![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Crosswind calculation |
Wind speed x Sin (angle) |
|
|
Headwind calculation |
Wind speed x Cos (angle) |
|
|
Crosswind rule of thumb |
15 degrees 1/4 30 degrees 1/2 45 degrees 3/4 Over 60 degrees same |
|
|
Aqua planning formula |
Speed = 9 x square root of PSI |
|
|
Calibrated airspeed (CAS) |
IAS adjusted for pitot system position and installation error |
|
|
Equivalent airspeed (EAS) |
CAS adjusted for compressibility effects |
|
|
True airspeed (TAS) |
EAS adjusted for air density |
|
|
TC-TWO |
Threats Charts Terrain Weather Operational |
|
|
Engine pressure ratio |
Intake air pressure VS outlet pressure |
|
|
Newton's third law |
For every force acting on a body there is an equal and opposite force |
|
|
Gas turbine cycle referred to as |
Brayton cycle |
|
|
Convergent ducts |
Increase velocity, decrease pressure and temp |
|
|
Divergent ducts |
Decrease velocity, increase pressure and temp |
|
|
One stage of an axial flow compressor |
A rotor blad and a stator vane |
|
|
Blade creep |
Turbine blades get longer over time due to high temp and centrifugal force |
|
|
Turbine performance depends on |
RPM airspeed Altitude Density Temperature |
|
|
Subsonic flow |
Convergent increase V, decrease P Divergent decrease V, increase P Density remains the same |
|
|
Supersonic flow |
Convergent decrease V, increase P, increase D Divergent increase V, decrease P, decrease D |
|
|
LSS formula |
39x square root temp (kelvin) |
|
|
Mach number formula |
TAS/LSS |
|
|
Mach tuck |
The C of P moving rearward generating a nose pitch down moment |
|
|
Airframe design to prevent shockwaves |
Wing taper Aspect ratio Sweep back Fuselage area ruling |
|
|
Lift formula |
CL 1/2 pV2 S CL coefficient of lift P (rho) value of air density V velocity of airflow over wing S surface area of the wing |
|
|
Types of drag |
Parasite drag Induced drag |
|
|
M crit |
The lowest mach number at which the airflow over some point on the a/c reaches the speed of sound |
|
|
ILS localiser scale |
2.5° full left or right Ie. 5 °full sweep |
|
|
ILS glide slope scale |
0.35° up or down 0.7° full scale |
|
|
Arc distance |
60/arc = degree per nm Ie. 60/12 = 5 |
|
|
NSW on a taf |
No significant weather |
|
|
NOSIG on a taf |
No significant change |
|
|
Circling area |
Cat A 1.68nm Cat B 2.66nm Cat C 4.2nm Cat D 5.28nm |
|
|
Factors effecting Mcrit |
Weight - higher weight = higher AoA = lower Mcrit Sweep back - more sweep back = higher Mcrit |
|
|
Factors effecting Vmcg |
Weight Temp Density Runway condition Power setting Crosswind |
|
|
Contaminated runway |
More than 25% covered with water/slush/snow 3mm in depth, or ice on any part of the runway surface |
|
|
Wet runway |
Means a runway with sufficient moisture on its surface to cause it to appear reflective but without significant areas of standing water |
|
|
Types of aqua planning |
Dynamic (standing water) Viscous (damp runway) Reverted rubber |
|
|
Horned formula |
Aquaplaning V = 9x square root of psi |
|
|
ROC required |
Gradient% x GS x 1.013 |
|
|
Feet per Nm |
Vsi x 60 divided by GS |
|
|
Carbon brakes benifits |
Higher efficiency and safety, better service weight and weight consistency |
|
|
Types of yaw dampers |
Parallel - moves rudder pedals aswell (turn off for take off and landing) Series - works independent (always on) |
|
|
Dutch roll cause |
Strong lateral stability Weak directional stability Fixed by yaw damper |
|
|
Balanced field |
TODA=ASDA |
|
|
Vr |
Rotate speed Must be greater than V1 |
|
|
V1 |
Speed by which time the decision to continue flight if an engine fails has been made. Ie. Commit to fly speed |
|
|
V2 |
Speed at which the airplane will climb in the event of an engine failure. Known as the take off safety speed |
|
|
Leadership behaviours |
Aim high Passion for people Step up Know your customer Own it |
|
|
Factors effecting Vmc |
Thrust - less thrust, less yaw, lower speed CofG - forward means greater moment, lower speed Critical engine - VMC based of crit engine Weight - little effect Windmilling prop - increases, VMC based on Windmilling prop |
|
|
QNE |
Question nil elevation Setting 1013 on the altimeter |
|
|
QNH |
