![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cell body |
Cells life- support center |
|
|
|
Dendrites |
Receives messages from other cells |
|
|
|
Axin |
Passes messages away from cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands |
|
|
|
Neural impulse( action potential) |
Electrical signal traveling down the axon |
|
|
|
Myelin sheath |
Covers axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses |
|
|

Describe this process |
Sodium is going in and potassium is going out |
|
|
|
Terminal branches of axon |
Form junctions with other cells |
|
|
|
What's an agonist |
Agonist mimics neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
Antagonist |
Antagonist completely blocks neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
What is reuptake? |
Recycles neurotransmitters so it doesn't cause an over indulgence |
|
|
|
What are the two parts of the nervous system |
Peripheral, central |
|
|
|
What does the peripheral nervous system do? |
Autonomic( controls the self-regulated action of internal organs and glands
(Arousal) |
|
|
|
What does the central nervous do and consist of? |
Consisted of brain and spinal cord. It controls the voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
(Calming) |
|
|
|
What do interneurons in the spine do? |
Skin receptors send info from Sensory neuron to the brain but the interneuron senses the response and immediately triggers the motor neuron to signal the brain and cause a reflex |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Brain region controlling the pituitary gland |
|
|
|
Thyroid gland |
Affects the metabolism, among other things |
|
|
|
Adrenal glands |
Inner part helps trigger the flight or fight response |
|
|
|
What is Synapse |
Process the Action Potential sends its signal or neuron to other nerves |
|
|
|
Testis |
Secretes male sex hormones |
|
|
|
Pituitary gland |
Secretes many different hormones some of which affect other glands |
The master gland |
|
|
Parathyroids |
Helps regulate the level of calcium in the blood |
|
|
|
Pancreas |
Regulates the level of sugar in blood |
|
|
|
Ovary |
Secretes female sex hormones |
|
|
|
EEG |
Electroencephalogram |
Ability to read action potential in brain |
|
|
MRI |
Magnetic resonance imaging |
Shows the fluid and mass of brain |
|
|
Fmri |
Shows increased activity in visual cortex of brain when a person is looking at a photo |
|
|
|
Pons |
Relays messages to brain that |
|
|
|
Medulla |
Part of brain stem that controls breathing and other involuntary responses of the heart and lung |
Breathing, pumping blood |
|
|
What holds the neurotransmitters while going to other cell? |
Vesicles |
|
|
|
Synaptic gap |
Gap between the terminal branches and the other cells dendrites |
|
|
|
What are the receptor sites on the receiving neuron |
Opening that accept the neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
What is serotonin |
A neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal |
|
|
|
What is dopamine |
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion |
|
|
|
What is Acetylcholine |
Neurotransmitters that enables muscle action, learning, memory |
|
|
|
What is norepinephrine |
Neurotransmitters that help control alertness and arousal |
|
|
|
How neurotransmitters activate receptors |
Neurotransmitter molecule has a molecular structure that precisely fits the receptor site on the receiving neuron |
Key and lock |
|
|
Brain stem consists of what? |
Pons and medulla |
|
|
|
What is reticular formation |
Sleep and consciousness. Has projections from the thalamus and cerebral cortex which allows it to exert some control of sensory signals that reach the cerebrum |
|
|
|
What is the thalamus |
Relays sensory impulses from receptors to send to voluntary parts of the body |
|
|
|
What is the cerebellum and what's it do |
Most neuron dense part of the brain. Also stores learned sequences of movements and other learned material |
Little brain |
|
|
What is the cerebellum and what's it do |
Most neuron dense part of the brain. Also stores learned sequences of movements and other learned material |
Little brain |
|
|
What is the limbic system |
a complex system of nerves and networks in the brain, involving several areas near the edge of the cortex concerned with instinct and mood. It controls the basic emotions (fear, pleasure, anger) and drives (hunger, sex, dominance, care of offspring). |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus does what? |
a region of the forebrain below the thalamus that coordinates both the autonomic nervous system and the activity of the pituitary, controlling body temperature, thirst, hunger, and other homeostatic systems, and involved in sleep and emotional activity |
