![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
143 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Wilhelm Wundt |
First Scientific Laboratory |
|
|
|
Francis Bacon |
Created Scientific Method |
|
|
|
Biological Approach |
Personality is linked to genetics |
|
|
|
Behavioral Approach |
Study and Observe behavior - blank slate |
|
|
|
Humanistic |
All people are inherently good |
|
|
|
Cognitive Approach |
How the mind learns and thinks |
|
|
|
Structuralism |
Classification of the mind's structures |
|
|
|
Psychoanalytical |
Actions are based on unconscious motivation |
|
|
|
Functionalism |
William James - the "how" part of behavior |
|
|
|
Nature vs. Nurture |
Whether or not biology plays a part in personality |
|
|
|
Variable |
A changing part of the person |
|
|
|
Constant |
A variable that always stays the same |
|
|
|
Dependent Variable |
The variable the experiment is trying to get information about |
|
|
|
Independent Variable |
The variables that the experimenter controls |
|
|
|
Correlation Research |
How much one variable changes in relation to each other |
|
|
|
Clinical Psychologist |
Doctoral degree in Psychology, cannot prescribe medicine |
|
|
|
Psychiatrist |
A medical doctor with a degree in Psychotherapy, can prescribe drugs |
|
|
|
Ethics |
Principals and standards of behavior including morals |
|
|
|
Autonomic Nervous System |
Involuntary system |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Part of the endocrine system |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic Nervous Systen |
Calming part of the system |
|
|
|
Sympathetic Nervous System |
Arousing part of the system |
|
|
|
Hippocampus |
Stores memories |
|
|
|
Limbic System |
Memory and emotion center |
|
|
|
Cerebral Cortex |
Most developed and largest part of the brain |
|
|
|
Occipital Lobe |
Vision |
|
|
|
Temporal Lobe |
Hearing |
|
|
|
Frontal Lobe |
Voluntary muscles and intelligence |
|
|
|
Parietal Lobe |
Body Sensations |
|
|
|
Pons |
Control breathing and heart rate |
|
|
|
Cerebrum |
The two large halves of the brain |
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
Coordinates all movements and muscles |
|
|
|
Brain Stem |
Sends commands to all other parts of the body |
|
|
|
Thalamus |
Main relay station for sensory signals |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Regulates internal temperature |
|
|
|
Gregor Mendel |
Father of genetics |
|
|
|
Cloning |
Reproduction done with just the somatic cell |
|
|
|
Somatic Cell |
A full set of chromosomes |
|
|
|
Zygote |
First part of a human |
|
|
|
Gametes |
Reproductive cells (eggs and sperm) |
|
|
|
Vestibular Sense |
Balance and body movement |
|
|
|
Absolute Threshold |
How much sensation one has to have to feel something |
|
|
|
Sclera |
White part of the eye |
Holds its shape |
|
|
Iris |
Colored part of the eye |
|
|
|
Pupil |
Part of the eye that is black, opens and closes to let in light |
|
|
|
Cornea |
A clear membrane that protects the eye |
|
|
|
Lens |
Transparent and located in front of the eye |
|
|
|
Retina |
Back of the eyes. Contains rods and cones. |
|
|
|
Cones |
Use to view color |
|
|
|
Noise |
Irrelevant stimuli that competes for attention |
|
|
|
Frequency |
The number of full wavelengths that pass through a point in a given amount of time |
|
|
|
Pitch |
Ear's interpretation of a sound's frequency |
|
|
|
Amplitude |
Amount of pressure produced by a sound wave and is measured in decibels |
|
|
|
Loudness |
A sound wave's amplitude |
|
|
|
Timbre |
The perceptual quality of sound |
|
|
|
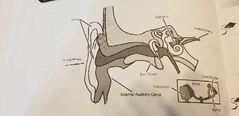
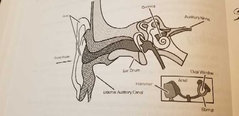
Outer Ear |
Includes pinna and external auditory canal |
|
|
|
Middle Ear |
Eardrum, Anvil, Stirrup |
|
|
|
Cochlea |
A fluid filled structure in the inner ear that looks like a snail |
|
|
|
Organ of Corti |
A part of the ear inside the cochlea |
|
|
|
Gestalt Psychology |
People organize their perceptions by patterns |
|
|
|
Depth Perception |
