![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Most common forms of cancer in men?
|
They arise in the prostate, lung and colorectum
excluding non melanoma skin cancer |
|
|
Most common forms of cancer in women?
|
They arise in the breast, lung, colon and rectum.
excluding non melanoma skin cancer |
|
|
Explain why the incidence of primary liver cancer is increasing.
|
There is a large number of individuals that have been affected by the hepatitis C virus in the past 30 years and they are all slowly developing liver cancer
|
|
|
What two cancers are responsible for approximately 60% of pediatric cancer deaths?
|
acute leukemia and primitive neoplasms of the central nervous system.
|
|
|
Most inherited forms of cancer are tissue specific in their pathology except for one. Which one?
|
Li Fraumeni Syndrome
|
|
|
What type of heredity do failures in DNA repair generally cause? What is the exception?
|
They are generally autosomal recessive. However, Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer is autosomal dominant and the most common cancer predisposition syndrome.
|
|
|
Name the cancer syndromes caused by a failure in DNA repair.
|
Bloom Syndrome, Xeroderma Pigmentosum, Ataxiatelangiectasia
|
|
|
parenchyma vs stroma
|
parenchyma = clonal proliferation and determines the name of the neoplasm
stroma = nonclonal supporting tissues(connective/angio) desmoplasia = when a neoplasm is invading the tissue around it, pathologist calls it desmoplasia |
|
|
Neoplasm with little stroma will be...what does it look like? example?
|
soft...burkitt lymphoma, lots of cells clumped together
|
|
|
Neoplasm with dense stroma will look like...what does it look like? example?
|
hard...breast cancer, lots of collagenous tissue around it
|
|
|
Benign mesenchymal ends with(includes endothelium)
|
-oma
|
|
|
malignant mesenchymal ends with(includes endothelium)
|
sarcoma
|
|
|
benign epithelial ends with...
|
-oma
|
|
|
malignant epithelial ends with...
|
carcinoma
|
|
|
What is malignant endothelium?
|
angiosarcoma
|
|
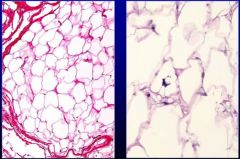
What is this? Which one is which?
|
the left is a lipoma, the right one is a liposarcoma
|
|
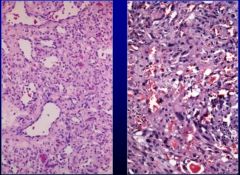
What is this?
|
On the left is a hemangioma and on the right is an angiosarcoma. Not blood vessels in benign are surrounded by regular cells and the malignant one there are mitotic figures and highly irregular cells.
|
|
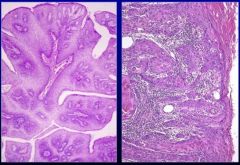
What is this?
|
On the left is squamous papilloma and on the right is squamous cell carcinoma. Both are epithelial neoplasms. note higher nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio. Pleiomorphism(one cell looks radically different from other cells) in cancer cell. Clear differentiation in benign.
|
|
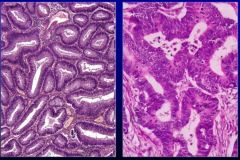
What is this?
|
On the left is tubular adenoma and on the right is adenocarcinoma. Both are epithelial neoplasms.
|
|
|
A tumor with both epithelial and mesenchymal components is called....
|
a carcinosarcoma
|
|
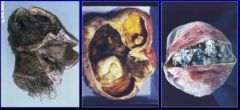
What is this
|
teratoma
|
|
|
Bad names for neoplasm(they don't follow the rules)
|
lymphoma, melanoma, seminoma, hepatoma, hydatidiform mole, melanocytic nevus, choristoma, hamartoma, hematoma
|
|
|
Distribution of cancer location and mortality is dependant on...
|
many things including race, geography, gender, environment, genetics, etc.
Also, obesity, alcohol, sexual activity, smoking, age |
|
|
age related cancer variation
|
in adults:
carcinoma > leukemia/lymphoma > sarcoma in children: leukemia>CNS>sarcoma>>carcinoma |
|
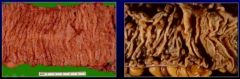
What is this...
|
It is Familial adenomatous polyposis(FAP) due to APC mutation
|
|
|
What conditions increase risk of benign tumors turn into cancer?
|
idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease(ulcerative colitis, Crohn disease)
Helicobacter pylori gastritis, viral hepatitis and other inflammatory syndromes. |

