![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What hair is:
non-pigmented non-medullated? |
Lanugo hair
|
|
|
What replaces lanugo hair?
|
vellus hair on body
terminal hair on scalp |
|
|
What condition results when lanugo hair is not replaced by vellus hair?
|
Congenital hypertrichosis lanuginosa
|
|
|
What areas of the body are not affected in congenital hypertrichosis lanuginosa?
|
palms, soles, dorsal surface of digits and prepuce
|
|
|
Name the following dz:
Paraneoplastic disease Lung, colon, prostate cancer Can precede the diagnosis of cancer May be associated with other paraneoplastic etiologies Burning tongue, acanthosis nigricans, PPK, sign of Leser-Trelat Occurs over short period of time Can occur in areas of androgenetic alopecia May be localized to face only |
Acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa
|
|
|
What are cancers are assoc with hypertrichosis?
|
Lung, Colon, Prostate
(may precede dx of cancer) |
|
|
What are some other paraneoplastic signs?
|
Burning tongue, acanthosis nigricans, PPK, sign of Leser Trelat
|
|
|
Name Four Hereditary d/o characterized by congenital generalized hypertrichosis?
|
Congenital hypertrichosis lanuginosa
Universal hypertrichosis Ambras syndrome X-linked hypertrichosis |
|
|
Describe Congenital hypertrichosis lanuginosa
|
AD
fine, downy, silvery-gray to blond lanugo hair may shed over the first year of life occasional dental anomalies |
|
|
Describe Universal hypertrichosis
|
AD
Thicker, longer hair most prominent on the frontal, temporal and preauricular areas of the face, the back and the proximal extremities Increases during infancy and tends to persist |
|
|
Describe Ambras syndrome
|
AD, Chr 8
Fine, silky long hair (ex., >10cm) uniformly distrib on the face (incl nose), ears and shoulders Persists for life Minor facial dysmorphism, dental anomalies, supernumerary nipples |
|
|
Describe X-linked hypertrichosis
|
Xlinked
Curly, shorter, dark hair, most prominent on the face and upper body Anteverted nostrils, prognathism, occasional dental anomalies, deafness |
|
|
Most common drugs assoc with acquired generalized hypertrichosis
|
Minoxidil
Phenytoin Cyclosporin |
|
|
Name the localized hypertrichosis syndromes
|

|
|
|
Generalized Becker's Nevi syndrome is aka?
|
Michelin Tire Baby syndrome
|
|
|
What is SNUB Syndrome?
|
Supernumerary Nipples, Uropathies and Becker's Nevus
|
|
|
What other dermal tumors/lesions can have associated hypertrichosis?
|
Blue nevus (plaque type)
Fibrous hamartoma of infancy Dermal dendrocyte hamartoma Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma Tufted angioma |
|
|
Difference between Primary and Secondary Nevoid Hypertrichosis
|
Nevoid hypertrichosis: uncommon congenital alteration of terminal hair growth in circumscribed area
1. Primary (skin normal) No extracutaneous findings Can follows Blaschko’s lines 2. Secondary (associated with lipodystrophy, scoliosis, hemihypertrophy, abnormalities of underlying vasculature) |
|
|
What is spinal dysraphism?
|
Cutaneous findings that 'mark' an underlying defect.... ex. 'faun tail' in the lumbosacral region as a marker for spina bifida occulta
|
|
|
What is another name for Vaniqa? How does it work?
|
Vaniqa is 13.9% eflornithine cream:
Enzyme inhibits orthinine decarboxylase involved in polyamine synthesis and, if inhibited, has been shown to affect cell division/synthetic functions (affects rate of hair growth) Works approx 1/3rd of the time Go back to normal after cessation of therapy of note: eflornithine is also used to treat sleeping sickness from trypanosome brucei gambiense |
|
|
What is HAIRAN syndrome?
|
HyperAndrogenemia
Insulin Resistance Acanthosis Nigricans |
|
|
What % of hirsute pts have SAHA?
