![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
143 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
adip/o |
fat |
Adipocele: hernia containing fat or fatty tissue |
|
|
lip/o |
fat |
Lipocyte: fat cell |
|
|
steat/o |
fat |
steatitis: inflammation of fatty tissue |
|
|
cutane/o |
skin |
Cutaneous pertaining to the skin |
|
|
dermat/o |
Skin |
Dermatologist physician specializing in treating skin disorders |
|
|
derm/o |
skin |
Hypodermic: under or inserted Under the Skin, as in a hypodermic injection |
|
|
hidr/o |
sweat |
Hidradenitis: inflammation of a sweat gland |
|
|
sudor/o |
sweat |
sudoresis: condition of profuse sweating, also called diaphoresis and hyperhidrosis |
|
|
ichthy/o |
dry, scaly |
ichthyosis: any of several dermatologic conditions characterized by non-inflammatory dryness and scaling of the skin and commonly associated with other abnormalities of lipid metabolism |
|
|
kerat/o |
horny tissue; hard; cornea |
keratosis: any condition of the skin characterized by an overgrowth and thickening of the skin |
|
|
melan/o |
black |
melanoma: malignant tumor of melanocytes that commonly begins in a darkly pigmented mole and can metastasize widely |
|
|
myc/o |
fungus (plural, fungi) |
dermatomycosis: fungal infection of the skin |
|
|
onych/o |
nail |
onychomalacia: abnormal softening of the nails |
|
|
pil/o |
hair |
pilonidal: growth of hair in a dermoid cyst or in a sinus opening on the skin |
|
|
trich/o |
hair |
trichopathy: any disease of the hair |
|
|
scler/o |
hardening; scler (white of eye) |
scleroderma: chronic disease with abnormal hardening of the skin caused by formation of new collagen |
|
|
seb/o |
Sebum , sebaceous |
Seborrhea: increase in the amount, and commonly, an alteration of the quality of the fat secreted by the sebaceous glands |
|
|
squam/o |
scale |
Squamous: covered with scales or scale like |
|
|
xer/o |
dry |
Xeroderma:chronic skin condition characterized by excessive roughness and dryness, xeroderma is a mild form of ichthyosis |
|
|
-derma |
Skin |
Pyoderma any pyogenic infection of the skin, py/o : pus |
|
|
-oid |
Resembling |
Resembling skin |
|
|
-phoresis |
Carrying, Transmission |
Diaphoresis condition of profuse sweating, also called sudoresis and hyperhidrosis |
|
|
-plasty |
Surgical repair |
Dermatoplasty: surgical repair of the skin |
|
|
-therapy |
Treatment |
Cryotherapy: treatment using cold as a destructive medium Warts and actinic keratosis are some of the common skin disorders treated with cryotherapy |
|
|
The two layers of tissue that skin is composed of |
The outer epidermis and the inner layer, the dermis |
|
|
|
Epidermis |
Protective covering of the body, does not have blood or nerve Supply. Dependent on thermoses network of capillaries for nourishment. Oxygens and nutrients flow out of the capillaries in the dermis passed through tissue fluid, supplying nourishment to the deeper layers of the epidermis. |
|
|
|
Dermopathy |
Disease of the skin |
|
|
|
Most important two layers of the epidermis |
Stratum corneum and basal layer |
|
|
|
Stratum corneum |
layer of the epidermis, Composed of dead flat cells, thickness correlated with normal wear of the area it covers |
|
|
|
Basal layer |
Layer of the epidermis, composed of living cells, where new cells are continuously reproduced |
|
|
|
Melanocytes |
Specialized cells of the basal layer that produce a black pigment called melanin |
|
|
|
Albinism |
Deficiency or absence of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes due to an abnormality in the production of melanin |
|
|
|
melanin |
A pigment produced by melanocytes gives color to Hair Skin eyes |
|
|
|
derm/is |
Second layer of the skin that contains hair follicle, sebaceous oil gland and sudoriferous sweat gland |
|
|
|
aden/oma |
a benign neoplasm which the tumor cells form glands or gland like structures. The tumor is usually well circumscribed tending to compress other than infiltrate or invade adjacent tissue |
|
|
|
adip/ectomy |
Excision of fat |
|
|
|
