![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the leading cause of infant mortality
|
genetic diseases
|
|
|
what is another way of saying family history
|
pedigree
|
|
|
how many chromosones does each person have.
|
46 chromosomes in pairs or 23 pairs
22 pair are autosomes 1 pair is sex chromosome |
|
|
where are the genes located?
How many genes per trait? |
genes are located on the chromosome
there are 2 genes for every trait |
|
|
The genetic code
how is it sequenced? |
it is a sequence of 3 letter words made up from a 4 letter alphabet. there are 64 Possible code words.
|
|
|
How many codes does it take to make one amino acid?
|
three
|
|
|
What is the human genome project?
|
an international effore to map the genomes. have found so far that there are less genes than thought. and 99.9% of all our DNA is the same as someone elses
|
|
|
Terminology
|
Genetics
genomics-another name for genetics. it is interaction b/w genes and environment not statid pharmacogenetics-looking to prescribe meds that fit out genetic level |
|
|
What is a genotype
|
A genotype is the genetic expression.(genetic make-up) The pair of genes present for a particular characteristic or protein
|
|
|
what is a phenotype
|
Physical expression; the expression of the genes present in an individual. i.e eye color or blood type
|
|
|
What is a karyotype?
|
a picture taken of chromosomes in numeric order shows sex and any chromosomal defects
|
|
|
What is meiosis?
|
The division of a sex cell
|
|
|
Autosomal abnormalities of chromosome number
NONDISJUNCTION DURING MEIOSIS |
a pair of chromosmomes fail to seperate equally causing the new pair to either have one extra or one less
|
|
|
What happens if you have one more: 47 chromosomes
|
called a trisomy
|
|
|
What happens if you have one less :45 chromosomes
|
monosomy and it is NOT compatible with life.
|
|
|
TRISOMAL ABNORMALITIES
Trisomy 21/ down syndrome |
sm rounded skull, outward slanting eyes, ears and nose small, *SIMIAN CREASE* hands short and wide, feet short.HYPOTONIC, caridac anomolies, weak immune so freq infections, developmental delays
|
|
|
TRISOMAL ABNORMALITIES
Trisomy 13/ Patau syndrome |
very small, cardiac defects, structural defects, abn genitalia, finges overlap thumbs, low set ears MOST DO NOT SURVIVE FIRST YEAR OF LIFE, more severe than trisomy 21
|
|
|
TRISOMAL ABNORMALITIES
Edwards syndrome/trisomy 18 |
developmental and motor delays, SEVERE COMMUNICATION PROBLEMS, not as severe as trisomy 13 but more than 21
|
|
|
NONDISJUNCTION DURING MITOSIS
|
ERROR in cell division after fertilization (therefore after miosis)
|
|
|
Mitosis with 45 chromomsome
|
not compatiable with life
|
|
|
trisomy defects
|
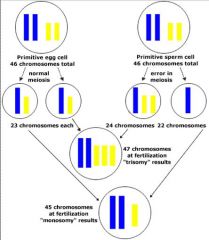
NONDISJUNCTION DURING MIOSIS
|
|
|
MOSAICISMS ARE FORMED WITH 47
variable effects-could be classified as downs but would be less severe |

NONDISJUNCTION DURING MITOSIS
|
|
|
ABNORMALITIES OF CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE
Deletion |
portion of one chromosome is deleted and added to another, or may be deficient
effects can be mild or severe |
|
|
CRI DU CHAT
|
example of deletion infant has low birth wt. hypotonic, and VERY high pitch cry, organ/cardiac defects and mental retardation
|
|
|
ABNORMALITIES OF CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE
Translocation |
Genetic material transferred from one chromosome to another. normal chromosome in each pair, individual may be unaffected but a carriet, or may have an extra copy
|
|
|
MOSAICISMS ARE FORMED WITH 47
variable effects-could be classified as downs but would be less severe |

