Phi () is the angle of rotation about the bond between the nitrogen and -carbon atoms. Psi () is the angle of rotation about the bond between the -carbon and the carbonyl carbon atoms
|
|
|
what is protein secondary structure
|
Polypeptide chains can fold into regular structures such as:
Alpha helix Beta sheet Turns Loops |
|
|
how does hydrogen bonding occur in an alpha helix
|
The CO group of residue n forms a hydrogen bond with the NH group of residue n+4
|
|
|
what is ferritin and what is it an example of
|
Ferritin, an iron storage protein, is built from a bundle of helices
and is an example of A largely helical protein |
|
|
how does coilin occur in the alpha helices
where are such structures found |
The helices wind around one another to form a superhelix.
Such structures are found in many proteins including keratin in hair, quills, claws and horns |
|
|
what can beta sheets be stabilised by
|
Beta sheets are stabilised by hydrogen bonding between polypeptide strands
|
|
|
what 2 forms can beta sheets be in
|
Beta sheets can be antiparallel with adjacent β strands running in opposite directions
Beta sheets can be parallel with adjacent β strands running in the same direction |
|
|
describe the hydrogen bonding for a beta helix on an antiparralel sheet
|
Hydrogen bonds between NH and CO groups connect each amino acid with a single amino acid on an adjacent strand, stabilising the structure
|
|
|
describe the hydrogen bonding for a beta helix in a parallel sheet
|
Hydrogen bonds connect each amino acid on one strand with two different amino acids on the adjacent strand
|
|
|
a protein rich in beta sheets also contains...
|
Proteins also contain loops and turns which contribute to both structure and function
|
|
|
what is protein tertiary structure
|
The 3-dimensional folding of polypeptide chains is referred to as its tertiary structure
|
|
|
what is this folding often devoid of
in globular protiens give an e.g, what does the interior consist almost entirely of? where are charged amino acids often found |
This folding is often devoid of symmetry
In globular proteins e.g. myoglobin the interior consists almost entirely of nonpolar residues Charged amino acid residues are often located on the surface |
|
|
what is protein quaternary structure
|
Some proteins contain more than one polypeptide chain
|
|
|
what is a subunit
polypeptide chains can assemble into what type of strucutre |
Each polypeptide chain in such a protein is called a subunit
Polypeptide chains can assemble into multisubunit structures |
|
|
what may these multisubunit structures contain
|
These multisubunit structures may contain many copies of the same subunit (e.g.Virus coat proteins) or they may be made of different subunits
|
|
|
what is the cro protein
|
The Cro protein of bacteriophage is a dimer of identical subunits
|
|
|
The amino acid sequence of a protein determines its
|
The amino acid sequence of a protein determines its three dimensional structure
|
|
|
Amino acids have different propensities for forming
|
Amino acids have different propensities for forming alpha helices, beta sheets and beta turns
|
|
|
what are polypeptides and how are they orientated
|
Polypepides are linear chains oriented from amino terminus to carboxy terminus
|
|
|
the properties of amino acid side chains dictate
|
The properties of the amino acids side chains dictate the structure and function of proteins
|