|
|
|
Amygdala |
a roughly almond-shaped mass of gray matter inside each cerebral hemisphere, involved with the experiencing of emotions. Mainly anger |
|
|
|
Hippocampus |
the elongated ridges on the floor of each lateral ventricle of the brain, thought to be the center of emotion, memory, and the autonomic nervous system mainly fear |
|
|
|
Hippocampus |
the elongated ridges on the floor of each lateral ventricle of the brain, thought to be the center of emotion, memory, and the autonomic nervous system mainly fear |
|
|
|
What is the corpus callosum |
a broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain. |
|
|
|
Hippocampus |
the elongated ridges on the floor of each lateral ventricle of the brain, thought to be the center of emotion, memory, and the autonomic nervous system mainly fear |
|
|
|
What is the corpus callosum |
a broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain. |
|
|
|
What is the frontal lobe |
each of the paired lobes of the brain lying immediately behind the forehead, including areas concerned with behavior, learning, personality, and voluntary movement. |
|
|
|
Hippocampus |
the elongated ridges on the floor of each lateral ventricle of the brain, thought to be the center of emotion, memory, and the autonomic nervous system mainly fear |
|
|
|
What is the corpus callosum |
a broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain. |
|
|
|
What is the frontal lobe |
each of the paired lobes of the brain lying immediately behind the forehead, including areas concerned with behavior, learning, personality, and voluntary movement. |
|
|
|
Parietal lobe |
The Quick Facts Location: Upper, back part of the cortex Function: Processes sensory information that had to do with taste, temperature, and touch The parietal lobe carries out some very specific functions. As a part of the cortex, it has a lot of responsibilities and has to be able to process sensory information within seconds. The parietal lobe is where information such as taste, temperature and touch are integrated, or processed. Humans would not be able to to feel sensations of touch, if the parietal lobe was damaged.
|
|
|
|
Temporal lobe |
The Quick Facts Location: Bottom middle part of cortex, right behind the temples Function: Responsible for processing auditory information from the ears (hearing)
The Temporal Lobe mainly revolves around hearing and selective listening. It receives sensory information such as sounds and speech from the ears. It is also key to being able to comprehend, or understand meaningful speech. In fact, we would not be able to understand someone talking to us, if it wasn't for the temporal lobe. This lobe is special because it makes sense of the all the different sounds and pitches (different types of sound) being transmitted from the sensory receptors of the ears.
|
|
|
|
Occipital lobe |
The Quick Facts Location: Bottom, back part of the cortex Function: Responsible for processing visual information from the eyes The occiptial lobe is important to being able to correctly understand what your eyes are seeing. These lobes have to be very fast to process the rapid information that our eyes are sending. Similar to how the temporal lobe makes sense of auditory information, the occipital lobe makes sense of visual information so that we are able to understand it. If our occipital lobe was impaired, or injured we would not be able to correctly process visual signals, thus visual confusion would result.
|
|
|
|
Prefrontal cortex |
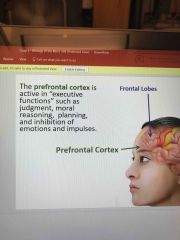
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Prefrontal cortex |
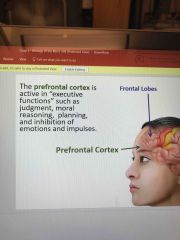
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is plasticity |
If brain is damaged. It does not repair damaged neurons but it can restore some functions. Can form new connections, reassign existing networks and insert new neurons some of which grow from stem cells |
|
|
|
Prefrontal cortex |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is plasticity |
If brain is damaged. It does not repair damaged neurons but it can restore some functions. Can form new connections, reassign existing networks and insert new neurons some of which grow from stem cells |
|
|
|
What does the left hemisphere mainly do |
Thoughts and logic Details such as trees Language words and definitions Linear and literal Calculation Pieces and details |
|
|
|
What does the right hemisphere do |
Feeling and intuition Big picture such as forest Language: tone, inflection, context Inferences and associations Perception |
|

