![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the motives for internationalising?
|
Seeking a new market for product
Seeking assets - Natural resources, low cost production factors, skilled labour |
|
|
What are the different overseas entry modes?
|
Exporting:
Sale of good to another country Licensing: Granting the right to intangible property for a specific time period, which makes it possible for the licencee to manufacture and sell a similar product in the host country as that the licensor produce in the home country. Licensor receives royalty fee from licensee. Franchising: A specialised form of licensing in which the franchisor not only sells intangible porperty to the franchisee, but also insist that the franchisee agrees to abide by stricy rules as to how it does business joint venture: Establishment of a firm that is jointly owned by two ore more otherwise independent firms. Wholly owned subsidisary: 100% owned by firm. Either by greenfield venture (setting up new unit) or acquisition (buying existing firm) Franchising, Joint Ventures, Wholly owned subsidiary |
|
|
What level of control over foreign activites/product and resource commitments are had/made in the different overseas entry modes?
|

Advantages:
-Low development cost and risk -Help relaise location and expericne curve economies Disadvantages: -Costly where there are barriers to trade, transportation costs etc -Lack of control of local agents - Lack of foreign country's responsiveness |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Exporting?
|
Advantages:
- Low develoment cost and risks - Ability to earn returns from process technology skills in countries where FDI is resticted Disadvantages: - Creating Competitors - Lack of long term market presence |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Licensing/ Franchising?
|
Advantages:
- Low development costs and risks - Reach new markets not accessible via exports - Minimisation of political risk - Rapid expansion possible Disadvantages: - Lack of control over technology, quality - Risk to reputation and trademark - Lower income than other entry modes |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Joint ventures?
|
Advantages:
- Access to a local partner's skills etc - Sharing costs and risk - Pooling resources - Conform to host government's demands Disadvantages: - Management problem arising from shared control - Risk of asymmetries between partners - Lack of control over e.g. Technology |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Wholly owned subsidiaries?
|
Advantages:
- Protection of technology etc. - tight control over oerations, hence can realise cost economis and other benefits from global integration Disadvantages: - High costs and risks |
|
|
What are the Key considerations in selecting a mode of entry over another?
|
Is the firm’s competitive advantage country-based or firm-specific?
Is the product tradable and are there barriers to trade? Does the firm possess the full range of resources and capabilities for establishing a competitive advantage in the host country? Can the firm protect its resources and capabilities – this in turn depends on the nature of its core competencies? What transaction costs are involved i.e. costs of drawing up, monitoring and enforcing the contracts/transactions? Other costs involved? |
|
|
What are Cross Border Strategic Alliances (SAs)?
|
Cooperative agreements between firms. Range from formal joint-ventures to short-term contractual agreements
|
|
|
What are the advantages of SAs ( Cross border strategic alliances) ?
|
Advantages/motives:
Facilitate market entry by linking up to a local partner and tapping into resources, skills that the other partner lacks Cost and risk sharing Pooling of complementary skills and assets that neither company could develop on its own e.g. joint product development, technology sharing -Can be necessitated by rapid technological change; global competition; industry convergence; need for economies of scale Conforming to host governments’ requirements |
|
|
What are the risks of SAs (Strategic Alliances)?
|
Unbalances between the parties and opportunistic behaviour by one partner
-E.g. a partner uses the know-how gained from the alliance to compete against the other party - E.g. a partner abandons the other once it has learnt from the alliance Issues related to the ongoing management of the alliance as a result of control sharing |
|
|
What are the key issues to be managed in order to achieve success when it comes to SAs?
|
Partner selection
-Appropriate partner in light of strategic goals and complementarity of capabilities -Common vision re. the purpose of the alliance -A partner that can be relied on not to be opportunistic Alliance structure -Protect technology that is not meant to be transferred -Have contractual safeguards to guard against the risk of opportunism by a partner -Allow early skills and technology swaps, providing equitable gains for each partner -Extract significant commitment from the other partner Building interpersonal relationships and trust between managers Importance of cross-cultural sensitivity Staffing issues – balance of staff from each partner Mechanisms for ensuring learning takes place |
|
|
What are the advantages of Cross border mergers and acquisitions?
|
Quick to execute
Enable firms to pre-empt their competitors May be less risky than greenfield ventures |
|
|
What are the risks of failure, when it comes to Cross-border mergers and acquisitions?
|
The acquiring firm overpays for the acquired firm
Cultural clashes between the acquiring and acquired firm Difficulties of realising anticipated synergies Lack of pre-acquisition screening |
|
|
What are the Key factors to success when it comes to cross-border mergers and aquisitions?
|
Due diligence into the firm to be acquired
Carefully and (rapidly) managing the integration plan |
|
|
Why is market research essential when entering new markets?
|
Business environment
Needs/wants/preferences in market Decide on standardisation vs adaptation Reduces uncertainties and increases knowledge Basic concepts may differ Functions of similar products may differ |
|
|
Steps in the research process
|
1. Define research problem and establish research objectives
2. Determine sources of information needed to answer the questions 3. Gather relevant data from primary and/or secondary sources 4. Analyse, interpret and present the results. 5. Provide recommendations |
|
|
Conceptual equivalence
|
Do concepts have the same meaning in different cultures?
|
|
|
Functional equivalence
|
Similar products might perform different functions in different cultures
|
|
|
Best Entry Mode?
|
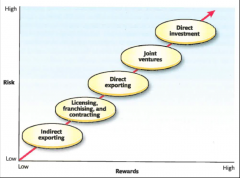
|
|
|
Market Entry method selection and criteria
|
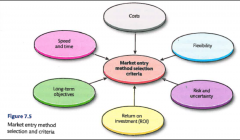
|

