![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A 31-year-old patient was hospitalized 3h after ingestion of an unknown quantity of phenobarbital. The drug concentration in the plasma was found to be 6 mg/L after admission. Assume that in this patient pharmacokinetic parameters for phenobarbital are as follows: oral bioavailability, 100%, V= 80L, CL = 38L/day; half-life = 2 days. Which of the following dose of phenobarbital patient ingested? (Mukherjee)
600 mg 228 mg 480 mg 160 mg 240 mg |
480 mg
|
|
|
A 26-year old electrician has a “Nervous Disposition.” He easily startled, worries about inconsequential matters. Diazepam is prescribed. Diazepam are thought to cause sedative and/or anxiolytic effects by (Mukherjee)
Enhancing the actions of dopamine Acting as a partial agonist at 5-HT receptors Increasing functional activity at GABA receptors Facilitating GABA mediated increases in chloride ion conductance Blocking the NMDA glutamate receptor subtype |
Facilitating GABA mediated increases in chloride ion conductance
|
|
|
n the management of toxicity caused by ingestion of methanol in wood spirits. Which one of the following statements is MOST accurate? (Mukherjee)
Hemodialysis will not remove methanol from blood Naltrexone is a suitable antidote is poisoning due to methanol Treatment should involve the administration of disulfiram in the ER Ethanol will prevent formation of formaldehyde in methanol poisoning Delirium treatments is characteristics of methanol poisoning |
Ethanol will prevent formation of formaldehyde in methanol poisoning
|
|
|
A 25-yaer old young woman suffer from a seizure disorder characterized by tonic rigidity of the extremities followed in 20-30s of tremor progressing of massive jerking of the whole body. This clonic phase last for 1 to 2 mins, leaving the patient in a stuporous state. Which of the following drugs is MOST suitable for her long-term management? (Mukherjee)
Clonazepam Tiagabine Ethosuximide Lamotrigine Felbamate |
Lamotrigine
|
|
|
A 30-year old male patient is on drug therapy for a psychiatric problems for 4 years. He has been recently diagnosed having “long QT syndrome.” Which one of the following drugs used in the management of CNS dysfunction is MOST likely to cause problems in this patient? (Mukherjee)
Alprazolam Ethosuximide Buspirone Lithium Ziprasidone |
Ziprasidone
|
|
|
A 41-year old school teacher is taking haloperidol for a psychotic disorder. Which of the following adverse effects is Likely to occur in this patient? (Mukherjee)
Weight loss Increase seizure threshold Orthostatic hypotension Agranulocytosis Prolong QT interval |
Orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
A 25 year old woman is brought to the ER by her classmate. She shows following symptoms attributed to a drug over dose. Increase heart rate and blood pressure, Mydriasis, behavioral excitation, aggressiveness, paranoia, and hallucination. Which one of the following drugs is MOST likely to be responsible for these symptoms? (Mukherjee)
Ethanol Marizuana Amphetamine Fentanyl Codeine |
Amphetamine
|
|
|
A 21 year old man is suffering from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). He has prior history of drug dependence that includes the illicit use of secobarbital and alcohol. The physician also prescribes a drug that can be helpful in GAD and that has the advantage of no abuse liability. The drug prescribed was MOST likely to have been (Mukherjee)
Phenobarbital Diazepam Lorazepam Buspirone Oxazepam |
Buspirone
|
|
|
A college student is brought to the emergency department by friends. The physician is informed that the student had taken a drug and then went “crazy.” The patient is continuously laughing, increased heart rate and reddening of conjunctiva. Which of the following drugs MOST likely to be involved is (Mukherjee)
Cocaine MDMA, “ecstasy” Marijuana Heroin Phencyclidine |
Marijuana***
|
|
|
Which of the following drug in overdose is known to cause the potentially fatal “serotonin syndrome?” (Mukherjee)
LSD Nicotine MDMA “ecstasy" Coacaine Phencyclidine |
MDMA “ecstasy”***
|
|
|
The intense craving experienced by those who are trying to recover from chronic alcohol abuse can be ameliorated by which of the following drugs? (Mukherjee)
Disulfiram Fomepizole Naltrexone Thiamine Haloperidol |
Naltrexone***
|
|
|
A 6 year old child is having learning difficulties at school. Electroencephlogram studies reveal brief 3-HZ spike and wave discharges appearing synchronously in all leads every 5 to 10 min. Which drug would be MOST effective in this child without the disadvantages of excessive sedation or tolerance development? (Mukherjee)
Diazepam Phenobarbital Valproic Acid Clonazepam Ethosuximide |
Ethosuximide***
|
|
|
A 32 year old pregnant woman with alcoholism presented to ER in early stages of labor. She consumes large amounts of alcohol beverage throughout her pregnancy. This patient’s infant is at risk of a syndrome that includes (Mukherjee)
Underdevelopment of the lungs Limn malformation Mental retardation and craniofacial abnormalities Spina bifida Fetal hydration syndrome |
Mental retardation and craniofacial abnormalities***
|
