![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
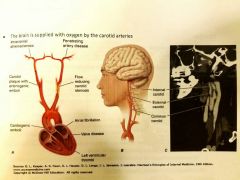
How is the brain supplied with oxygen? |
The carotid arteries |
|
|
|
What is a function if the carotid arteries? |
Supply the brain with oxygen |
|
|
|
Which layer of the artety are endothelial cells found? |
Tunica intima |
|
|
|
Between which artery layers can elastin ve found? |
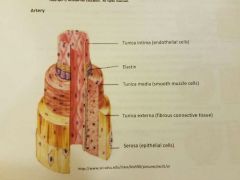
Tunica intima and tunica media |
Between endothilial cells and smooth muscle cells |
|
|
Which layer of the artery are epithelial cells found? |
Serosa |
'Ser'-face layer |
|
|
What causes ⬆ LDL accumulation in the intimal layers of blood vessels? |
Hyperlipidemia |
Tunica intima consists of endothelail cells |
|
|
What slows the transport of unused LDL from the intima of arteries back into circulation? |
Associations with proteoglycans (components of the extracelluar matrix) in the intima |
|
|
|
What are proteoglycans? |
Components of the extra cellular matrix |
|
|
|
What is the cause of oxidative modification of LDL? |
Lack of exposure to plasma antioxidants |
|
|
|
Define Coronary Heart Disease |
Refers to a ⬇in blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to plaque formation leading to parital or complete occlusion of the coronary arteries |
Used interchangeably with CAD coronary artery disease |
|
|
What types of conditions may be included in CHD? |
IHD ACS CSA UA NSTEMI STEMI |
Coronary heart disease |