adip/oma, lip/oma |
Benign tumors consisting of fat cells fatty tumor |
|
|
|
Subcutaneous tissue |
Pertaining to under or below the skin |
Attaches the dermis to the underlying structures of the skin |
|
|
lip/o/cytes |
Fat cells |
|
|
|
fibrosis |
Scarring |
|
|
|
Systemic sclerosis |
A form of Scleroderma that causes fibrosis and sclerosis of multiple body systems |
Characterized by formation of thickened collagenous fibrous tissue thickening of the skin and adhesion to underlying tissues. The disease progresses to involve tissues of the heart lungs muscles genitourinary tract and kidneys |
|
|
Accessory organs of the skin |
Sebaceous oil glands, sudoriferous sweat glands hair, and nails |
|
|
|
comedos |
Discolored, dried sebum plugging an excretory duct of the skin |
Blackhead |
|
|
pustules |
whiteheads |
|
|
|
anhidrosis |
Absence of sweating |
|
|
|
myc/osis |
Abnormal condition caused by fungi |
myc/o refers to a fungus |
|
|
nail root |
Where the nail is formed |
nail is composed of keratin a hard fibrous protein which is also the main component of hair |
|
|
matrix |
Active cells beneath the cuticle where the nail grows from |
|
|
|
Epithelial layer |
Nail bed |
Where the nail stays attached and slides forward |
|
|
Nail body |
Appears pink because of the underlying blood vessels |
|
|
|
Lunula |
The crescent-shaped area at the base of the nail |
|
|
|
6 Parts of structure of the fingernail |
Nail root, Matrix, cuticle, nail bed, nail body, lunula |
|
|
|
albino/o |
white |
Albinism white condition |
|
|
cyan/o |
blue |
cyanoderma blue skin, caused by a deficiency of oxygen and an excess of carbon dioxide in the blood a person who is rescue from drowning exhibits cyanosis |
|
|
erythr/o |
red |
Erythroderma red skin |
|
|
leuk/o |
white |
Leukoderma white skin |
|
|
melan/o |
black |
Melanoderma black skin |
|
|
xanth/o |
yellow |
Xanthoma yellow tumor |
|
|
leuk/emia |
White blood |
The disease of unrestrained growth of immature white blood cells. Progressive malignant disease of blood-forming organs characterized by proliferation and development of immature leukocytes in the blood and bone marrow |
|
|
neo/plasm |
New growth |
|
|
|
2 most common skin cancers |
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
|
Basal cell Carcinoma |
Type of skin cancer that affects the deepest layer of the epidermis |
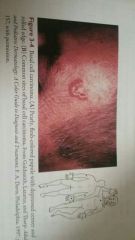
|
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma |
A skin cancer of the squamous cells or top layer of the epidermis |
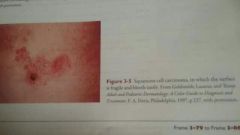
|
|
|
sarc/o |
flesh ( connective tissue) |
Kaposi sarcoma a malignant skin tumor commonly associated with patients who are diagnosed with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is usually fatal initially the tumor appears as a purplish Brown Lesion |
|
|
AIDS |
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome |
|
|
|
necr/o |
death , necrosis |
Necrotic a word that means pertaining to necrosis or death |
|
|
Necrosis |
The term used to denote the death of areas of tissue or bone surrounded by healthy tissue |
Cellular necrosis means that the cells are dead |
|
|
Gangrene |
A form of necrosis associated with loss of blood supply |
|
|
|
-auto |
self, own |
Auto examinationan : examination of oneself , autograft : a skin transplanted from oneself |
|
|
Dermatome |
An instrument used to in size or cut |
When there is a need to graft a thin slice of skin The Physician asks for an instrument called a dermatome |
|
|
auto/graft |
Grafts done tissue transplanted from patients own skin |
|
|
|
Abrasion |
Scraping or rubbing away of a surface such as Skin by friction |
May be the result of trauma such as Skinned knee , therapy as in dermabrasion to remove scar tissue, or normal function such as wearing down of a tooth by mastication |
|
|
Abscess |
Localized collection of pus at the site of an infection |

Treatment includes oral antibiotics and I&D to drain the purulent material |
|
|
Furuncle |