Makes people see objects in three dimensions |
|
|
|
Visual Cliff |
Proof that babies have depth perception |
Baby on one side of a glass table and mother calling out to baby on the other side, the baby refused to go because it believes it will fall. |
|
|
Erik Erickson |
Psychoanalyst |
|
|
|
Most important thing to Erikson |
Development of trust |
|
|
|
Trust vs. Mistrust |
Infant |
|
|
|
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt |
Toddler |
|
|
|
Initiative vs. Guilt |
Preschooler |
|
|
|
Industry vs. Inferiority |
School-Age |
|
|
|
Identity vs. Role Confusion |
Adolescent |
|
|
|
Intimacy vs. Isolation |
Young Adult |
|
|
|
Generativity vs. Stagnation |
Middle-Age Adult |
|
|
|
Ego Integrity vs. Despair |
Old age |
|
|
|
Jean Piaget |
Cognitive theorist |
|
|
|
Accommodation |
The difference made to one's mind or concepts by the process of assimilation |
|
|
|
Classification |
The ability to group objects together on a basis of common features |
|
|
|
Class Inclusion |
The understanding of more advanced than simple classification, that some classes or sets of objects are also sub-sets of a larger class |
|
|
|
Conservation |
The realization that objects or sets of objects stay the same even when they are changed about or made to look different |
|
|
|
Developmental Norm |
A statistical measure of typical scores for categories of information |
|
|
|
Egocentrism |
The belief that you are the center of the universe and everything revolves around you |
|
|
|
Elaboration |
Relating new information to something familiar |
|
|
|
Operation |
The process of working something out in your head |
|
|
|
Recognition |
The ability to identify correctly something encountered before |
|
|
|
Recall |
Being able to reproduce knowledge from memory |
|
|
|
Schema |
The representation in the mind of a set of perceptions, ideas, and/or actions, which go together |
|
|
|
Stage |
A period in a child's development in which he or she is capable of understanding some things but not others |
|
|
|
Reflexive Stage (0-2 months) |
Simple reflex activity such as grasping and sucking |
|
|
|
Primary Circular Reactions (2-4 months) |
Reflexive behaviors occur in stereotypes repetition such as opening and closing fingers repetitively |
|
|
|
Secondary Circular Reactions (4-8 months) |
Repetition of change actions to reproduce interesting consequences such as kicking one's feet to move a mobile suspended over the crib |
|
|
|
Coordination of Secondary Reactions (8-12 months) |
Responses become coordinated into more complex sequences. Actions take on an "intentional" character. |
|
|
|
Tertiary Circular Reactions (12-18 months) |
Discovery of new ways to produce the same consequence or obtain the same goal such as the infant may pull a pillow toward him in an attempt to get a toy resting on it |
|
|
|
Invention of New Means Through Mental Combination (18-24 months) |
Evidence of an internal representational system. Symbolizing the problem solving sequence before actually responding. Deferred imitation. |
|
|
|
Preoperational Phase (2-4 years) |
Increased use of verbal representation but speech is egocentric. The beginnings of symbolic rather than simple motor play. |
|
|
|
Intuitive Phase (4-7 years) |
Speech becomes more social, less egocentric. The child has an intuitive grasp of logical concepts in some areas. |
|
|
|
Period of Concrete Operations (7-11 years) |
Evidence for organized,logical thought. There Is the ability to perform multiple classification tasks, order objects in a logical sequence. And comprehend the principle of conservation. |
|
|
|
Period of Formal Operation (11-15 years) |
Thought becomes more abstract, incorporating the principles of formal logic. The ability to generate abstract propositions, multiple hypotheses and their possible outcomes is evident. |
|
|
|
Oral stage |
Birth-1 Year |
|
|
|
Anal Stage |
1-3 Years |
|
|
|
Phallic Stage |
3-6 Years |
|
|
|
Latency Stage |
6-11 Years |
|
|
|
