![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
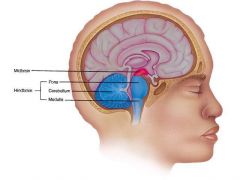
Hindbrain |
- Medulla - Cerebellum - Pons |
|
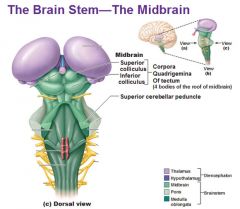
Midbrain |
- Tectum - Tegmentum |
|
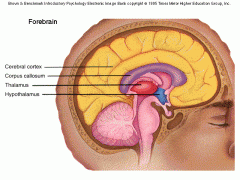
Forebrain |
- Telencephalon - Diencephalon |
|
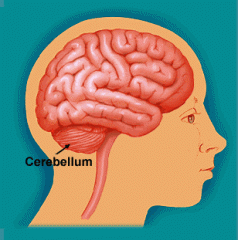
Cerebellum
(hindbrain) |
- Coordinates force, rate, direction of body movements - Evaluates body position and momentum (where the body is and where its going) - Aims to ensure smooth coordinated movements - Injury can result in loss of muscle tone, strength and coordination |
|
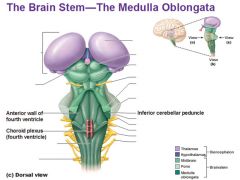
Medulla (oblongata)
(hindbrain) |
- Controls force/rate of heart contractions - Regulates blood pressure - Controls rate/depth of breathing - Maintains respiratory rhythm - Regulates vomiting, hiccupping, swallowing, coughing, sneezing |
|
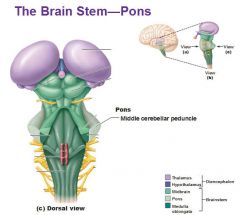
Pons
(hindbrain) |
- Divides cerebellum into right and left halves - Connects medulla to midbrain - Controls gross motor coordination - Helps maintain normal rythm of breathing |
|
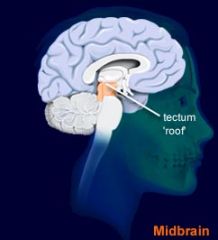
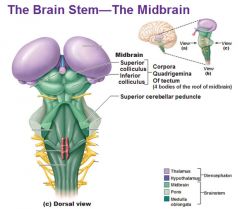
Tectum
(midbrain) |
- Superior Colliculus - Inferior Colliculus |
|
Superior Colliculus
(tectum - midbrain) |
coordinates head and eye movements when we visually follow a moving object, even if we are not consciously looking at it |
|
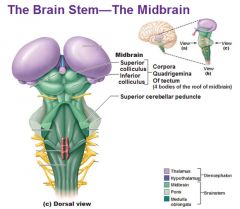
Inferior Colliculus
(tectum - midbrain) |
Acts in reflex responses to sound by causing you to turn your head toward an unexpected sound |
|
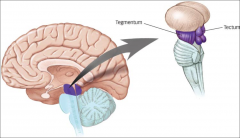
Tegmentum
(midbrain) |
- Reticular formation - Substantia Nigra |
|
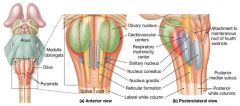
Reticular Formation
(Tegmentum - midbrain) |
- Recticular Activating System (RAS) - Arm of the RF - Receives info from all sensory tracts (sight,sound,hear,smell,touch) Filters the flood of sensory info going to cerebrum (repetitive,familiar, weak signals are filtered out, but unusual)
|
|
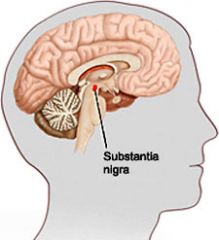
Substantia Nigra
(Tegmentum - midbrain) |
- Dark color reflects a high content of melanin pigment - Releases dopamine into the Caudate Nucleus - Degeneration of the dopamine releasing neurons is the ultimate cause of Parkinson's |
|
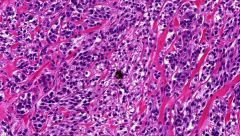
Melanin Pigment
(substantia nigra - tegmentum - midbrain) |
A precursor of the neurotransmitter Dopamine which is released by these neurons |
|
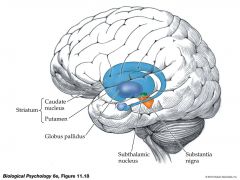
Caudate Nucleus
(substantia nigra - tegmentum - midbrain) |
A structure of the Basal Ganglia which appears to be important in starting, stopping and monitoring the intensity of movements executed by the cortex |
|
Red Nucleus
(Tegmentum - midbrain) |
- Lies deep in the substantia nigra - Reddish color is due to its rich blood supply - Red nuclei are relay nuclei in some motor pathways that effect limb flexion - Largest nuclei of the reticular formation |
|
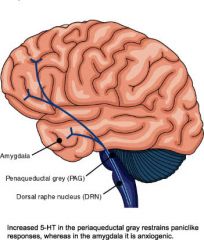
Periaqueductal Gray Matter
(Tegmentum - midbrain) |
- Involved in pain suppression - Link between fear perceiving amygdala and ANS pathways that control the "fight or flight" response - Includes nuclei that controls two cranial nerves; the oculomotor and the trochlear nerves |
|
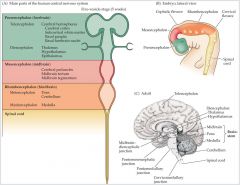
Telecephalon
(Forebrain) |
- Cerebral Cortex - Limbic System - Basal Ganglia |
|
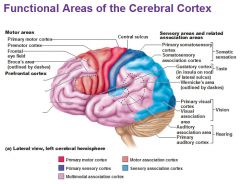
Cerebral Cortex
(Telecephalon - Forebrain) |
- Consists of 2 hemispheres each containing 4 lobes a. Frontal (motor) b. Temporal (hearing) c. parietal (sensation) d. occipital (vision
|
|
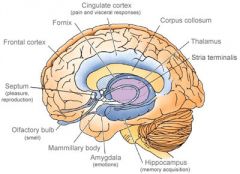
Limbic System
(Telecephalon - Forebrain) |
- Considered to be our emotional or effective brain - Consists of the following structures: Hypothalamus - Amygdala - Thalamus - Hippocampus Cingulate gyrus - Fornix - Orfactory bulb - Mamillary bodies |
|
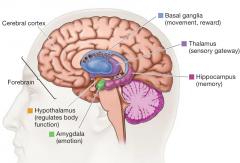
Basal Ganglia
(telecephalon - forebrain) |
- Consists of the following structures: Caudate Nucleus Putamen Globus Pallidus Nucleus Accumbens |
|
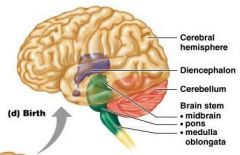
Diencephalon
(forebrain) |
- Thalamus - Hypothalamus |
|
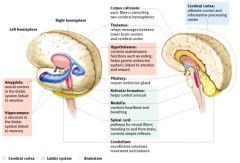
Thalamus (Relay Station)
(diecephalon - forebrain) |
- Sensory and motor pathways from all over the body pass through it. Olfactory system is the only system that does not pass through it
|
|
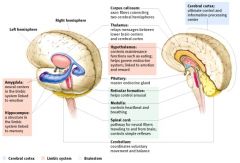
Hypothalamus
(diecephalon - forebrain) |
- Controls body temperature, hunger, sleep, sexual behavior, etc |

