![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Main Pulmonary diagnostic procedures |
|
|
|
Management of cases in general |
|
|
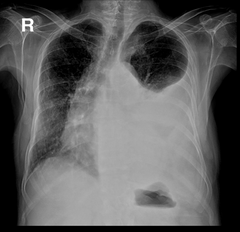
Dx? |
There is obvious pleural effusion in the left lung that has blunted the costophrenic angle and is pushing the mediastinum and deviating the trachea to the opposite side, it can be parapneumonic if there is infection, Step E here is Thoracentesis |
|
|
How to differentiate between Transudate vs Exudate effusion?
|
|
|
|
Indications for Chest tube insertion
|
|
|
|
Complications of Thoracentesis
|
|
|
|
What type of dullness is found on Pleural effusion?
|
Stony Dullness |
|
|
If the patient came with Pleural effusion signs and symptoms but he was stable and was chronic, what test should be done in this case?
|
|
|
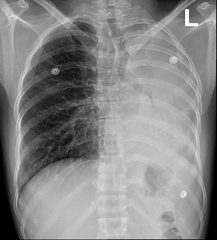
Dx?
|
|
|
|
Indications of Bronchoscopy
|
Anything that can indicate a history of aspiration |
|
|
Spirometry
|
Decreased in COPD Normal or increased in Restrictive diseases |
|
|
Lung volumes
|
Decreased in restrictive lung diseases , diagnosis of air trapping |
|
|
Diffusion Capacity ( DLco )
|
Decrease indicated loss/damage to gas exchanging surfaces in the lung :
|
|
|
Respiratory muscle strength
|
Not very imp but, Guillain-Barre can cause ascending motor paralysis and cant affect breathing |
|
|
What disease can cause 4 pathologies that can be seen on PFT and spirometry and Disrupted diffusion capacity? Case from the doctor |
Interstitial lung diseases from autoimmune or granulomatous diseases , Classic example is Sarcoidosis |
|
|
Indications of HRCT
|
Used to evaluate lung structure in high details for:
|
|
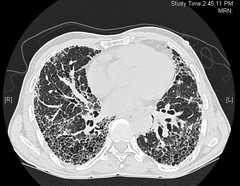
Dx?
|
This is a very advanced case of pulmonary fibrosis, sometimes doctors neglect it and don't auscultate correctly at first patient visit and miss it! , on auscultation, we should hear coarse crackles, however, we till the patient to cough hard to clear secretions because it might be pseudocrackles from the secretions |
|
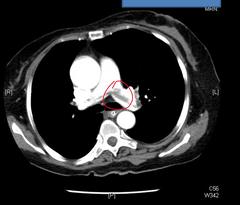
CT Angiography ( Spiral )
|
It is the best modality for detecting Pulmonary embolus |
|
|
When do we do V/Q test?
|
If we suspect PE and the patient has contraindications to CTA ( Pregnant lady ) |

