![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
157 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
brain death
|
the brain shows no activity and responds to no stimulus
|
|
|
|
spatial neglect
|
a tendency to be unconscious of the left side of the body, the world, and od objects
|
left
|
|
|
binocular rivalry
|
the alternation between seeing the pattern in the left retina and the pattern in the right retina
|
|
|
|
readiness potential
|
increased motor cortex axtivity prior to the start of the movement
|
|
|
|
jet lag
|
a period of discomfort and inefficiency while your internal clock is out of phase with your new surroundings
|
|
|
|
circadian rhythm
|
a rhythm of activity and inactivity lasting about a day
|
|
|
|
electroencephalograph (EEG)
|
measures brain activity
|
|
|
|
polysomnograph
|
combine EEG measure with a simultaneous measure of eye movements
|
|
|
|
sleep spindles
|
waves of activity at about 12-14 per second (that result from exchange of information between the cerebral cortex and the underlying thalamus)
|
|
|
|
sleep apnea
|
fail to breathe for a minte or more and then wake up gasping for breath
|
|
|
|
narcolepsy
|
sudden attacks of sleepiness during the day
|
|
|
|
lucid dreaming
|
awate that is is a dream (one part of the brain is awake-prefrontal cortex-and thenl other is asleep
|
|
|
|
periodic limb movement disorder
|
prolonged creepy craly sensations in their legs, accompanied by repetitive leg movements strong enough to awaken the person during the first half of the night (restless leg syndrome)
|
|
|
|
night terror
|
causes someone to awaken to unpleasant screaming and sweating with a racing heart rate, and sometimes flailing of the arms
|
|
|
|
insomnia
|
not enough sleep for the person to feel rested the next day
|
|
|
|
manifest content
|
the content that appears on the surface
|
|
|
|
latent content
|
hidden ideas that the dream experience represents symbolically
|
|
|
|
activation synthesis theory
|
dreams occur because the cortex takes the haphazard activity that occurs during REM sleep plus whatever stimuli strike the sense organs and does best to make sense of it
|
|
|
|
REM sleep
|
a spatial stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movements, a high level of brain activity and relaxed muscles
|
|
|
|
the iceberg theory of consciousness (freud)
|
consciousness-above the iceberg (thoughts and perceptions)
preconscious-slightly under water (memories stored & knowledge) subconscious-deep under water (fears, immoral urges, violent motives etc.) |
|
|
|
stage 1 of sleep
|
brain creates a sensory experience w/o external stimulation (theta waves)
|
|
|
|
stage 2 of sleep
|
the brain makes sleep spindles or bursts of rapid rhythmic brain activity and sleep talking can occur
|
|
|
|
stages 3 & 4 of sleep
|
large slow delta waves occur from brain into deep sleep (bedwetting and sleep walking may occur)
|
|
|
|
sleep cycle
|
1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 3, REM, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2, REM (each sleep cycle is 90 to 100 mins but all the while REM and stage 2 increase in duration)
|
|
|
|
hypnosis
|
a condition if increased suggestibility that occurs in the context of a special hypnotist-subject relationship
|
|
|
|
posthypnotic suggestion
|
a suggestion to do or experience something after coming out if hypnosis
|
|
|
|
meditation
|
a systematic procedure for inducing a calm, relaxed state through the use of special techniques
|
|
|
|
deja vu experience
|
a feeling that an event is uncannily familiar
|
Denzel Washington
|
|
|
homeostasis
|
the maintenance of an optimum level of biological conditions within an organism
|
|
|
|
drive
|
a state of unrest or irritation that energizes one behavior after another until one of them removes the irritation (ie. splinter pain keeps reminding you to take it out)
|
splinter
|
|
|
incentives
|
stimuli that pulls us toward an action
|
|
|
|
allostasis
|
maintaining levels of biological conditions that vary according to an individual's needs and circumstances
|
|
|
|
self-actualization
|
the need for creative activities to fulfill your potential
|
Maslow hierarchy of needs
|
|
|
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
|
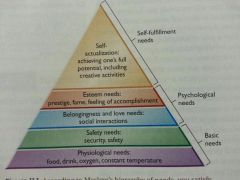
an organization from the most insistent needs to the ones that recieve attention only when others are in control
|
|
|
|
delay of gratification
|
declining a pleasant activity now in order to get greater pleasure later (I can give you a marshmallow now or I can give you 2 later)
|
marshmallow
|
|
|
mere measurement effect
|
simply estimating your probability of doing some desirable acrivity increases your probability of that action
|
|
|
|
scientific management approach to job design (Theory X)