|
|
Which of the statements concerning the adverse effects of antipsychotic drugs is accurate? (Mukherjee)
Clozapine causes a small but important incidence of agranulocytosis Renal pigmentation is a dose-dependent toxic effects of clozapine Blurring of vision and urinary retention are common adverse effects of haloperidol Failure to ejaculate is not common adverse effects of pehnothiazines Aripiprazole can cause hyperglycemia, hyperprolactimia or weight gain |
Clozapine causes a small but important incidence of agranulocytosis***
|
|
|
An antipsychotic drug that is quite sedating and associated with significant weight gain, hyperlipidemia, and increased risk of Type II diabetes is (Mukherjee)
Haloperidol Aripiprazole Chlorpromazine Risperidone Clozapine |
Clozapine***
|
|
|
MAO inhibitors
Blocks reuptake of serotonin Blocks reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin Degrades transmitters Allows transmitters to work for a long time Increases depression |
Allows transmitters to work for a long time***
|
|
|
Lithium salts are used prophylactically in treating
Fear and anxiety Aggression Compulsive disorder Excitement induced urination Manic depression |
Manic depression***
|
|
|
The following statements concerning antidepressants are true EXCEPT
Patients taking antidepressants exhibit mental and physical dependence Antidepressants drugs are extremely dangerous especially with the tricyclics Antidepressants cause weight gain Antidepressants potentiate effects of alcohols and sedatives Majority of antidepressants drugs are known to have a short half-life and can be given frequently to calm the patient |
Majority of antidepressants drugs are known to have a short half-life and can be given frequently to calm the patient***
|
|
|
A 2 year old girl has a history of near-drowning, having been submerged in a semi-frozen lake for 20 minutes. As a result of this experience, there are bilateral infarcts in the hippocampal complex. Which of the following behavioral disorders is this patient most likely to display?
Aphasia Social crudeness A loss of long-term memory A loss of immediate and short-term memory Hypersexuality |
A loss of immediate and short-term memory***
|
|
|
The type of receptor that is critical for the induction of hippocampal LTP, by virtue of its admitting calcium into a dendritic spine, is called:
An AMPA receptor An NMDA receptor A glycine receptor A cholinergic GPCR A noradrenergic GPCR |
An NMDA receptor***
|
|
|
Weak stimulation of a pathway in the hippocampus will not by itself trigger long-term potentiation. However, if one pathway is weakly activated at the same time that a neighboring pathway onto the same cell is strongly activated, both synaptic pathways undergo long-term potentiation. This phenomenon is termed
Input specificity State dependent potentiation Associativity Retrograde signaling Habituation |
Associativity***
|
|
|
Epileptic seizures can be caused by a variety of acquired or congenital factors, including all of the following EXCEPT:
Cortical damage from trauma Cutting the corpus callosum Stroke Tumors Congenital cortical dysgenesis (failure of the cortex to grow properly) |
Cutting the corpus callosum***
|
|
|
A 12 year old boy has a seizure in which he experiences loss of consciousness and contraction of all of his muscles. A minute later he fails and begins to jerk, during which his extremities are flexed. His classmates were worried and stood around him as he continued to twitch for about 2 minutes. Soon the twitching subsided and he became immobile, and did not respond to calling of his name or shaking to try to awaken him. As one of his classmates ran for help, the boy began to respond but seemed extremely confused and tired. The classification of this type of seizure is
Absence seizure Complex partial Petit mal Simple partial Generalized tonic-clonic |
Generalized tonic-clonic***
|
|
|
Language and speech require the participation of both Wernicke’s area and Broca’s area. These two regions of the brain communicate with each other via a fiber bundle called:
The thalamocortical tract The arcuate fasciculus The perforant path The fornix Middle forebrain bundle |
The arcuate fasciculus***
|
|
|
The MRI of a 57 year old, right-handed woman reveals a lesion in the lateral aspect of the left hemisphere involving the inferior frontal gyrus, lateral portions of the pre-and postcentral gyri, the inferior parietal lobule, and portions of the adjacent superior temporal gyrus. Which of the following is the MOST prominent deficit in this patient?
Blindness in the left eye Aphonia Paralysis of all eye movement Language comprehension and use Right-sided paralysis of the lower extremity |
Language comprehension and use***
|
|
|
A 72 year old retired butcher suffered a stroke affecting his left posterior temporal lobe. A sample of his speech is as follows: “Boy, I’m sweating, I’m awful nervous, you know, once in awhile I get caught up, I can’t mention the tarripoi, a month ago, quite a litte, I’ve done a lot well, I impose a lot, while, on the other hand, you know what I mean, I have to run around, look it over, trebbin and all that sort of stuff.”
