![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Microorganisms |
ubiquitous, small or minute organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye except with the aid of a microscope. |
|
|
|
Pathology terminologies |
Pathogen: Disease causing organism. Pathogenicity: The diseases caused by the organism. Pathogenic: The ability of an organism to cause disease. Pathogenesis: The way and manner in which the diseases/infections are caused by pathogens. |
|
|
|
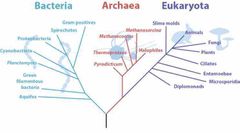
Bacteria: Mycoplasma, archaea |
Unicellular, thus known as prokaryotes. *Contain cell wall or peptidoglycan, which can be used to classify as gram positive or gram negative. *Mycoplasma and archaea do not contain cell wall. Mycoplasma: parasitic or saprotropic. Genus of bacteria; do not possess cell wall, or peptidoglycan. This enables it to show resistance to antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis. Archaea: similar structure to bacteria, single-celled. Does not possess peptidoglycan but possesses cell wall, cell membrane is linked with ether linked lipids instead of ester linked lipids as in bacteria. Grows in extreme temperature (cold region). Gental violent can be used as primary stain instead of crystal violent. |
|
|
|
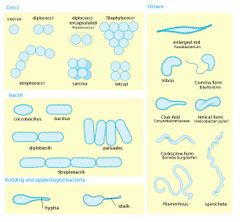
Morphology of bacteria |
Cocci: Coccus, Diplocpcci, diplococci encapsulated (pneumococcus), staphylocci, streptococci, sarcina (eights), tetrad (fours). Bacilli: Coccobacillus, bacillus, diplobacilli, Palisades, Streptobacilli. Budding and appendaged bacteria: hypha, stalk. Others: enlarged rod (fusobacterium). Vibrio, Comma form (B. Dellovibrio), club rod (corynbacteriaceae), helical form (helictobacter pylori), corkscrew form (borellia burgdorferi), filamentous, spirochete. |
|
|
|
Diseases caused by bacteria and their prevalence. |
Staphylococcus aureus Folliculitis: infection of hair follicles. Cellulitis: skin infection Endorcatis (inflammation of heart valves). Osteomyelitis (Inflammation of the bone, generally in leg, arm or spine) Pneumonia (inflammation of lungs) as a result of tissue fluid, toxic shock syndrome (hypersensitivity/UTI) food poisoning. Prevalence: 52% in neonatal septicemia, 34% in surgical site operations. E.coli, Gastroenteritis (inflammation of the small intestine), UTI, E.coli 153H7 (inflammation of the colon, colitis). Prevalence: 5% of stool samples had E.coli 157H7 in stool samples in Jos and 6% in Lagos. Salmonella: Gastroenteritis and enteric fever Prevalence: 4.2% positive for food handlers in SouthWest Nigeria. Vibrio Cholerae: Severe diarrhoea Pre balance: 43,996 cases and 836 deaths in 20 states in 2018 |
|