|
most employees are lazy, indifferent, and uncreative so employers should make the work foolproof and supervise
|
|
|
|
human-relations approach to job design (Theory Y)
|
employees like variety in their job, a sense of accomplishment, and a sense of responsibility so employers should enrich the jobs and give each employee responsibility for meaningful tasks
|
|
|
|
job burnout
|
a long-lasting sense of mental and physical exhaustion and discouragement
|
|
|
|
transformational leader
|
articulates a vision of the future, intellectually stimulates subordinates, and motivates them to use their imagination to advance the organization
|
motivational
|
|
|
transactional leader
|
tries to make the organization more efficient are doing what is already doing by providing rewards (paycheck) for effective work
|
|
|
|
glucose
|
the most abundant sugar in the blood, us an important souce of energy for the body and almost the only source the brain uses
|
|
|
|
insulin
|
increases the flow of glucose and several other nutrients into body cells
|
|
|
|
set point
|
a level that the body works to maintain
|
|
|
|
leptin (hormone)
|
the body's fat cells release in amounts proportional to their mass & satisfy hunger (your body has enough fat so eat less)
|
fat ppl dont have leptin
|
|
|
obesity
|
excessive accumulation of body fat
|

|
|
|
anorexia nervosa
|
a condition in which someone intensely fears gaining weight and refuses to eat a normal amount
|
|
|
|
bulimia nervosa
|
alternate between self-deprivation and periods of excessive eating, with a feeling of loss of control
|
binge and purge
|
|
|
acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
|
an STD that attacks the body's immune system
|
|
|
|
testosterone
|
male hormone
|
|
|
|
estrogen
|
female hormone
|
|
|
|
intersexes
|
people with an anatomy that appears intermediate between male and female
|
|
|
|
gender identity
|
the sex that someone regards himself or herself as being
|
|
|
|
sexual orientation
|
someone's tendency to respond sexually to male or female partners or both or neither
|
|
|
|
bisexuality
|
attraction to both sexes
|
|
|
|
autonomic nervous system
|
controls organs such as heart and intestines
|
|
|
|
mircoexpressions
|
very brief, sudden emotional expressions
|
|
|
|
sympathetic nervous system
|
arouses the body for vigorous action
|
fight or flight
|
|
|
parasympathetic nervous system
|
decreases the heartrate and promotes disgestion and other nonemergency functions
|
|
|
|
James-Lange Theory
|
your interpretation of stimulus evoles autonomic changes and sometimes muscle actions (perception causes emotion)
|
|
|
|
nervous system
|
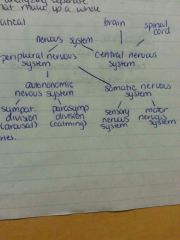
|
|
|
|
pure autonomic failure
|
the autonomic nervous system stops regulation the organs
|
|
|
|
Schachter and Singer Theory (of emotion)
|
the intensity of the physiological state determines the type of emotion (cognitive labeling causes emotion)
|
|
|
|
broaden-and-build hypothesis
|
a happy mood increases your readiness to explore new ideas and opportunities
|
|
|
|
emotional intelligence
|
the ability to percieve, imagine, and understand emotions and to use that information in making decisions
|
|
|
|
anxiety
|
an increase in the startle reflex
|
|
|
|
polygraph
|
or lie detector test records sympathetic nervous system arousal (blood pressure, breathing and heart rate, and electrical conduction of the skin ie. sweating)
|
|
|
|
guilty knowledge test
|
a modified version of a polygraph but produces more accurate results by aaking questions that should be threatening only to someone who knows the facts of a crime
|
|
|
|
contempt
|
a reaction to a violation of community standards (take credit for another persons work or fails to do their share of the work)
|
|
|
|
positive psychology
|
studies the features that enrich life (happiness, hope, creativity, coursge, spirituality, and responsibility)
|
|
|
|
subject well-being
|
a self-evaluation of one's life as pleasant, interesting, satisfying, and meaningful
|
|
|
|
health psychology
|
addresses how people's behavior influences health
|
|
|
|
stress
|
an event or events that are interpreted as threatening to an individual and which elicit physiological and behavioral responses
|
|
|
|
cortisol (hormone)
|
enhances metabolism and increases the supply or sugar and other fuels to the cells
|
|
|
|
type A personality
|
highly competitive, insisting on always winning, impatient and hostile
|
intense
|
|
|
type B personality
|
easy-going, less hurried and less hostile
|
chill
|
|
|
post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
|
profound result of severe stress characterized by prolonged anxiety and depression
|
|
|
|
problem-focused coping
|
