![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DNA REPLICATION IS
|
DNA replication is the copying of one molecule of DNA to produce two identical molecules.
|
|
|
DNA REPLICATION IS ESSENTIAL IN ORDER TO
|
DNA replication is essential in order to allow cells to divide
|
|
|
DNA replication requires
|
A TEMPLATE AND A PRIMER
|
|
|
THE BACKBONES OF DNA AND RNA ARE FORMED BY
|
Backbones of DNA and RNA
These are formed by 3’ to 5’ phosphodiester linkages |
|
|
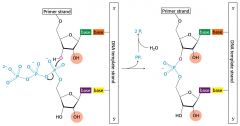
DRAW HOW A PHOSPHODIESTER BOND LINKAGE IS FORMED WITH THE BIPRODUCT
|

|
|
|
DRAW AN ALTERNATIVE REPLICATION OF THE SUGAR PHOSPHATE BACKBONE OF NUCLEIC ACIDS
|

|
|
|
SOME DNA MOLECULES ARE .... AND SOME ARE
|
Some DNA molecules are Circular and Supercoiled
|
|
|
WHICH BASES ARE DOUBLE RINGED
WHICH BASES ARE SINGLE RINGED HOW MANY HYDROGEN BONDS BETWEEN G-C AND A-T |

|
|
|
DNA REPLICATION PROCEEDS USING WHAT MECHANISM, AND DEFINE IT
|
A SEMI CONSERVATIVE MECHANISM
The normal process of DNA synthesis, in which the two original strands of the molecule separate, and each acts as a template on which a new complementary strand is laid down. |
|
|
WHAT HAPPENS DURING EACH ROUND OF DNA REPLICATION
|
During each round of DNA replication the original parent molecule is unwound to provide two, single-stranded molecules which act as templates for the synthesis of complementary strands
|
|
|
Unwinding of DNA to allow replication requires ....
|
specific DNA-binding proteins and enzymes (helicases) and also energy derived from the hydrolysis of ATP
|
|
|
WHAT DOES THIS UNWINDING HAVE AN EFFECT ON
|
This unwinding puts a strain on the molecule by causing the overwinding of nearby regions
|
|
|
WHAT DO DNA POLYMERASES REQUIRE
|
DNA polymerases require a template and a primer
|
|
|
WHAT IS DNA REPLICATION PRIMED BY
WHAT HAPPENS TO IT AT A LATER STAGE OF REPLICATION |
DNA replication is primed by a short stretch of RNA that is synthesised by primase. The RNA primer is removed at a later stage of replication
|
|
|
WHAT DO All DNA polymerases have structural features in common
|
THEY HAVE A
THUMB PALM EXONUCLEASE AND FINGERS |
|
|
on cursory examination both strands of a DNA template appear to.........
|
replicate continuously and in the same direction
|
|
|
The formation of a phosphodiester bridge is catalysed by
|
The formation of a phosphodiester bridge is catalysed by DNA polymerases
|
|
|
DRAW HOW The formation of a phosphodiester bridge is catalysed by DNA polymerases
|

|
|
|
DNA polymerases can only add new nucleotides to an
|
DNA polymerases can only add new nucleotides to an existing 3’-hydroxyl group
|
|
|
DNA can only be synthesised in one direction
|
5’ to 3’.
|
|
|
Both strands are synthesised in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
BUT WHAT DIFFERS BETWEEN EACH STRAND |
leading strand is synthesised continuously whereas the lagging strand is synthesised in short pieces termed Okazaki fragments
|
|
|
DEFINE
TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION |
Transcription – the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template
Translation – the synthesis of Proteins using RNA |
|
|
NAME TEH PERCENTAGE OF EACH TYPE OF RNA IN E.COLI
|

|
|
|
Transcription mechanism of the chain-elongation process catalysed bY
SHOW HOW THIS IS DONE |
Transcription mechanism of the chain-elongation process catalysed by RNA polymerase
|
|
|
Transcription is Initiated at
|
Transcription is Initiated at Promoter Sites on the DNA Template
|
|
|
WHERE ARE PROMOTER SEQUENCES LOCATED
|
Promoter sequences are located just upstream of the transcription start site
|
|
|
RNA synthesis is carried out by
REQUIREMENTS |
RNA synthesis is carried out by RNA polymerases
RNA polymerases require a template but do NOT require a primer in order to initiate RNA synthesis |
|
|
RNA polymerase unwinds about
|
RNA polymerase unwinds about 17 base pairs of template DNA
|
|
|
NAME 4 FEATURES IN THE TRANSCRIPTION BUBBLE AND WHAT IT CONSISTS OF
|

|
|
|
DESCRIBE WHAT HAPPENS INSIDE IT
|
Duplex DNA is unwound at the forward end of the RNA polymerase and rewound at its rear end. The RNA-DNA hybrid rotates during elongation
|
|
|
Some genes terminate transcription via
|
Some genes terminate transcription via stable stem-loop structures followed by a series of uracil (U) residues
|
|
|
WHAT IS THE SECOND METHOD OF TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION
WHAT IS IT |
rho DEPENDENT TERMINATION
The Rho protein is an ATP-dependant helicase that binds the nascent RNA chain and pulls it away from RNA polymerase and the DNA template |
|
|
WHY IS THE CODING STRAND CALLED WHAT IT IS
|
The other strand of DNA (black) is called the coding strand as it contains the same sequence as the mRNA except for thymine (T) in place of uracil (U).
|
|
|
WHAT HAPPENS FOLLOWING TRANSCRIPTION TO MRNA
|
Following transcription the mRNA is used as a template for protein synthesis via translation.
|
|
|
THE LAGGING STRAND IS SYNTHESISED IN
|
The lagging strand is synthesised in discontinuous sections from RNA primers
|