|
2-5%
|
|
|
What % of women have PCOS? Of those, what % are hirsuite?
|
5% of women in reproductive age have PCOS
90% are hirsute |
|
|
What are the clinical findings in PCOS?
|
obesity
large cystic ovaries infertility secondary amenorrhea mesnstrual alterations |
|
|
What are some findings in:
Ovarian hyperthecosis |
PCOS but with more testosterone
Normal LH, FSH Elevated estrone |
|
|
What are some findings in:
Ovearian hirsutism |
Mild hirsutism with virilization in older, postmenopausal women
|
|
|
What are some findings in:
Pituitary hirsutism |
ACTH and prolactin secretion (anterior pituitary)
Amenorrhea-galactorrhea syndrome, infertility |
|
|
What are some findings in:
Iatrogenic hirsutism |
Lateral aspects of face and back
Anabolic steroids (danazol) OCP’s of the non-steroidal progestogen type Resolution with drug cessation |
|
|
If hair is found localized to the areola or lateral neck/face -- what hormonal source would you consider?
|
Suspect ovarian (vs adrenal)
|
|
|
If hair is increased centrally, what hormonal source would you consider?
|
Suspect adrenal
|
|
|
How does Cyproterone acetate work?
|
interferes with DHT binding to androgen receptor and by inhibiting FSH and LH secretion due to its progestogen action
|
|
|
How does spironolactone work?
|
anti-androgen activity, decreases levels of total testosterone
|
|
|
How does flutamide work?
|
pure non-steroidal antiandrogen, used to tx prostatic hyperplasia
|
|
|
How does finasteride (propecia) work?
|
inhibits 5-alpha-reductase isoenzyme 2, blocking conversion of testosterone to DHT
|
|
|
How does Drosperinone work?
|
17-alpha-spironolactone derivative with progestonic, anti-androgenic and anti-aldosterone activity
|
|
|
Name subtypes of Telogen Effluvium
|
Immediate anagen release
Delayed anagen release Short anagen Delayed telogen release Immediate telogen release Chronic telogen effluvium |
|
|
Which HLA type is a susceptibility marker for all forms of AA? severe alopecia totalis/universalis?
|
1. HLA-DQ3
2. HLA DR4 & DQ7 |
|
|
Proposed Classification of Alopecia
|
Group 1: Lymphocytic
Group 2: Neutrophilic Group 3: Mixed Group 4: Other |
|
|
Name the Lymphocytic Alopcias
|
Chronic cutaneous LE
Lichen planopilaris (Classic, Frontal fibrosing alopecia, Graham Little Syndrome) Classic Pseudopelade (Brocq's alopecia) Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia Alopecia mucinosa Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans |
|
|
Name the Neutrophilic Alopecias
|
Folliculitis decalvans
Dissecting cellulitis |
|
|
Name the Mixed Alopecias
|
Acne keloidalis
Acne necrotica Erosive pustular dermatosis |
|
|
what % with other findings of LP?
|
50%
Condition more common in women |
|
|
Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans
|
XLD
Clinical: cictricial alopecia, follicular papules on face, trunk and extremities, atopy, PPK, photophobia, corneal abnmls |
|
|
Hair abnmls assoc w/ increased fragility
|
Trichorrhexis invaginata (bamboo hair)
Monilethrix Pili torti Trichorrhexis nodosa Trichothiodystrophy |
|
|
Hair abnmls NOT assoc w/ increased hair fragility
|
Acquired progressive kinking of the hair
Loose anagen hair Pili annulati and pseudo pili annulati Pili bifurcati Pili multigemini Spun-glass hair (uncombable hair) Woolly hair |
|
|
What Dz assoc are seen with Pili Torti?
|
"B/C" My Cousin is a BRAT:
B-Bjornstadt C-Crandall M-Menkes C-Citrullinemia B-Bazek’s follicular atrophoderma R-RetinoidS A-Anorexia T-Trichothiodystrophy |
|
|
Trichoptilosis?