Doing something to improve the situation
|
|
|
|
Reappraisal
|
Reinterpreting a situation to make it seem less threatening
|
|
|
|
Emotion focused coping
|
Regulating one's emotional reaction
|
|
|
|
inoculate
|
exposing yourself to small amoints of the events
|
|
|
|
altruistic behavior
|
helping others despite the cost to ourselves
|
|
|
|
the prisoners dilemma
|
a situation where people choose between a cooperative act and a competitive act that benefits themselves but hurts others
|
|
|
|
diffusion of responsibility
|
we feel less responsibility to act when other people are equally able to act
|
somebody else will call the police
|
|
|
pluralistic ignorance
|
a situation in which people say nothing and each person falsely assumes that others have a better-informed opinion
|
|
|
|
social loafing
|
the tendency to work less hard when sharing work with other people
|
|
|
|
frustration-aggression hypothesis
|
the main cause of anger and aggression is frustration- an obstacle that stands in the way of doing or obtaining something
|
|
|
|
social psychologist
|
study social behavior and how people influence one another
|
|
|
|
social perception and cognition
|
the processes of learning about others and making inferences from that information
|
|
|
|
primacy effect
|
first information we learn about somebody influences us more than later information does
|
|
|
|
self-fulfilling prophecy
|
expectation that increase the probability of the predicted event.
|
|
|
|
stereotype
|
a belief or expectation about a group of people
|
|
|
|
prejudice
|
an unfavorable attitude toward a group of people
|
|
|
|
discrimination
|
unequal treatment of different groups
|
|
|
|
implicit association test (IAT)
|
measures reactions to combinations of categories such as flowers and pleasant
|
|
|
|
multiculturalism
|
accepting, recognizing, and enjoying the differences among people and groups
|
|
|
|
internal attributions
|
explanations based on someone's attitudes, personality traits, abilities etc.
|
|
|
|
external attributions
|
explanations based on the situation, including events that eould influence almost anyone
|
|
|
|
consensus information
|
how the person's behavior compares with other people's behavior
|
|
|
|
consistency information
|
how the person's behavior varies from one time to the next
|
|
|
|
distinctivenes
|
how the person's behavior varies from one situation to another
|
|
|
|
actor-observer effect
|
people are more likely to make internal attributions for other people's behavior and more likely to make external attributions for their own
|
|
|
|
self-serving bias
|
attributions we adopt to maximize credit for success and minimize blame for failure
|
|
|
|
self-handicapping strategies
|
intentionally put themselves at a disadvantage to provide excuse for failure
|
|
|
|
fundamental attribution error
|
make internal attributions for people's behavior even when we see evidence for external influence on behavior
|
|
|
|
cognitive dissonance
|
a state of unpleasant tension that people experience when they hold contradictory attitudes or when their behavior contradicts their stated attitudes, especially of the inconsistency distresses them
|
self-hipocracy
|
|
|
central route to persuasion
|
when people take a decision seriously, they invest the necessary time and effort to evaluate the evidence and logic behind each message
|
|
|
|
peripheral route to persuasion
|
when people listen to a message on a topic they consider unimportant they attend to more superficial factors (ie. the speakers appearance or length of the speech)
|
|
|
|
bait and switch technique
|
offers an extremely favorable deal, gets the other person to commit the deal and then makes other commands (ie. offer a low deal for a product then claim the product is gone and sell the product they wanted to sell all along)
|
|
|
|
foot in the door technique
|
starts with a modest request, which you accept, then follows with a larger request (ie. give me $1 *10 days time* now give me $5)
|
|
|
|
thats-not-all technique
|
someone makes an offer and then improves the offer before you have a chance to reply
|
|
|
|
sleeper effect
|
delayed persuasion by an initially rejected message
|
|
|
|
fore-warning effect
|
informing people that they are about to hear a persuasive speech activates their resistance and weakens the persuasion
|
|
|
|
inoculation effect
|
people first hear a weak argument and then a stronger argument supporting the same conclusion
|
|
|
|
mere exposure effect
|
the more often we come into contact with someone or something the more we tend to like that person or object
|
|
|
|
proximity
|
we are most likely to become friends with people who live or work in proximity to us
|
|
|
|
exchange or equity theories
|
