![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three types of Income Tax? |
Non Savings Income (earnings from employment)
Savings Income (interest from bank accounts)
Dividend Income (dividends payable by companies and investment funds) |
|
|
What are the three steps to calculate income tax? |
1 - All the income from the three categories is added up for the year
2 - Deduct the annual personal allowance from the bottom pile of income
3 - Calculate the tax due on the remaining income after deducting the personal allowance |
|
|
What are the income rates of tax for 2013/14? |
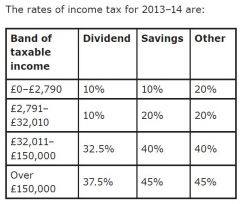
|
|
|
What types of income can be tax free? (6) |
Premium Bond Prizes Interest on National Savings Certificates Incomes from ISA's Gambling National Lottery Wins Compensation from loss of employment (up to 30k) |
|
|
What is Interest Income referred to by the HMRC? |
Non Dividend Savings Income - Taxed after earned income |
|
|
What does Non-Dividend Savings income apply to? |
UK and Overseas savings income from the following sources
Interest from banks and building societies Interest from gilts and corporate bonds Purchased life annuities Some distributions from unit trusts |
|
|
What is the starting rate of tax for Saving Incomes Only? |
10% |
|
|
What is the amount of tax on Savings between £2,791 - £32,010? |
20% |
|
|
What is CGT? |
Capital Gains Tax |
|
|
Explain Capital Gains Tax |
A tax levied on an increase in the capital value of an asset.
Usually paid when disposed of/sold on |
|
|
What may Capital Gains Tax be added on? |
Shares Unit Trusts Certain Bonds Property (Except Main Home) |
|
|
What is exempt from Capital Gains Tax? |
Main Home Car and other possessions up to £6,000 Gains on Gilts Betting, Lottery or Pools Winnings Transfers between spouses |
|
|
What is the "Annual Exempt Amount"? |
Annual tax free allowance which allows a certain amount of gains tax free each year |
|
|
What is the annual tax free allowance on Capital Gains? |
£10,900 |
|
|
What are the three excess charges for Capital Gains tax? |
18% and 28% for individuals (rate used depends on amount of total taxable income and gains)
28% for trustees or personal representatives
10% for gains qualifying for Entrepreneurs Relief |
|
|
What is Inheritance Tax based on? |
The value of assets that are transferred during an individuals lifetime or that are remaining at death |
|
|
What is the Nil Rate Band set at for Inheritance Tax? |
£325,000 any transfer in excess of this is charged at 40% |
|
|
What is exempt from Inheritance Tax? |
Assets left to a spouse Assets left to registered charitites Gifts made more than 7 years before death |
|
|
When would Inheritance Tax change from 40% to 36%? |
If 10% or more of a net estate (after deductions) is left to charity |
|
|
What is Stamp Duty? |
A tax paid on UK share trades where a stock transfer form is used |
|
|
What is Stamp Duty Reserve Tax? |
A tax paid when an individual buys shares electronically with no stock transfer form |
|
|
When is no Stamp Duty added? (5) |
When purchasing foreign shares Bonds OEIC's Unit Trusts ETF's |
|
|
What is VAT? |
Value Added Tax
A charge added by firms and individuals whose turnover exceeds a certain amount when they supply taxable goods or services |
|
|
What is the standard rate of VAT? |
20% |
|
|
What are Investment Wrappers? |
A way for individuals to own both savings and shares with certain tax advantages |
|
|
What do Investment Wrappers include? (4) |
ISA's Child Trust Funds/Junior ISA's Pensions Investment Bonds |
|
|
Who creates the rules around Investment Wrappers? |
The HMRC (Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs) |
|
|
What is an ISA? |
Individual Savings Account
An account that holds other savings and investments such as deposits, shares, OEIC's and unit trusts
They are invested in a tax efficient manner |
|
|
Who are ISA's available for? |
Stocks and Shares ISA's - UK residents over 18 Cash ISA's - Aged 16 or over |
|
|
What are the tax incentives for ISA's? |
They are free of Income Tax and Capital Gains Tax