Split-brain Broca’s aphasia Wernicke’s aphasia Aprosodia Conduction aphasia |
Wernicke’s aphasia***
|
|
|
A blindfolded Meharry medical student is asked to identify a common object presented to her left hand. She is not allowed to touch the object with her right hand. Which of the following structures must be intact for her to complete this task?
The primary somatic sensory cortex on the left side of her brain The primary visual cortex on the right side of her brain The corpus callosum The fonix The hippocampus |
The corpus callosum***
|
|
|
Computerized Tomography (CT):
Is a superior imaging modality than magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in every way except visualizing calcification Does not utilize radiation to generate images Cannot distinctly visualize gray and white matter in the presence or absence of surrounding bony structures Is not a useful tool to visualize structural shift in brain tissue or CSF volume change Cannot acquire a whole 3-D volume of brain images |
Cannot distinctly visualize gray and white matter in the presence or absence of surrounding bony structures***
|
|
|
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
Relies upon radio-frequencies to derive anatomical images Was developed the same year as CT Does not acquire image volumes in three dimensions Utilizes the same dipole relaxation rates for fat, protein, CSF and water Is the safest imaging modality for women of child-bearing age |
Relies upon radio-frequencies to derive anatomical images***
|
|
|
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS):
Requires CT scans to define anatomic areas of interest Is most useful in the diagnosis of dementia and mental status changes Can be utilized to quantify brain metabolite concentrations Alone can generate anatomic images of psychiatric brain abnormalities Cannot define metabolism changes that occur with clinical pathology |
Can be utilized to quantify brain metabolite concentrations***
|
|
|
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT):
Cannot measure cerebral blood flow Needs magnetic resonance imaging to define brain anatomy Utilizes a single photon that is detected simultaneous in two directions Deploys the same radiation theory and procedure as Computerized Tomography to derive brain images Utilizes MRI to detect radiation |
Needs magnetic resonance imaging to define brain anatomy***
|
|
|
Positron Emission Tomography (PET):
Cannot be utilized for brain receptor studies targeting specific neurotransmitters Is a non-invasive imaging procedure Is less expensive than Computerized Tomography imaging Has less image resolution than Single Photon Emission Computerized Tomography Utilizes a photon detecting device that does not generate anatomic images |
Utilizes a photon detecting device that does not generate anatomic images***
|
|
|
Significant bone density is a major disadvantage of:
Computerized tomography Magnetic Resonance Imaging Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Single photon emission computed tomography Positron Emission Tomography |
Computerized tomography***
|
|
|
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
Uses T2 sequences to define tumor location Uses T1 sequence that are no better than CT to localize anatomy in the occipital area of the brain Uses T1 sequences for anatomical resolution that are much better than CT Uses T1 sequences that are better than T2 to localize white matter and gray matter difference Uses T2 sequences that are no better than Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy to localize anatomy in the occipital area of the brain |
Uses T2 sequences to define tumor location***
|
|
|
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI):
Generates its images from changes in hemoglobin concentrations Generates its images from changese in cerebral blood flow rates Generates its images from X-rays Generates its images from radioactive tracers Generates its images from changes in neurotransmitter receptor densities |
Generates its images from changes in hemoglobin concentrations***
|
|
|
Missing stem
It is sufficient to demonstrate catatonic behavior to be diagnosed with schizophrenia Males are disproportionally affected with schizophrenia Substance abuse is rare among female patients with schizophrenia A particular disturbance, which should last at least six months Both mono and dizygotic twins have about 10% of concordance rate for schizophrenia |
A particular disturbance, which should last at least six months
|
|
|
A 68 year old man comes to the office with complaints of memory loss. He says he forgets where puts items, names of familiar people and what he is about to do. He continues with his duties as treasurer of his civic club. His wife says he seems normal to her. His examination is normal except for a MMSE score of 29 out of a possible 30; he missed one of three words to remember after 3 minutes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Age associated memory change Mild cognitive impairment Dementia of the Alzheimer type Lewy body disease |
Age associated memory change***
|
|
|
A 68 year old man is brought to the office by his family because of memory loss. Patient insists he is normal. Family relates instances of short term memory loss, disorientation, difficulty with house hold chores, and inability to correctly handle financial matters. His examination is normal except for a MMSE score of 21 out of a possible 30. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Age associated memory change Mild cognitive impairment Dementia of the Alzheimer type Lewy body disease |
Dementia of the Alzheimer type***
|
|
|
A 68 year old man comes to the office with complaints of memory loss. He says he forgets where he puts items, names of familiar people and what he is about to do. He continues with his duties as treasurer of his civic club. However, he must make lists of tasks to do or else he will forget them. Wife says he has bad memory but normal otherwise. His examination is normal except for a MMSE score of 27 out of a possible 30; he could not remember any of the 3 words after three minutes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Age associated memory change Mild cognitive impairment Dementia of the Alzheimer type Lewy body disease |
Mild cognitive impairment***
|
|
|
A 67 year old man comes to your office with his wife. Both report that he has had mental changes. He has reported seeing little people in the house. They are not threatening but follow him around. He wanders in the neighborhood and has gotten lost on a few occasions. On several occasions he has fallen for no known reason. On exam he has an expressionless face. There is a resting tremor and the motor tone is increased in a cog wheel type rigidity. On the Mini Mental State Examination he missed 2 of the 3 words to remember after 3 minutes, and he had difficulty copying the drawing of intersecting pentagons. Which of the following diagnoses are more likely?