|
Longitudinal shaft splitting
aka 'split ends' |
|
|
What hormone is linked with male-pattern baldness? Enzyme? Different forms of the enzyme? locations on the body?
|
Expression related to dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
5a-reductase converts testosterone to DHT Both DHT & 5a-reductase increased Type I: scalp follicle, liver, sebaceous gland Type II: scalp follicle, liver, chest & beard hair, prostate Genetic absence of Type II 5a-reductase is protective from the development of male androgenetic alopecia |
|
|
Where on hair follicle are the 5a-reductase enzymes located?
|
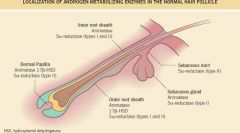
|
|
|
Treatment options for male pattern alopecia?
|
Minoxidil 5% (Rogaine)
2,4-pyrimidinediamine,6-(1-piperidinyl)-3-oxide 1 ml AAA bid Finasteride (Propecia) 1mg po qd Hamilton type III, IV Stops hair loss in 90% men for at least 5 years Regrows hair in 65% men Continued use necessary to sustain regrowth & stopping medication associated with resumption of hair loss Hair transplant Bald men have higher risk of CAD, especially younger patients with early onset, severe disease |
|
|
Classification for Male baldness? female baldness?
|
Male: Hamilton & Norwood
Female: Ludwig |
|
|
Treatment for female pattern baldness?
|
Minoxidil 2-5% topical solution …plus
Iron supplement to maintain ferritin levels Biotin supplementation…2.5mg/day “Re-Activate” shampoo – proprietary name for my new ketoconazole otc shampoo product. $80/bottle. Postmenopausal females: consider anti-androgen therapy…spironolactone 200mg/day. Or send to Tijuana for Diane-35. |
|
|
What is Leukonychia
|
Leukonychia
Normal nail plate surface with loss of transparency: Distal nail matrix damage --> parakeratotic cells within ventral portion makes nail look white |
|
|
What part of the matrix produces which part of the nail?
|
Proximal matrix --> dorsal nail plate
Distal Matrix (lunula) --> ventral nail plate |
|
|
What is the growth rate of nails?
|
fingernails: 3mm / month
toenails: 1mm / month |
|
|
What are some manifestations of damage to the proximal nail matrix?
|
Beau's lines
Pitting Longitudinal ridging Longitudinal fissuring Trachyonychia |
|
|
What are some manifestations of damage to the distal nail matrix?
|
True Leukonychia
|
|
|
What are some manifestations of damage to both the proximal and distal nail matrix?
|
onychomadesis
koilonychia nail thinning |
|
|
What are some manifestations of nail bed damage?
|
onycholysis
subungual hyperkeratosis apparent leukonychia splinter hemorrhages |
|
|
What is onychomadesis?
|
Proximal detachment of the nail
|
|
|
What is onychorrhexis?
|
thinning
longitudinal ridging longitudinal fissuring -- diffuse nail matrix damage by LP |
|
|
What is trachyonychia?
|
twenty nail dystrophy
nail roughness -- caused by proximal nail damage |
|
|
What is true leukonychia?
|
distal nail matrix damage; white opaque discoloration
|
|
|
What is onycholysis? photoonycholysis?
|
detachment of the nail plate, usu due to psoriasis or onychomycosis; photoonycholysis -- occurs with TCN use, and sun exposure.
|
|
|
What is onychauxis?
|
nail thickening, subungual hyperkeratosis
|
|
|
Another name for Racquet thumbs
|
Brachyonychia (broad and short thumbnail)
|
|
|
Common extracutaneous problem for pts with nail-patella syndrome
|
40% have nephropathy leading to renal insufficiency in 8%
|
|
|
what is a nail finding seen with indinavir use?
|
paronychia with pyogenic granulomas (also seen with retinoids and EGFRI)
|

