![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Integumentary System
|
Body system composed of the skin and its accessory organs.
|
|
|
Epidermis
|
Outer portion of the skin formed of epithelial tissue that rests on or covers the dermis.
|
|
|
Dermis
|
Dense, irregular connective tissue that forms the deep layer of the skin.
|
|
|
Hypodermis
|
Loose areolar connective tissue found deep to the dermis that connects the skin to muscle or bone.
|
|
|
Subcutaneous Tissue
|
Tissue under the dermis; same tissue as the hypodermis.
|
|
|
Hair Shaft w/ Accessory Organs - Diagram
|
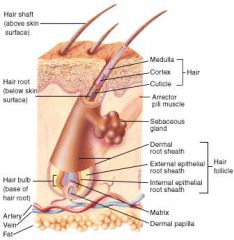
|
|
|
Skin & tissues
|
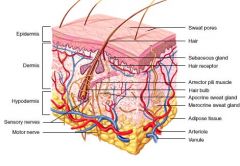
|
|
|
Skin - Function
|
Provides a barrier against microorganisms, water, solar radiation, and others. Upon exposure to UV radiation, the skin synthesizes an inactive form of vitamin D. The skin is the most extensive sense organ and is important in thermoregulation.
|
|
|
Hair - Description
|
A slender filament of mostly dead keratinized epithelial cells that grow from a follicle.
|
|
|
Hair - Structure
|
-Medulla - a core of loose cells and air spaces, surrounded by:
-Cortex - densely packed keratinized cells covered by the cuticle -Bulb - a swelling at the base where the hair originates -Root - the remainder of the hair within the follicle -Shaft - the portion of the hair above the skin surface |
|
|
Hair follicle
|
Has two principal layers: the connective tissue root sheath derived from the dermis and the epithelial root sheath, which is an extension of the epidermis and has an internal and external layer.
|
|
|
Arrector Pili Muscle
|
That which raises hair; Smooth muscle attached to the hair follicle and dermis that raises the hair when it contracts. Responds to cold, fear, and other stimuli.
|
|
|
Arrector Pili Muscles - Function
|
This response may serve as a mechanism for either thermoregulation or protection in other mammals; however, in humans it is believed to serve no useful purpose.
|
|
|
Hair shaft w/ Accessories - Diagram
|
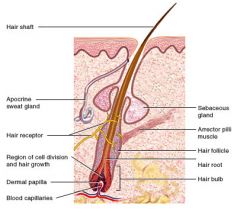
|
|
|
Sweat Glands - Diagram
|

|
|
|
Sudoriferous
|
sudoriferous gland: a sweat gland.
|
|
|
2 Types of Sweat Glands
|
1. Merocrine sweat glands
2. Apocrine sweat glands |
|
|
Exocrine Gland
|
Gland that secretes to a surface or outward through a duct.
|
|
|
Merocrine Sweat Gland
|
-Gland that secretes products with no loss of cellular material
-Most common sweat gland -Most numerous in palms of hands and soles of feet -Open directly to the surface of the skin -Found evenly distributed throughout the body's surfaces |
|
|
Apocrine Sweat Gland
|
-Sweat glands that produce organic secretions
-Most numerous in the axillae and the genitalia and around the anus -Ducts lead into nearby hair follicles -Become active at puberty, triggered by sex hormones -Ex. Mammary glands are considered modified apocrine sweat glands |
|
|
Sebaceous Glands - Diagram
|
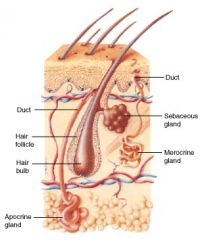
|
|
|
Sebaceous Gland
|
Gland of the skin, located in the dermis. Usually associated with a hair follicle, that produces sebum; Also exocrine gland.
|
|
|
Sebum
|
An oily, white substance rich in lipids. Prevents the skin from drying and provides protection against some bacteria.
|