Normal pressure hydrocephalus Lewy body disease Multi-infarct dementia Parkinson’s disease dementia A and B B and D |
B and D
|
|
|
Cholinesterase inhibitors are indicated in various disorders of memory disturbance. Which of the following should not be expected from their use?
Temporary stabilization of global function and cognition in a demented patient Inhibit the transition from mild cognitive impairment to dementia Reduce time burden on care giver for a Alzheimer’s disease patient Delay nursing home placement for a Alzheimer’s disease patient |
Inhibit the transition from mild cognitive impairment to dementia
|
|
|
When evaluating a patient with probably Alzheimer’s disease you plan a series of tests to answer what question(s)
Are there amyloid plaques in the brain How severe is the Alzheimer’s disease Is there another possible cause of patient’s symptoms Does the patient have Parkinson’s disease |
Is there another possible cause of patient’s symptoms
|
|
|
Characteristics of normal pressure hydrocephalus that help in distinguishing it from Alzheimer’s disease are all of the one below except
Difficulty initiating walking (apraxia of gait) Urinary and fecal incontinence Normal appearance and ability to carry on a superficial conversation Decrease spontaneous activity and reduced level of interest |
Normal appearance and ability to carry on a superficial conversation
|
|
|
Causes of dementia are:
Multiple strokes Normal pressure hydrocephalus Creutzfeld-Jakob (prion) disease Lewy body disease A, C, and D All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
A 60 year old male with history of transient episode of right hand tingling presents with no blink to threat on the right. Soft tissue window from an axial non-contrast head CT is shown. Which of the following is the diagnosis? (Disher)
Right MCA territory infarction Left temporal lobe acute hemorrhage Right temporal lobe acute hemorrhage Subdural hygroma Left MCA territory infarction |
Left MCA territory infarction
|
|
|
The following nerves are sensory to the dura mater: (Jackson)
Oculomotor nerve Trochlear nerve Sixth cervical spinal nerve Trigeminal nerve Abducens nerve |
Trigeminal nerve
|
|
|
The following statements concern the blood-brain barrier EXCEPT: (Jackson)
It protects the brain from toxic compounds of low molecular weight It is present in the pineal gland The endothelial cells of the blood capillaries are nonfenestrated The endothelial cells of the blood capillaries are held together by localized tight junctions L-dopa has difficulty passing through the barrier in the treatment of Parkinson disease |
The endothelial cells of the blood capillaries are nonfenestrated
|
|
|
A 21 year old male baseball player is brought to the emergency department after feeling severe dizziness. During physical examination the patient demonstrates lack of equilibrium and memory impairment. A 3-cm would is noted in his scalp from an injury suffered in a game several weeks earlier. A lumbar puncture does not reveals blood in the cerebrospinal fluid. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? (Jackson)
The middle meningeal artery was torn, resulting in epidural hematoma There is a fracture in the pterion with injury to the adjancent vasculature The injury resulted in the bursting of a pre-existing aneurysm of the anterior communicating artery of the cerebral circle A cerebral vein is torn The cavernous sinus has a thrombus |
A cerebral vein is torn
|
|
|
Over a period of three months a 57 year old woman has suffered from progressively severe headaches, difficulty using right hand and difficulty walking. When examined in the clinic she was awake and oriented. She had difficulty saying what she wanted to say and to follow complex commands. The lower part of the right side of face was weak. She had moderate weakness of the right upper extremity. Right leg was weak but she could walk. The Babinski sign was present on the right side. Where is the problem (Singh)
Right side of pons Left internal capsule Left cerebral hemisphere Right temporal lobe |
Left cerebral hemisphere
|
|
|
Over a period of three months a 57 year old woman has suffered from progressively severe headaches, difficulty using right hand and difficulty walking. When examined in the clinic she was awake and oriented. She had difficulty saying what she wanted to say and to follow complex commands. The lower part of the right side of the face was weak. She had moderate weakness of the right upper extremity. Right leg was weak but she could walk. The Babinski sign was present on the right side (Singh)
Stroke Brain tumor Gunshot wound Multiple sclerosis |
Brain tumor
|
|
|
Basic science and clinical studies have led to an understanding of the basic defect underlying the Lambert-Eaton syndrome. Which of the following best characterizes this defect? (Chirwa)
The production of excess quantities of acetylcholine The production of antibodies that act against nicotinic Ach receptors A reduction in brain catecholamines Reduction in presynaptic Ca++ channels Viral encephalitis |