NONDISJUNCTION DURING MITOSIS
|
|
|
Sex Chromosome disorders
Klinefelter syndrome |
Most common male disorder
trisomy of sec chromosome, 2X's and 1Y, has female charecteristics |
|
|
Sex chromosome disorders
Turner Syndrome |
Most common female disorder
mOnly 1 X, (only 45 chromo that is compatible with life) Has more male charecteristics |
|
|
Patterns of Genetic Transmission
Multifactoral |
combo of genetics and environment
mild-severe familial -cleft lip -pyloric stenosis -neural tube defects(caused by genetics and nutrional (folic acid) and envornment |
|
|
Patterns of genetic transmission
Unifactorial MENDELIAM |
single gene defect
-autosomal dominant -autosomal recessive -X linked dominant -X-lined recessive |
|
|
Autosomal dominant inheritance of birth defect
|
1 abnormal gene-(can get trait)
50% risk for each child to get defective gene ex:huntingtons, polydacytily and Marfan |
|
|
a
|
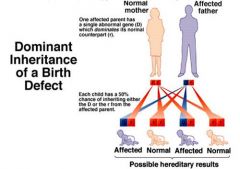
Autosomal dominant
|
|
|
a
|
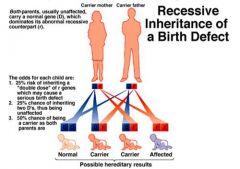
a
|
|
|
a
|
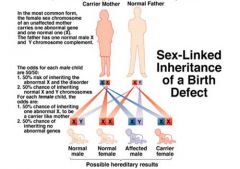
a
|
|
|
What is huntington's disease
|
dominantly inherited disease of the CNS marked by involuntary writhing, ballistic or dancelike movements)
|
|
|
Marfan Syndrom
|
Disorder of the CT
Weakness and streatching. will see tall, thin. arm span is longer than ht. |
|
|
Neurofibromatosis
|
nerve tumors
1/2 of all cases occur as spontaneous genetic mutations other 1/2 are autosmal dominant |
|
|
Recessive inheritance of a birth defect
|
Both parents usually unaffected. carries a normal gene which dominates and recessive counterpart
25% risk of inheritin 50%risk of being a carrier |
|
|
Sex linked inheritance of a birth defect
|
females only a carrier
50/50 for woman to be carrier 50/50 males to be infected ex;hemophilia, muscular dystropy |
|
|
X-linked dominant inheritance
fragile X |
affected females have normal gene but dominat gene so if male has affect X than daughter will get it.
most common form is learning disablitly tends to affect mens intelligence more than womans |
|
|
Genetic Screening
Chorionic Villi Sampling |
done at 10-12wks done if hx of genetic disease, adv maternal age, previous child with defect
|
|
|
Genetic Screening
Chorionic Villi Sampling Side Effects |
Miscarriage
infection hemorrhage preterm labor |
|
|
Amniocentisis
|
done after 14wks under ultrasound done if hx of genetic disease, adv maternal age, previous child with defect
|
|
|
Amniocentisis
S/E |
Miscarriage
infection hemorrhage preterm labor |
|
|
what is formed when an ova and sperm unite
|
a zygote
|
|
|
where does fertilization occur
|
in the ampulla (outer 1/3 of the fallopian tube)
|
|
|
what is the ectoderm
|
Ecto0 outer layer of cells in the develping embryo-produces skin structures, the teeth and glands of the mouth, the nervous system, orgnas of special sense, part of pit, pineal and supradrenal glands
|
|
|
What is the endoderm
|
the innermost of the three layer. it gives rise to the epithelium of the digestive tract and its associated glands, the respiratory organs, bladder, vagina and urethra
|
|
|
What is the mesoderm
|
middle layer-all CT, muscular, skeletal, circulatory, lymphatic and urogential systems and the lining of the body cavities
|
|
|
What are the two layer of the blastocyst
|
inner layer-forms embryo/amnion
Outer layer0forms chorion/fetal placenta |
|
|
What happens to each layer after implantation in the endometrium?
|
the amnion blends with the unbilical cord and the chorion blends with the placenta
|
|
|
What is fetilizated egg called at 8 wks
|
embryo
|
|
|
what is the funciton of the amniotic fluid?