Genital Stage |
Adolescence |
|
|
|
Denial |
Complete rejection of the feeling or situation |
|
|
|
Suppression |
Hiding feelings and not acknowledging them |
|
|
|
Reaction Formation |
Turning a feeling into the exact opposite feeling. For example, saying you hate someone you are interested in. |
|
|
|
Projection |
Projection is transferring your thoughts and feelings onto others. For example, someone who is being unfaithful themselves constantly accuses their partner of cheating. |
|
|
|
Displacement |
Feelings are redirected to someone else. Someone who has a bad day at work and can't complain goes home and yells at their kids instead. |
|
|
|
Rationalization |
You deny your feelings and come up with ways to justify your behavior |
|
|
|
Regression |
Reverting to old behavior to avoid feelings |
|
|
|
Sublimation |
A type of displacement, redirection of the feeling into a socially productive activity |
|
|
|
Self-Actualization |
Highest need in hierarchy - Level 5 |
|
|
|
Esteem Needs |
Level 4 need |
|
|
|
Belonging and Love |
Level 3 need |
|
|
|
Safety |
Level 2 need |
|
|
|
Physical Needs |
Level 1 need |
Food, Water, Shelter |
|
|
Instructional Conditioning |
Gives a negative sanction |
|
|
|
Operant Conditioning |
Reinforces good behavior |
|
|
|
Extinction |
The process of unassociating the condition with the responses |
Refers to the gradual weakening of a conditioned response that results in the behavior decreasing or disappearing. Like teaching a dog to handshake and it stops being interesting, leaving a lack of response when triggered. |
|
|
Egocentric Behavior |
A child does not take into consideration other people's needs |
|
|
|
Social Learning Theory |
Explicit role instruction (stereotypes), boys play with trucks and cars, girls wear make-up |
|
|
|
Baby Albert |
Was kept in a box and conditioned |
Was made to fear rats. Ultimatley grew up to be afraid of anything furry. |
|
|
Stimulus Generalization |
Something from conditioning carries over to another related area |
Baby Albert |
|
|
Naturalistic Observation |
Research conducted by watching the subject |
|
|
|
Id |
Primitive part of the subconscious which wants food and sex |
|
|
|
Ego |
The mediator between ego and id |
|
|
|
Super Ego |
Ethical, super good part of the subconscious |
|
|
|
Harry Harlow |
Monkey experiment - monkeys liked the soft one better |
2 surrogate mothers - One made of Terry cloth without milk One made of wood and wire w/ milk |
|
|
Visual Cliff |
Experiment to prove infants have depth perception |
Baby on one end of glass table and mother calling out on other end. Baby is scared of the "cliff" |
|
|
Object Permanence |
Understanding that an object does not cease to exist once it has left your vision |
|
|
|
Who made the first IQ test? |
Alfred Binet |
|
|
|
Formula to find out IQ? |
IQ = Mental Age/Calculated Age x 100 |
|
|
|
Hyperactivity affects what percentage of children? |
0.03% |
|
|
|
Divergent Thinking |
Creative process of thinking |
|
|
|
Naturalistic Observation |
Research conducted by watching the subject |
|
|
|
Convergent Thinking |
Follower thinking |
|
|
|
Independent Variable |
The one the researchers have direct control over |
|
|
|
Cross-Sectional Studies |
When people of different ages are studied at one particular time |
|
|
|
Longitudinal Studies |
Where the people are followed over a long period of time and checked up on at certain points |
|
|
|
Quantitative |
The number or amount of something |
|
|
|
Qualitative |
Used in statistics, similar in structure or organization |
|
|
|
Four Steps of the Scientific Method |
Gather information, generate hypothesis, test hypothesis, revise |
|
|
|
Kohberg's Theory of Moral Development |
How morality is linked to behavior |
|
|
|
Preconventional Morality |
Punishment of obedience phase |
|
|
|
Conventional Morality |
Motivation to obey is done from influence of other people |
|
|
|
Postconventional Morality |
Motivation is because law is a higher order |
|