Reduction in presynaptic Ca++ channels
|
|
|
While reviewing the lecture note from Dr. Chirwa, a group of freshmen found that there are several agents that act pre-synaptically and inhibit cholinergic functions. Which of the following agents inhibits cholinergic activity by blocking the storage of Ach into its vesicles? (Maleque)
Alpha-bungarotoxin Botulinum toxin Vesamicol Hexamethonium |
Vesamicol
|
|
|
Which of the following drugs is an antagonist at nicotinic (N1) receptors? (Maleque)
Atropine Dopamine Succinylcholine Trimethaphan Acetylcholine |
Trimethaphan
|
|
|
Visual field loss in the nasal visual field of each eye most likely reflects pathology where>
The optic chiasm The temporal lobes The occipital lobe Both eyes |
Both eyes
|
|
|
Local anesthetic agents act primarily:
At a cortical level to decrease the patient’s awareness of pain impulses At the neuromuscular junction to decrease frequency of pain impulses reaching the CNS On the axon membrane to prevent depolarizing potentials At ganglion sites to decrease central pain input On the muscle membrane to decreasing blood flow |
On the axon membrane to prevent depolarizing potentials
|
|
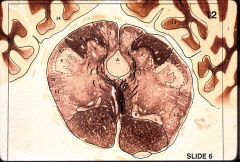
Axons of neurons in the nucleus indicated by label 5 terminate in the: (Mokha)
Ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) Medial dorsal nucleus Ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) |
Ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM)
|
|
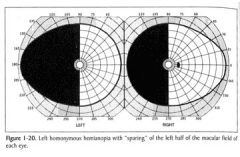
Visual field losses depicted above can be produced by a tumor in the vicinity of the:
Optic radiations in the right temporal lobe Optic radiations in the left temporal lobe Tip of the Right occipital lobe Optic radiations in the left parietal lobe Left optic tract Right optic tract Optic chiasm |
Tip of the Right occipital lobe
|
|
|
Lesion of the left ventral posterolateralis (VPL) nucleus of the thalamus will initially produce pain and temperature loss in the:
Right hand Left hand Left leg Left side of the face Right side of the face |
Right hand
|
|
|
Which one of the following clinical conditions will produce a visual field deficit that does not obey horizontal and vertical meridians:
Aneurysm of the internal carotid artery Pituitary tumor compressing the optic chiasm Stroke of the posterior cerebral artery Retinitis pigmentosa Tumor in the white matter of the left temporal lobe |
Retinitis pigmentosa
|
|
|
Stroke involving the left middle cerebral artery will produce loss or impaired perception of mechanosensory (touch) information in all of the following EXCEPT:
Right hand Right side of the face Right foot Right shoulder Right side of the chest |
Right foot
|
|
|
Neurological examination of a hypertensive patient revealed impaired (reduced) perception of pain and temperature on the right side of the body with the exception of the facial region. In the facial region, pain and temperature sensations were reduced on the left side. Proprioception and touch sensations were not impaired in the right upper and lower extremities or the left facial region. The symptoms of this can be explained by damage to the:
Left dorsolateral sector of the midbrain Left dorsomedial sector of the medulla Right dorsolateral sector of the midbrain Left dorsolateral sector of the medulla Left VPL and VPM Right dorsal columns in the cervical region Left posterior limb of the internal capsule |
Left dorsolateral sector of the medulla
|
|
|
Neurological examination of a hypertensive patient revealed impaired (reduced) perception of pain and temperature on the right side of the body with the exception of the facial region. In the facial region, pain and temperature sensations were reduced on the left side. Proprioception and touch sensations were not impaired in the right upper and lower extremities or the left facial region. Symptoms can be explained by a stroke involving the:
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery Anterior inferior cerebellar artery Middle cerebral artery Posterior spinal artery Anterior cerebral artery Posterior cerebral artery Paramedian branches of the basilar artery |
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
|
|
|
Neurological examination revealed that the left eye did not adduct (move towards the nose) during an ipsilaterally (to the right) directed nystagmus elicited by flooding the right external auditory meatus with warm water. It can be explained by damage to the:
Left abducens nucleus Left medial longitudinal fasciculus Right medial longitudinal fasciculus Right oculomotor nucleus Left inferior colliculus |
Left medial longitudinal fasciculus
|
|
|
A 35 year old woman has recently started a regiment of antipsychotic therapy with a typical neuroleptic drug. A side effect of her medication is that she begins to lactate. This side effect is due to the fact that neuroleptic drugs block receptors in the pituitary gland for which of the following substances?