|
the fetus drinks and voids into the fluid. it is sterile, it suspends and protects the growing fetus
|
|
|
What is the function of the placenta
|
transport and exchange of gases and nutrients
|
|
|
What are some things that don't pass through the placenta
|
meds such as insulin and heparin
lg. viruses |
|
|
what could happen if the placenta is not working
|
hypoxiam cardiac arrest
|
|
|
does the blood of the mom and baby mix
|
normally no but there is only a thing layer that seperates them so if a break occurs then it could happen
|
|
|
how do you differentiate moms HR from FHR
|
funic souffle-swish over umbilical cord-baby
Uterine souffle-blood through placenta-moms HR |
|
|
Endocrine function of the placenta
hCG |
human chorionic gonadotropin- present 8-12d after feritilization. matains corpus luteum which helps maitan preg
|
|
|
What are some things that don't pass through the placenta
|
meds such as insulin and heparin
lg. viruses |
|
|
what could happen if the placenta is not working
|
hypoxiam cardiac arrest
|
|
|
does the blood of the mom and baby mix
|
normally no but there is only a thing layer that seperates them so if a break occurs then it could happen
|
|
|
how do you differentiate moms HR from FHR
|
funic souffle-swish over umbilical cord-baby
Uterine souffle-blood through placenta-moms HR |
|
|
Endocrine function of the placenta
hCG |
human chorionic gonadotropin- present 8-12d after feritilization. matains corpus luteum which helps maitan preg
|
|
|
Endocrine function of the placenta
human placental lactogen hPL |
produced by placenta and it changes moms metabolism so that there is increased nutrient supply-like a growth hormone
|
|
|
Endocrine function of the placenta
Progesteron |
steroid it decreases the irritability of uterine contractions/stimulates breast development
High at begining low at end |
|
|
Endocrine function of the placenta
Estrogen |
steroid-maintains the endometrium or decidua. stimulates uterine growth, increases blood flow to uterus/placenta. stimulates contractility. growth of breast tissue
low at begin/high at end |
|
|
UMBILICAL CORD
|
contains baby blood
fromed from amnion has 3 vessels whartons jelly |
|
|
what is the function of the 2 arteries and 1 vein in the umbilical cord?
|
the arteries carry AWAY the blood and the vein carries it to (reverse than when born)
|
|
|
what is the role of whartons jelly
|
protects the cord. after birth helps dry out the cord
|
|
|
Stages of development
pre-embryonic |
first two weeks (any injury results in SpAb)
|
|
|
Stages of development
Embryonic Fetal |
15d- 8wk
8wk -delivery injury to fetus less significant as fetal age increases. |
|
|
What is the endometrium called after inplantation
|
the decidua
|
|
|
what does the amnion blend with and what does the chorion blend with?
|
amnion-the umbilical cord
chorion-placenta |
|
|
Developmental milestones for the embryo/fetus
|
4wks-fetal heart beings to beat
8wks- well eyes/ears/nose/mouth/digits 12wk-sex recognizable 16wk-mother feel quicking 20-lanugo 24-hearing 28-weak cry/suck reflex 36-plump/surfactant/ myellination of brain begins |
|
|
Factores that influence enbryoic/fetal develpment
|
chromosomal or genetics
environmental teratogens i.e. etoh, smk, caffine, x-rays, meds, consider paternal exposure as well |
|
|
critical periods for exposure
|
not susceptiable in 1st 2wk/ if are embryo would die
depending on tetragon susceptiable between wk3-16 |
|
|
Results of specific diseases
Toxoplasmosis |
10-15% SpAb or still birth
preemie, pyschomotor deficits, retardation |
|
|
Results of specific diseases
Gonorrhea |
eye infection
|
|
|
Results of specific diseases
Syphillis |
early detection is improtant. treatment does not cross placenta until 16-18wk. if exposued:preemie, target organs affected ie liver, splees, adrneals
|
|
|
Results of specific diseases
Hep B |
if baby born with it affects liver function 75% mortality rate and child may become carrier.
given immunoglobin at birth |
|
|
Results of specific diseases
HIV |
may be asymptomatic
see: failure to thrive secondary infections |
|
|
Results of specific diseases
Rubella |
check titer if antibiodies in baby 1:8 would indicate eubella see: growth retardation, cataracts, failure to thrive, heart defects
|
|
|
Results of specific diseases
cytomegalovirus |
miscarrage or stillbirth. 90-95% are asymptomatic and may only dectect hearing loss. see learning disabilities, SGA, mentatl retardation and learning diabilities
|
|
|
Results of specific diseases
Herpes |
encepholitis
local infection in the eye/skin or mouth |
|
|
Prevention for specifice diseases
toxo, syphillis, rubella, HIV/Herpes |
toxo-no cleaning litter box
seek early treatment/diagnosis for rubella safe sex for hiv and herpes |
|
|
Teratogenic medications
|
streptomycin-affects 8th craninal nerve
tetracycline-yellow teeth, affects bones diethlstillbesterol (DES) cervical CA Coumading-skeletal defects, facial anomolies orinase-limb abnoiles |
|
|
Drug categories for drugs
|
category A-Safest
Cat X- contraincicated in preg |
|
|
Cocaine addicted newborn
|
moms on cocaine- high BP, low blood flow to uterus
babies born-preemine, SGA, addicted. HIGH pitch cry, high SID rate, diffcult to console |
|
|
Environment-Fetal alcohol sprectrum disorders
|
FAS- charecterstic quality to facial expression m/b omcreased hyperactivity
1st clue is facial see cardiac problems and failure to thrive |