Abscess that originates in hair follicle also called boil |
|
|
|
Carbuncle |
Cluster of furuncles in the subcutaneous tissue |
|
|
|
Acne |
Inflammatory disease of sebaceous follicles of the skin marked by comedos, papules, and pustules |
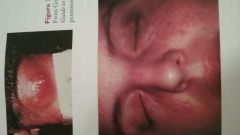
|
|
|
Alopecia |
Absence or loss of hair, especially if the head also known as baldness |
|
|
|
Cyst |
Closed Sac or pouch in or under the skin with a definite wall that contains fluid, semifluid, or solid material |
|
|
|
Sebaceous cyst |
A cyst filled with sebum [ fatty material from a sebaceous gland] |
|
|
|
Eczema |
Redness of the skin caused by swelling of the capillaries |
|
|
|
Hemorrhage |
Loss of a large amount of blood in a short period, externally or internally |
Hemorrhage maybe arterial venous or capillary |
|
|
Contusion |
Hemorrhage of any size Under the Skin in which the skin is not broken |
Also known as a bruise |
|
|
Ecchymosis |
Skin discoloration consisting of a large irregularly formed hemorrhagic area with colors changing from blue black to greenish brown or yellow |
|
|
|
Ecchymosis |
Skin discoloration consisting of a large irregularly formed hemorrhagic area with colors changing from blue black to greenish brown or yellow |
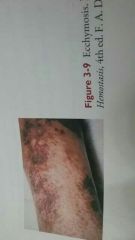
|
|
|
Petechia |
Minute pinpoint hemorrhagic spot on the skin |
A petechia is a smaller version of a ecchymosis |
|
|
Hematoma |
Elevated localized collection of blood Trapped Under the Skin that usually result from trauma |
|
|
|
hirsutism |
condition characterized by excessive growth of hair or presence of hair in unusual places especially in women |
Hirsutism may be caused by hypersecretion of testosterone or it may be due to an adrenal neoplasm |
|
|
Impetigo |
Bacterial skin infection characterized by isolated pustules that become crusted and rupture |
|
|
|
Psoriasis |
Autoimmune disease characterized by itchy red patches covered with silvery scales |
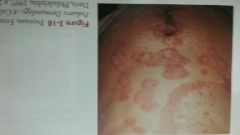
|
|
|
Scabies |
Contagious skin disease transmitted by the itch mite |
|
|
|
Skin lesion |
area of pathologically altered tissue caused by disease injury or wound due to external factors or internal disease |
Skin lesion are described as primary or secondary they help with diagnosis of skin disorders |
|
|
Primary lesion |
Skin lesion caused directly by a disease process |
A primary lesion is the initial reaction to pathologically altered tissue and may be flat or elevated |
|
|
Secondary lesion |
Skin lesion that evolve from a primary lesion or that is caused by external forces such as infection scratching trauma or the healing process |
|
|
|
Macule |
Flat, pigmented, circumscribed area less than 1 centimeter in diameter |
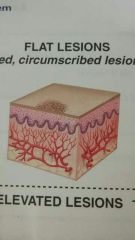
Examples Freckle, flat mole, or rash that occurs in rubella |
|
|
Papule |
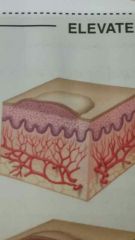
Solid, elevated lesion less than 1 centimeter in diameter that may be the same color as the skin or pigmented |
Examples: Nevus, wart, pimple, ringworm, psoriasis, eczema |
|
|
Nodule |
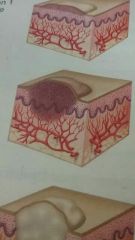
Palpable, circumscribed Legion larger and deeper than a papule (.6 - 2) centimeters in diameter, extends into the dermal area |
Examples: intradermal nevus, benign or malignant tumor |
|
|
Tumor |
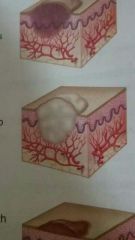
Solid, elevated lesion larger than 2 centimeters in diameter that extends into the dermal and subcutaneous layers |
Examples: lipoma steatoma dermatofibroma hemangioma |
|
|
Wheal |
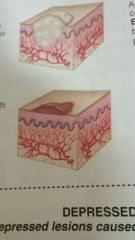
Elevated, firm, rounded lesion with localized skin edema (swelling) that varies in size, shape, and color; paler in the center than its surrounding edges; accompanied by itching |
Examples: hives, insect bites, urticaria |
|
|
Vesicle |
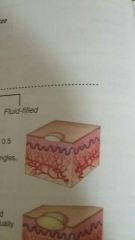
Elevated, circumscribed, fluid filled lesion less than .5 centimeter in diameter |
Examples: poison ivy, shingles, chicken pox |
|
|
Pustule |
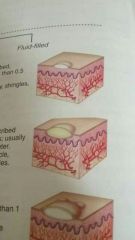