Epinephrine Dopamine Glycine Norepinephrine Serotonin |
Dopamine
|
|
|
A 75 year old woman with dementia showed a loss of neurons from the septal nuclei in the basal forebrain region of the cerebrum. Some cognitive improvement occurred when she was treated with a drug to enhance the function of these neurons. This drug most likely enhanced signaling in the brain from which of the following types of neuron?
Adrenergic Cholinergic Dopaminergic Glutaminergic Serotonergic Orexin/Hypocretin |
Cholinergic
|
|
|
Histamine cells projecting to the cerebellar cortex originate in which of the following?
Hypothalamus Pontine nuclei Olivary nucleus Reticular nucleus Raphe nuclei Locus coeruleus |
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
There are two areas exhibiting petechial hemorrhaging in the accompanying figure. The ventral area receives a major input from _________. (Clark)
Amygdala via the stria terminalis Midbrain via the medial forebrain bundle Ventral tegmental area via mesocortical projection Arcuate nucleus via tuberoinfundibular tract Hippocampus via fornix |
Hippocampus via fornix
|
|
|
An 80 year old woman complains that over the past 6 months she has been bothered by frequent urination and the need to drink a lot of water. She states “I think I must be going crazy. I have to get up so often during the night that I hardly get any sleep.” Blood glucose levels in this patient are within normal limits. However, MRI reveals a small lesion in her hypothalamus. Which hypothalamic nucleus is most likely involved?
Arcuate Suprachiasmatic Supraoptic Ventromedial Medial mammillary |
Supraoptic
|
|
|
A 54 year old man presents with a long-standing history of episodic fear and panic attacks. Sometimes during these panic attacks, the patient has displayed inappropriate and antisocial behaviors. Through electroencephalographic studies, it is shown that there is episodic seizure activity occurring in a particular part of the brain. Assuming that the patient’s history of aberrant behavior may have resulted from this part of the brain. Assuming that the patient’s history of aberrant behaviors may have resulted from this abnormal increase neuronal activity, which is the most likely site for the origin of the seizure activity?
Nucleus accumbens Amygdala Septal nuclei Hippocampus Cingulate gyrus Hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus |
Amygdala
|
|
|
A 32-year old woman is brought to the emergency department from site of an automobile crash. The initial exam reveals extensive facial and scalp lacerations. The patient is in a stupor. Suspecting brain injury, the physician orders a CT. The CT reveals fractures in the facial skeleton and bilateral damage to the rostral 3-4 cm of the temporal lobes. The lacerations are repaired, and the patient is hospitalized and medicated to control brain swelling. The behavioral aberrations in this patient, when correlated with the CT finding of bitemporal contusions, suggests that this woman most likely has which of the following?
Wernicke aphasia Wallenberg syndrome Korsakoff syndrome Kluver-Bucy syndrome Pick disease |
Kluver-Bucy syndrome
|
|
|
A patient comes to see you complaining of increased seizures. He was diagnosed with a seizure disorder 20 years earlier and has noticed an increased frequency of late. His seizures typically last less than 4 minutes and usually consist of strong feelings of déjà vu. Which of the following brain areas has the lowest seizure threshold?
Hypothalamus Pontomesencephalic reticular formation Amygdala Orbitofrontal gyrus Anterior calcarine cortex Anterior thalamic nucleus |
Amygdala
|
|
|
In a normal person, while changing from a standing position to lying down with feet elevated, firing rates of vagal neurons originating in the aortic arch, sacral parasympathetic neurons, lumbar sympathetic neurons are respectively:
High, high, high High, high, low High, low, high High, low, low Low, low, low Low, low, high Low, high, low Low, high, high |
High, high, low
|
|
|
Pyridoxine deficiency associated with isoniazid can result in seizures due to
Glutamate neurotoxicity GABA deficiency Cholinergic deficiency Serotonin syndrome Dopamine deficiency |
GABA Deficiency
|
|
|
Areas where the blood-brain barrier is compromised include which of the following?