Actual pressure a MSL |
|
|
QFE |
Station level pressure. When set will indicate height above or below the reference pressure point. Ie field |
|
|
Flying from a high to low |
Will overread. Ie saying you are higher than you actually are so very dangerous High to low look out below |
|
|
Flying from low to high |
Will underread. Ie saying you are lower than you actually are. Low To high touch the sky |
|
|
Reactors effecting density |
Pressure - directly related, increase P increase D Temp - inversely related, increase T decrease D Humidity - inversely related, increase H decrease D (because a water molecule has less mass than an air molecule |
|
|
Gas to solid |
Deposition |
|
|
Sublimation |
Solid to gas |
|
|
Reason a parcel of air cools as it rises |
Expansion |
|
|
Adiabatic |
A change in temp due to a change in pressure, without a change in the total heat energy of an air sample |
|
|
DALR |
3 degrees per 1000ft |
|
|
SALR |
1.5 degrees per 1000ft |
|
|
Atmospheric stability |
When the ELR is less than SALR |
|
|
Atmospheric instability |
When the ELR is greater than the DALR |
|
|
Conditional instability or stability |
ELR is less than DALR but more than SALR |
|
|
Buys Ballots law |
With your back to the wind the low pressure will be on the right (in the southern hemisphere) |
|
|
Passing of a cold front |
Fall in temp Backing of wind A rise in pressure |
|
|
Passing of a warm front |
Rise in temp Backing of the wind Steady or slight rise |
|
|
Occluded front |
Cold front has caught up with warm front |
|
|
Types of icing |
Hoar frost Rime ice Clear ice |
|
|
Clear ice |
Water drops 0 to -15 degrees. Needs to be large drops so usually in cumuliform clouds |
|
|
Rime ice |
Small super cooled water drops -10 to -20 degrees. Generally forms in stable cloud types |
|
|
BC |
Patches |
|
|
BL |
Blowing |
|
|
DR |
Drifting |
|
|
MI |
Shallow |
|
|
BR |
Mist |
|
|
DU |
Dust |
|
|
DS |
Dust storm |
|
|
DZ |
Drizzle |
|
|
FC |
Funnel cloud |
|
|
IC |
Ice crystals |
|
|
FU |
Smoke |
|
|
GR |
Hail larger than 5mm |
|
|
GS |
Small hail less than 5mm |
|
|
HZ |
Haze |
|
|
PL |
Ice pallets |
|
|
PO |
Dust devils |
|
|
SA |
Sand |
|
|
SG |
Snow grains |
|
|
SN |
Snow |
|
|
SQ |
Squals |
|
|
SS |
Sandstorm |
|
|
VA |
Volcanic ash |
|
|
VC |
Vicinity |
|
|
PY |
Spray |
|
|
Inter |
Intermittent phenomena, expected to occur frequently of periods of less than 30 mins |
|
|
Tempo |
A temporary phenomena, expected to last between 30 and 60 mins |
|
|
Jet streams |
Found at breaks in the tropopause Less than 100nm wide and a few thousand feet deep |
|
|
Clear air turbulence (CAT) |
Occurs from strong wind shear Most severe on the polar side and below the level of the core Also considered to be more severe in winter when the jet streams are stronger, and when the JS is over land and/or curved |
|
|
Two jet streams |
Sub tropical jet - found around 30 degrees Polar front jet - found just below the tropopause at the polar front |
|
|
High clouds |
Cirrus (ci) Cirrostratus (Cs) Cirrocumulus (Cc) |
|
|
Middle clouds |
Altostratus (as) - sheet of middle cloud, may produce rain or virga Altocumulus (ac) - heaped or lumpy cloud in the middle level, not usually associated with rain |
|
|
Low clouds |
Cumulus (Cu) - heaped or towering, may produce showers of rain or snow Cumulonimbus (CB) - tower thunderstorm cloud producing heavy showers Stratus (St) - a low sheet of cloud, may produce drizzle. Stratocumulus (Sc) - a sheet of heaped or towering cloud, may produce drizzle Nimbostratus (ns) - a sheet of heavy rain cloud, produces continuous rain or snow |
|
|
Vertical Separation standards |
1000ft below FL290 2000ft above FL290 (can be reduced to 1000ft in rvsm)
|
|
|
Metar /// |
Indicates cloud type is not identified |
|
|
Metar // |
When present weather sensor is inop |
|
|
NCD |
Indicates no cloud detected below 10,000ft at AA, CH, WN, or at any level at other aerodromes |
|
|
Metar //// |
Vis not reported |
|
|
Metar ///////// |
Cloud not reported Probably due to a raulty sensor |
|
|
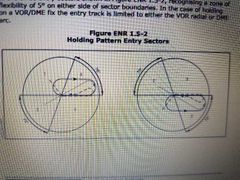
Splitting a hold left and right hand |
Left - inbound plus 70 and reciprocal of that Right - inbound minus 70 and reciprocal |

