![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Motivation
|
- willingness to exert high effort levels in order to achieve a goal and satisfy a need - motivation is an internal force, persistent, direction focused (not random) |
|
|
Need
|
- an internal state that makes certain outcomes appear attractive
|
|
|
Early Theories of Motivation (Needs Theory)
|
1. Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs 2. McGregor's Theory X and Y 3. Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory (Motivation-Hygiene Theory) |
|
|
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
|
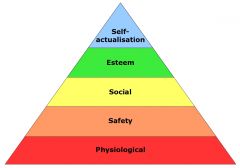
- 5 universal needs - each need is dependent on the previous needs being met - lowest unmet need is the strongest - Problem: assumes ppl have the same needs hierarchy |
|
|
McGregor's Theory X and Y
|
- based on 2 assumptions of human nature - one negative, the other positive - Theory X: employees lack drive, avoid responsibility, negative view of employees - Theory Y: employees are self-directed, desire responsibility and challenge, enjoy work - "Perspective dictates behaviour" |
|
|
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory (Motivation-Hygiene Theory) |
- identifies motivators and hygiene factors - motivators are internal (achievement, recognition, growth) - hygiene factors are external (ie money) - they simply keep people from becoming dissatisfied - hygiene factors are still needed; however, they do not motivate - Problem: hygiene factors are mistaken for motivatore |
|
|
Contemporary Theories of Motivation
|
1. Equity Theory 2. Expectancy Theory (Vroom's Model) |
|
|
Equity Theory
|
- perceived fairness and equal treatment stimulates motivation - employees compare input/output ratios - input: time, effort, loyalty, hard work, commitment, abilities - outputs: job security, salary, employee benefits, recognition, reputation, sense of achievement - distributive justice: perceived fairness of the amount and allocation of rewards among individuals - procedural justice: perceived fairness of the process used to determine the distribution of rewards |
|
|
Expectancy Theory (Vroom's Model)
|
- individual's action is based on the expectation that his behaviour will be followed by a particular outcome and on the attractiveness of that outcome. - unlike Maslow and Herzberg, Vroom concentrates on outcome and not need |
|
|
Expectancy Theory (Vroom's Model)
|
- Motivation depends on 3 factors or links: - E-P link (expectancy) - P-O link - Valence (attractiveness of outcome) How can we increase E-P link: support, help, train, educate How can we increase P-O link: create outcomes for performance, increase these outcomes, increased transparency How can we increase Valence: ask employees |