Anterior thalamic nucleus Hypothalamic Paraventricular nucleus Pineal gland Frontal cortex Intermediolateral column of spinal cord |
Pineal gland
|
|
|
Lesions of the cerebellum cause dysarthria. On the neurological examination, dysarthria is characterized by
Errors in direction and force of movement, i.e. pastpointing Unsteady gait Intentional tremor Slow and slurred speech Inability to maintain an upright posture |
Slow and slurred speech
|
|
|
The receptive field in the auditory system is a plot of the:
Intensity versus the spatial localization of sound Threshold intensity versus the frequency of sound Frequency versus the spatial localization of sound |
Frequency versus the spatial localization of sound
|
|
|
Stimulation of all of the following reduces pain EXCEPT:
Periacqeuductal gray (PAG) Nucleus raphe magnus Nucleus locus coeruleus Primary afferent fibers Parabrachial nucleus Ventral posterior lateral nucleus (VPL) |
Ventral posterior lateral nucleus (VPL)
|
|
|
All of the following are essential for the referral of visceral pain to a skin dermatome EXCEPT:
Pain fibers (C ) from the skin have localized termination in the dorsal horn Pain fibers (C ) from the viscera have diffuse terminations in the dorsal horn Pain fibers from the viscera and skin converge on to the same Spinothalamic tract neurons Visceral pain fibers inhibit whereas skin pain fibers excite the same Spinothalamic tract neurons Pain fibers from the visceral organ and skin area (region of referral) enter the dorsal horn through the same dorsal root |
Visceral pain fibers inhibit whereas skin pain fibers excite the same Spinothalamic tract neurons
|
|
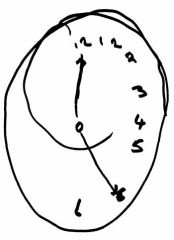
A patient is brought into the emergency department after a fall in which she lost consciousness. While there is not obvious damage on the CT scan, the nurse indicates that the patient is complaining that there is someone else’s leg and arm in her bed. When she has applied make-up, she has only applied it to the right side of her face. During the neurological examination, she is asked to draw a clock face and her picture is shown. Her vision, speech and reflexes appear normal. She is cooperative throughout the exam. The most likely site for damage that would explain these symptoms is: (DeRiemer)
Temporal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Frontal lobe Thalamus Cerebellum Brainstem Spinal cord |
Parietal lobe
|
|
|
A 7-year old girl developed nausea and vomiting. Diagnostic studies revealed a mass arising from the floor of the fourth ventricle, extending out the foramina of Luschka into the cerebellopontine angles. The best diagnosis is: (Breaux)
Astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Ependymoma Neuroblastoma |
Ependymoma
|
|
|
patient presents with a right hemiparesis, involving the right side of face and right arm and leg. Examination did not disclose aphasia, visual disturbance, cranial nerve disorder or sensory abnormality. There was a Babinski sign on the right. On what side of the nervous system is the lesion?
Right Left Bilateral Unable to determine based on information given |
Left
|
|
|
A patient presents with a right hemiparesis, involving the right side of face and right arm and leg. Examination did not disclose aphasia, visual disturbance, cranial nerve disorder or sensory abnormality. There was a Babinski sign on the right. On what side of the nervous system is the lesion?
Right Left Bilateral Unable to determine based on information given |
Left***
|
|
|
A patient presents with a right hemiparesis, involving the right side of face and right arm and leg. Examination did not disclose aphasia, visual disturbance, cranial nerve disorder or sensory abnormality. There was a Babinski sign on the right. At what level of the nervous system is the lesion?
Cerebral hemisphere Internal capsule Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata |
Cerebral hemisphere***
|
|
|
A patient presents with a left hemiparesis, involving the left side of face and left arm and leg. Examination also disclosed the right eye lid was shut, the eye was downward and laterally deviated, and the left pupil was dilated and fixed. There was a Babinski sign on the left. On what side of the nervous system is the lesion?
Right Left Front Back Middle |
Right***
|
|
|
Cranial nerve nucleus whose fibers emerge just lateral to the bulge of the olive and whose vascular lesion would most likely ALSO be associated with a hemianesthesia (loss of pain and temperature from the RIGHT face and LEFT body)?
RIGHT nucleus ambiguus LEFT dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus RIGHT hypoglossal nucleus LEFT facial nucleus LEFT nucleus ambiguus RIGHT motor nucleus of CN-V LEFT hypoglossal nucleus RIGHT abducens nucleus |
RIGHT nucleus ambiguus***
|
|
|
Cranial nerve nucleus most likely to receive efferent reflex axons from the caudal nucleus solitaries?
RIGHT nucleus ambiguus LEFT dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus RIGHT hypoglossal nucleus LEFT facial nucleus LEFT nucleus ambiguus RIGHT motor nucleus of CN-V LEFT hypoglossal nucleus RIGHT abducens nucleus |
LEFT dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus***
|
|
|
The classic syndrome of decreased pupillary size, upper eyelid drooping and decreased ipsilateral sweating can be caused by lesion in all of the following sites EXCEPT:
Lateral brainstem Lateral spinal cord Sympathetic chain Carotid plexus dissection Oculomotor nucleus lesion |
Oculomotor nucleus lesion***
|
|
|
Which of the following is TRUE regarding children with a diagnosis of Autism?