social relationships are transactions in which partners exchange goods and services
|
|
|
|
companionate love
|
markes by sharing, care and protection (marriage)
|
|
|
|
passionate love
|
sexual desire, romance, and friendship increases in parallel (honeymoon stage)
|
|
|
|
conformity
|
altering one's behavior to match other people's behavior or expectations
|
|
|
|
group polarization
|
if nearly all the people that compose a group feel the same way about an issue, a group discussion moves the group as a whole even further in that direction
|
|
|
|
groupthink
|
the members of a group suppress their doubts about a group's decision for fear of making a bad impression or disrupting group harmony
|
|
|
|
personality
|
all the consistent ways in which the behavior of one person differs from that of others, especially in social situations
|
|
|
|
chodynamic theory
|
relates personality to the interplay of conflicting forces, including unconscious ones, within the individual
|
|
|
|
catharsis
|
a release of pent-up emotional tension
|
|
|
|
psychoanalysis
|
Freud's method of explaining and dealing with personality, based on the interplay of conscious and unconscious forces
|
|
|
|
unconscious
|
memories, emotions, and thoughts, many are illogical that effect our behavior even though we cannot talk about them
|
|
|
|
Oedipus complex
|
when a son develops a sexual interest in his mother and competitive agression towards his father
|
|
|
|
psychosexual pleasure
|
all strong pleasant excitement arising from body stimulation
|
|
|
|
libido
|
psychosexual energy
|
|
|
|
fixated
|
a person continues to be preoccupied with the pleasure area associated with that stage
|
|
|
|
Freud's theory of psychosexual development
|

|
|
|
|
Id, Ego and the Superego
|
the id is the idiot in us all, the ego is the one that keeps balance and makes decisions, and the superego is the super uptight rule maker
|
|
|
|
Defense Mechanisms against the Ego (Anxiety)
|

|
|
|
|
Carl Jung
|
achetypes, problems in ur personality stem from traumatic events, personal (similar to the ID) and collective unconscious (human thoughts and beliefs shared by everyone ie. dont kill or steal etc. )
|
|
|
|
Karen Horney
|
humanist, fulfill ones true potential, focus on women, 10 neurotic needs, ideal self and real self
|
|
|
|
Alfred Adler
|
founded individual psychology, ides that we are all born with an inferiority complex and life is motivation by the need to overcome these feelings of inferiority and prove ourselves
|
|
|
|
individual psychology
|
Adler - a psychology of the person as a whole rather than parts
|
|
|
|
inferiority complex
|
Adler- an exaggerated feeling of weakness; inadequacy, and helplessness
|
|
|
|
striving for superiority
|
Adler- a desire to seek personal excellence and fulfillment
|
|
|
|
social interest
|
Adler- sense of solidarity and identification with others
|
|
|
|
gender role
|
the pattern of behavior that a person is expected to follow because of being msle or female
|
|
|
|
humanistic psychology
|
deals with consciousness, values, and abstract beliefs, including spiritual experiences and the beliefs that people live and die for (fulfilling your true potential and becoming a better person)
|
|
|
|
ideal self
|
Rogers- image of what they would like to be
|
|
|
|
self-concept
|
Rogers- image of what they really are
|
|
|
|
Carl Rogers
|
father of humanism, humans are basically good and peopek should strive for excellence to grow
|
|
|
|
unconditional positive regard
|
Rogers- the complete, unqualified acceptance of another person as he or she is
|
|
|
|
self-actualization
|
the achievement of one's full potential
|
|
|
|
Abraham Maslow
|
humanist believed that people are motivated by hierarchy of needs
|
|
|
|
trait approach to personality
|
people have consistent characteristics in their behavior
|
|
|
|
nomothetic approach to personality
|
seeks broad, general principles of personality
|
|
|
|
idiographic approach to personality
|
intensive studies of individuals
|
|
|
|
Big Five Personality Traits
|
neuroticism (experience unpleasant emotions frequently), extraversion (seek stimulation and enjoy the company of others), agreeableness (compassionate toward others), conscientiousness (show self-discipline, dutiful, and achieve) and openness (try new things)
|
|
|
|
biopsychosocial model
|
three aspects of abnormal behavior: biological, psychological, and sociological
|
|
|
|
systematic desensitization
|
reducing fear by gradually exposing people to the object of their fear
|
|
|
|
methadone (drug)
|
sometimes offered as a less dangerous substitute for opiates
|
|
|
|
alcoholism
|
type A- develops gradually, men= women, less severe, no family history
type B- develops rapidly, more often in men, severe, strong genetic basis |
|