Small, raised, circumscribed lesion that contains pus; usually less than 1 centimeter in diameter |
Examples acne, furunkle, pustular psoriasis, scabies |
|
|
Bulla |
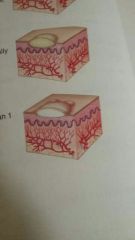
A vesicle or blister larger than 1 centimeter in diameter |
Examples: second-degree burns, severe poison oak, poison ivy |
|
|
Excoriations |
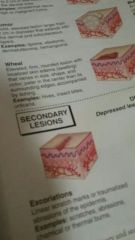
Linear scratch marks or traumatized abrasions of the epidermis |
Scratches, abrasions, chemical or thermal Burns |
|
|
Fissure |

Small slit or crack like sore that extends into the dermal layer could be caused by continuous inflammation and drying |
|
|
|
Ulcer |
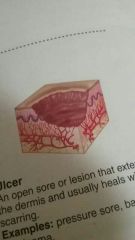
An open sore or lesion that extends to the dermis and usually heals with scarring |
Examples: pressure sore, basal cell carcinoma |
|
|
Tinea |
Fungal infection whose name commonly indicates the body part affected; also called ringworm |
Examples of 10 units include tinea barbae (beard) tinea corporis (body) tinea pedis (athlete's foot) tinea versicolor (skin) and tinea cruris (jock itch) |
|
|
Ulcer |
Lesion of the skin or mucous membrane marked by inflammation necrosis and sloughing of damaged tissues |
Ulcers may be the result of trauma, caustic chemicals intense heat or cold, arterial or Venous stasis, cancers, drugs, and infectious agents |
|
|
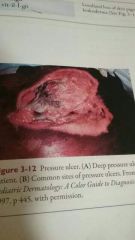
Pressure ulcer |
Skin ulceration caused by prolonged pressure, usually in a person who is bedridden also known as decubitus ulcer or bedsore |
Pressure ulcers are most commonly found in skin overlying a bony projection such as the hip ankle heel shoulder and elbow |
|
|
Urticaria |
Allergic reaction of the skin characterized by eruption of pale red elevated patches that are intensely itchy also called wheals or hives |
|
|
|
Verruca |
Rounded epidermal growth caused by a virus also called wart |
Type of warts include plantar warts, juvenile Wards, and venereal warts. Words may be removed by cryosurgery electrocautery or acids however they may regrow if the virus remains in the skin |
|
|
Vitiligo |
Localized loss of skin pigmentation characterized by milk white patches also called leukoderma |
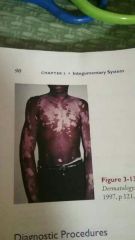
|
|
|
Biopsy (Bx, bx) |
Removal of a small piece of living tissue from an organ or other part of the body for microscopic examination to confirm or establish a diagnosis, estimate prognosis, or follow the course of a disease |
Types of biopsy include aspiration biopsy, needle biopsy, punch biopsy, shave biopsy, and frozen section |
|
|
Skin test |
Method for determining induced sensitivity allergy by applying or inoculating a suspected allergen or sensitizer into the skin in determining sensitivity allergy to the specific antigen by an inflammatory skin reaction to it |
The most commonly used in tests are the intradermal, patch, and scratch test |
|
|
Cryosurgery |
Use of sub-freezing temperature, commonly with liquid nitrogen, to destroy abnormal tissue cells, such as unwanted cancerous or infected tissue |
|
|
|
Debridement |
Treatment that involves removal of foreign material and dead or damaged tissue, especially in a wound, and is used to promote healing and prevent infection |
|
|
|
Excimer laser |
Aims a high-intensity ultraviolet B light dose of a very specific wavelength and a handheld one allows the energy to be delivered precisely to the affected areas without harming healthy skin around them also called exciplex laser |
Because the laser light never touches the surrounding skin it reduces the risk of UV radiation exposure eczema lasers are used to treat mild to moderate psoriasis and require fewer and less vigorous treatments than other light Therapies |
|
|
Fulguration |
Tissue destruction by means of a high-frequency electric current also called electrodesiccation |
This procedure is used to remove tumors and lesions with in and on the body |
|
|
Incision and drainage (I&D) |
Surgical procedure to release pus or pressure built up under the skin such as an abscess and remove its contents |
