![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Distinguish Osteoarthritis from Rheumatoid Arthritis based on presenting signs and symptoms
|
Osteo-
1.mechanical rather than inflammation and Rest helps 2. cartilage rather than bone holes 3. asymetric 4. Distal (DIP) Heberden's nodes) Defined as progressive deterioration and loss of articular cartilage, leading to loss of normal joint structure and function |
|
|
What are primary and second causes for developing OA?
|
1. primary causes: unknown- possible hereditary
2. Secondary: RA, trauma, structural abnormalities (Legg-Perthes Disease) |
|
|
What are two articular and 4 main predisposing factors to having OA?
|
1. Neurologic disorders- (loss of sensation, loss of proprioception)
2. Metabolic disorders- diabetes, hypothyroid, hemachromatosis, acromegaly 1. Age 2. Obesity 3. Gender 4. Genetics |
|
|
What are the radiographic finding in osteoarthritis?
|
1. Bone on bone (loss of joint space)
2. Osteophytes at joint margins 3. Sclerosis of subchondral bone 4. Subchondral cysts 5. RARE to see peri-articular osteoporosis and joint ankylosis |
|
|
RA vs OA radiographic findings...
|
RA shows ulnar deviaton more often
|
|
|
What are good treatments for patient suspected of Osteoarthritis?
|
Non-pharmacologic:
a. education b. exercise c. footwear d. diet/weight loss e. OMT f. PT/OT |
|
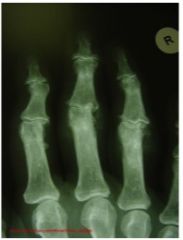
What does x-ray show?
|
osteoarthritis
|
|
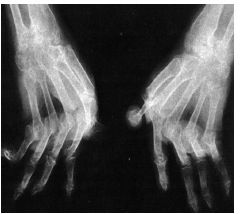
What is this radiograph showing?
|
RA
|
|
|
What is a cost effective initial treatment plan?
|
1. Excercise/diet/lifestyle
2. acetaminophen (no more than 4 g) |

