![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
List 3 benign liver tumors & its etiology? |
Epidemiology: m.c. hepatic hemangioma > focal nodular hyperplasia > hepatocellular adenoma (rare). M.c in young females 6:1. Etiology: unknown. Hepatic hemangioma - hormonal imblances, estrogen therapy. Hepatocellular adenoma - OCP & anabolic steroids Pathophysiology: Clinical features: lrg tumor- upper qudrant pain, fullness & nausea Dx: USS, constract-enhanced CT, MRI Tx: conservative, surgery resection for tumor > 5cm, discontinue OCP Complication? |
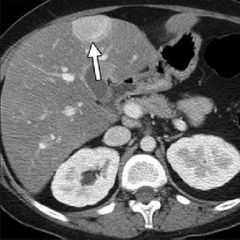
Hepatic adenoma |
|
|
What is an hepatic cyst? |
Epidemiology: >50yrsEtiology: unknown, congenital, genetic predisposition. Subtypes: simples, congenital polycystic liver, hydatid cystsClinical features: asymptomatic but sx develop as cyst enlarge.Dx: USS, CTTx: laproscopic resection if symptomaticDdx: malignant liver tumor(), biloma (bile in sac), liver abscess, localized non space occupying lesion of liver (pseudotumor- steatohepatitis, portal vein thrombosis). |
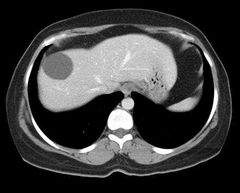
Simple cysts |
|
|
What do you understand by pyogenic liver absecess? |
Solitary , multiple collection of pus within the liver. Epidemiology: 2-3/100,000. Peak incidence -50-60yr, slightly m.c maleEtiology: source( biliary tract, portal vein, hepatic artery, contigious area) & organism - polymicrobial (80%, with E.coli & K.pneimonia) Riskfactors: DM, hepatobiliary disease, pancreatitis, GI malignancy.Clinical features: triad (fever, maliase & RUQ pain), other- anorexia, wt loss, nausea & vomitting, sx of diaphragmatic irritation - rt shoulder pain, hiccups. O/E - jaundice, tender hepatomegaly, intercostal/epigastric tenderness, decreased breath sound in rt lower lobeDx: blood investigations ( neutrophilic leukyocytosis, nomocytic normochromic anemia, increase ALP, AST, ALT, hypoalbuminemia,ESR, CRP), imaging ( abd USS & CT), precutaneous aspiration & culture. Ddx: space occupying lesion of liver, amebic liver abscess, benign liver tumor, HCC & liver metastasisTx: IV ABX (ampicilin, sulbactum, piperacillin + tazobactum, 3rd Gen cephalosporin + metronidazole), precutaneous drainage/ needle aspiration - solitary abscess (<5cm = needle apiration >5cm = drainage & intracavitary catheter placement) & surgery (open & laproscopic after 2 attempts of aspiration, avoid if INR > 1.5 & thrompocytopenia).Complication: rupture (peritonitis, empyema), sepsis, pneumonia, pleural effusion Prognosis: 100% mortality if untreated. Poor prognostic factors- pyogenic abscess with sepsis, advance age > 70yrs, multiple abscesses, polymicrobial infectoon, immunosuppression, need for surgical drainage. |
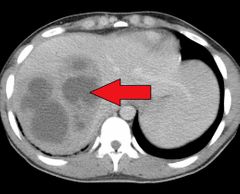
|
|
|
Types of hepatitis? |
Inflammation of liver tissue. Epidemiology:Etiology: acetaminophen (m.c), infectious (hepatitis A, B, C, D, & E), autoimmune. Hepatitis A: HAV- ssRNA, fecal oral Hepatitis B: HBV - DNA virus, spread via sexual intercouse & parenteral (30% needle stick injury) Hepatitis C: HCV- RNA virus, 6 genotype, transmitted sexual, perinatal & parenteral. Hepatitis D: HDV- ssRNA virus, transmitted sexually, parenteral & perinatally Hepatitis E: fecal oral AI hepatitis: m.c. in femalea 4:1, assoc with other AI conditions.Pathophysiology: liver damage due to cellular immunity CD8+ cyctotoxic T cells.Clinical features: in HAV- prodromal phase (1-2wk, fever, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, RUQ pain & tender hepatomegaly), icteric phase ( 2wks, jaundice, dark urine, pale stool, pruritus) & resolution. In HBV- serum sickness like syndrome (rash, polyarthritis, fever), acute (<6mths)& chronic infection (>6mths).Dx: blood investigation ( increase AST, ALT, ALP, GGT, leukocytosis, ferritin), urine analysis (increase urine bilirubin & urobilinogen), immunological test (anti-Hepatitis virus IgG & IgM,HBsAg, HBcAg, HBeAg, HBV DNA) & imaging (abd USS, pathology- councilman bodies in HBV), in HCV- PCR & ELISA. Autoantibodies- ANA & anti-smooth muscle antibodies.Ddx: viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatiti, cholangitisTx: self limiting, supportive tx, chronic HBV - antifungal tx (tenofovir), surgery ( liver transplant). HCV- interferon alpha for 6mths. AI hepatitis - immunosuppresant (prednisolone & azathiopione).Complication: coinfection ( HBV & HBD), acute liver failure, cirrhosis, HCC, PSC & PBC. Prevention: Pre-exposure prophylaxis & post exposure prophylaxis (within 2wks). Newborm immunization within 12 hrs with HBV vaccine & HBIG, mother with HBV allow to breastfed once passive - active PEP. |
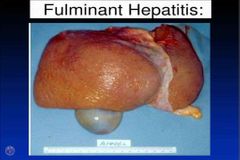
Fuliminant hepatitis B |
|
|
Alcohol liver disease |
A progressive liver condition caused by chronic & excessive alcohol consumption. Epidemiology: 10-20% develop cirrohosisEtiology: alcohol - > 210 g pure alcohol per week in males & > 140 g in femalesPathophysiology: hepatic degeneration of Ethanol -》 acetyl-CoA by alcohol dehydrogenase result in excess NADH which drives the formation of glycerol 3 phosphate from dihydroacetone phospate -》 incease G3P & fatty acid -》 steatohepatitis.Clinical features: 3 stages - alcohol fatty liver (asymptomatic, reversible, pressure sensation in upper abdomen, hepatomegaly), hepatitis (reversible, nausea, loss of appetite, wt loss, low grade fever with tachycardia, hepatomegalt & hepatic tenderness, jaundice, splenomegaly, ascites) & cirrhosis (irreversible).Dx: labs ( increase AST, ALT, ALP, GGT, PT carbohydrate deficient transcerrin [specific alcohol fatty liver], serum ferritin, microcytic anemia, thrombocytosis & absolute neutophillia), imaging (USS, CT), biopsy (cirrhosis)Ddx: non alcohol steatohepatitis Tx: cessation of alcohol , glucocorticoids Complication: decompensated cirrhosis ( decrease hepatic function -》 portan HTN, ascoties, hepatic encephalopathy, coagulopathy, hepatorenal syndrome, hyperestrogenism, end stage liver disease), other organ damage (gastritis, malabsorption, chronic pancreatitis, wernicke-Kotsakofd syndrome), |
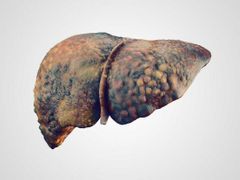
ALD |