|
|
|
Mohs surgery |
Procedure in which layers of cancer containing skin are progressively excised and examined until only cancer-free tissue remains |
|
|
|
Skin graft |
Surgical procedure to transplant healthy tissue to an injured site |
|
|
|
Allograft |
Transplantation of healthy tissue from one person to another person also called homograft |
In an allograft the skin donor is usually a cadaver this type of skin graft is temporary and used to protect the patient against infection and fluid loss the allograft is frozen and stored in a skin bank until needed |
|
|
Synthetic |
Transplantation of artificial skin produced from collagen fibers arranged in a lattice pattern |
With a synthetic skin graft the recipient's body does not reject the synthetic skin produced artificially and healing skin grows into it as the graft gradually disintegrates |
|
|
xenograft |
Transplantation (dermis only ) from a foreign donor (usually a pig) and transferred to a human; also called heterograft |
A xenograft is used as a temporary graft to protect the patient against infection and fluid loss |
|
|
Skin resurfacing |
Repair of damaged skin, acne scars, fine or deep wrinkles, or tattoos or Improvement of skin tone irregularities using topical chemicals, abrasion, or laser |
In cosmetic surgery skin resurfacing may involve dermabrasion, chemical peels, cutaneous lasers, and other techniques |
|
|
Chemical peel |
Use of chemicals to remove outer layers of skin to treat acne scarring and general keratoses as well as cosmetic purposes to remove fine wrinkles on the face also called chemabrasion |
|
|
|
Cutaneous laser |
Any of several laser treatments employed for cosmetic and plastic surgery |
Cutaneous laser includes treatment of pigmented lesions, wrinkles, vascular malformations, and other Cosmetic Skin surface irregularities |
|
|
Dermabrasion |
Removal of acne scars, Nevi, tattoos, or fine wrinkles on the skin through the use of sandpaper, wire brushes, or other abrasive materials on the epidermal layer |
|
|
|
Circumscribed |
Limited in Space by something drawn around or confining in area |
|
|
|
Crusting |
Dried serum, puss, or blood on the skin surface. Crests are seen and diseases in which the skin weeps, such as eczema impetigo and seborrhea they are often yellow brown dirty cream colored or honey colored |
|
|
|
Nevus |
1. A congenital discoloration of a circumscribed area of the skin due to pigmentation also known as birthmark or mole. 2. A circumscribed vascular tumor of the skin, usually congenital, due to hyperplasia of the blood vessels, angioma |
|
|
|
Trauma |
A physical injury or wound caused by external force or violence |
|
|
|
Vermilion border |
The vermilion border (sometimes spelled vermillion border) is the normally sharp demarcation between the lip and the adjacent normal skin. It is thus the edge (border) of the red (vermilion) of the lip. It represents the change in the epidermis from highly keratinized external skin to less keratinized internal skin. |
|
|
|
Bartholin gland |
One of two small compound mucous glands located one in each lateral wall of the vestibule of the vagina near the vaginal opening at the base of the labia majora |
|
|
|
Diabetes mellitus |
A chronic metabolic disorder marked by hyperglycemia |
|
|
|
diaAphoresis |
Profuse sweating |
|
|
|
Erythematous |
Redness of the skin |
|
|
|
Erythematous |
Redness of the skin |
|
|
|
Erythematous |
Redness of the skin |
|
|
|
Enteritis |
Inflammation of the intestines |
|
|
|
Macules |
Flat spots on the skin who's Color Me Be lighter or darker than the surrounding skin some common examples are freckles and vitiligo |
|
|
|
Sclerosed |
Hardened |
|
|
|
Syncope |
Transient and usually sudden loss of consciousness accompanied by inability to maintain an upright position fainting |
|
|
|
Syncope |
Transient and usually sudden loss of consciousness accompanied by inability to maintain an upright position fainting |
|
|
|
Vulgaris |
Ordinary, common |
|