As of 2005 is it no longer possible to reclaim tax credit on dividends |
|
|
How many ISA's are available for savers? |
One, with two components;
Cash or, Stocks and Shares |
|
|
What is the annual maximum overall subscription limit for ISA's? |
No more than 50% may be placed in the cash component |
|
|
What is the overall ISA subscription limit? |
£11,520, of which £5,760 can be subscribed to a cash ISA |
|
|
What is the time limit to transfer shares in ISA's? |
Within 90 days of receipt |
|
|
Can you transfer a cash ISA to a stocks and shares ISA? |
Yes, it cannot however be made the other way round |
|
|
What are Junior ISA's? |
A tax free savings account for children |
|
|
Who are eligible for Junior ISA's? |
All UK residents under 18 who do not already have a Child Trust Fund |
|
|
What is the annual subscription limit for JISA's? |
£3,720, indexed by the Consumer Price Index |
|
|
Who can open a JISA account? |
Anyone responsible for an eligible child. Any eligible child over the age of 16 can also open an account for themselves |
|
|
When can you withdraw from a JISA? |
At the age of 18, except in the case of terminal illness of death |
|
|
What is a Pension? |
An investment fund where contributions are made, uusually during a persons working life |
|
|
What are the main tax incentives for Pensions? (5) |
Tax relief on contributions made by individuals and employers
Not subject to income tax
You can have it at age 55
Option to take a tax free lump sum at retirement
Option to include death benefits as part of the scheme |
|
|
What are the two parts to a State Pension Scheme? |
Basic State Pension Additional State Pension |
|
|
How are State Pensions Provided? |
Through National Insurance contributions |
|
|
What age can you redeem a State Pension? |
If born after 6/10/1954 but before 06/04/1968 (66 years) If born after 1968 it will increase from 66 to 67 then 68 |
|
|
What is the Pension Credit Guarantee? |
A way for the basic state pension to be topped up if they have had long periods of unemployment |
|
|
What is the State Second Pension (S2P)? |
It is earning related, the higher the earnings the bigger the pension |
|
|
Explain Defined Benefit Scheme and Defined Contribution pension |
Defined Benefit Scheme - Pension is related to number of years service
Defined Contribution - Driven by contributions made and the performance of the fund |
|
|
What is a stakeholder pension? |
A type of personal pension that incurs low charges |
|
|
What government standards do Stakeholder Pensions have to satisfy in order to be offered? |
Low Charges - 1.5% cap for first 10 years Low and Flexible Contributions - minimum no greater than £20 Transferability - No charges Default Option - Can allocate funds between investment |
|
|
What is NEST? |
National Employment Savings Trust
A pension scheme employers can use to meet their new duties, providing a low cost pension scheme |
|
|
What are the 3 retirement option pensions available? |
Scheme Pension - Pension paid directly out of scheme assets Lifetime Annuity - Payable by insurance company the member has chosen Drawdown Pension - Member draws an income from the pension fund |
|
|
What is an Investment Bond described as? |
A single premium life assurance policy that is taken out for the purposes of investment |
|
|
What Investment Bonds are available? |
With profits investment bonds Distribution bonds Guaranteed equity bonds Unit linked bonds |
|
|
What is a Trust? |
The legal means by which one person gives property to another person to look after for someone else |
|
|
What are the three parties involved in a Trust? |
Settlor - Creator of Trust Trustee - Has the property Beneficiary - Who it is intended for |
|
|
What are the three types of Trusts? |
Bare or absolute - Where a trustee holds assets for one or more persons absolutely
Interest in possession - Beneficiary has right to the income of the trust during their life, capital passes to others on their death
Discretionary - Trustee has discretion over to who the capital and income is paid |