The vast majority of them will have an Axis II diagnosis of mental retardation Their auditory processing skills may be abnormal Their receptive and functional communication skills will be subnormal They will need special education consistent with Public Law 94-992 All of the above A, B, and C, only A and B, only |
A, B, and C, only***
|
|
|
Children with developmental learning disabilities:
Are often mentally retarded, also Have normal general/globial intelligence Often “grow out” of their disabilities Must receive psychological testing from a physician before a diagnosis is made All of the above |
Have normal general/globial intelligence***
|
|
|
Males are more likely to exhibit which of the following disorders:
Prader-Willi syndrome, mental retardation and autism Learning disabilities, Klinefelter’s syndrome, conduct disorder Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Gender Identity Disorder Fragile X syndrome, Rett’s Disorder, Maple Syrup Urine Disorder All of the above A, B, and C, only None of the above |
A, B, and C, only***
|
|
|
The case of the brain injury of U.S. congresswoman Gabrielle Giffords gives students of Integrated Neuroscience an up-close and ongoing opportunity for synthesizing their knowledge of the subject, since her medical progress has largely been reported in the public domain. Hence, we may make the following statements regarding Congresswoman Giffords:
Her rehabilitation has been excellent relative to the 6 to 112 month general expectation for brain injury recovery Her microsystem, mesosystem, and exosystem and chronosystem factors have converged to forma prognostically positive context for her recovery She has received medical care that the vast majority of Americans would not receive following a brain injury All of the above |
All of the above***
|
|
|
With regard to Congresswoman Giffords, we may also say that:
There are many parallels between her brain injury and that of Phineas Gage The Chronosystem of Phineas Gage was superior to that of the Congresswoman The frontal cortex was impacted in both the cases of Gage and Giffords The Exosystem of Phineas Gage was superior to that of the Congresswoman All of the above A and C, only B and D, only |
A and C, only***
|
|
|
Which of the following regarding Congresswoman Giffords is FALSE?
Her corpus callosum was impacted by the bullet Her right side motor ability was more impacted than the left side Her language skills were more affected than her creative skills Plasticity may account for some of her recovery ALL of the above |
Her corpus callosum was impacted by the bullet***
|
|
|
Which of the item(s) is/are FALSE regarding the Wechsler intelligence scales and the Stanford-Binet Scale?
Z-scores have a mean of 100 and a SD of 15 T-scores have a mean of 50 and a SD of 10 Mild mental retardation may be denoted by an IQ of 65 Medical students must score at the 150+ IQ level as part of admissions testing A and C, only B and D, only |
B and D, only***
|
|
|
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Scale II
It is a projective personality test It is comprised of 550 true-false items Raw scores are converted to Z-scores with a mean of 50 and a SD of 10 It consists of 10 clinical dimensions/scales and 3 validity scales A and B, only B and D, only A, B, and C, only |
B and D, only***
|
|
|
Which IQ classification(S) correspond(s) appropriately with the DSM classifications of Mental Retardation (MR)?
Profound MR = 20 to 25 Severe MR = 20-25 to 35-40 Moderate MR = 35-40 to 50-55 Mild MR = 50-55 to about 70 ALL of the above A and C, only B and D, only |
ALL of the above***
|
|
|
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale III consists of which of the following subtests?
Arithmetic, digit span and letter-number sequencing Vocabulary, similarities and information Picture completion and block design Digit symbol-coding and symbol search ALL of the above A and B only B and D, only |
ALL of the above***
|
|
|
The “Frontal lobe” is associated with which of the following cognitive and emotional attributes?
Thinking, planning and mood control Long-term memory and auditory perception Visual-spatial processing and attention Long term memory and emotions ALL of the above A and C, only B and D, only |
Thinking, planning and mood control***
|
|
|
Left hemispheric attributes include all of the following EXCEPT:
Analytical and logical thinking Capacity for scientific and detailed thinking Ability for precise and organized thinking Capacity for creative and imaginative thinking A and C, only B and D, only |
Capacity for creative and imaginative thinking***
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter behavioral impacts may include all of the following EXCEPT:
Dopamine = movement disorders; hallucinations and delusions Acetylcholine = dementias Gamma Amino-butyric acid = anxiety Norepinephrine = depression Serotonin = anxiety, mood regulation None of the above/they are all TRUE |
None of the above/they are all TRUE***
|
|
|
Which of the following statements are TRUE regarding neurotransmitters:
Glutamic Acid may play a role in the production of symptoms of schizophrenia GABA is associated with anxiety Serotonin is linked to anxiety Serotonin is linked to depression Dopamine is linked to depression and mania Norepinephrine is linked to depression All of the above None of the above |
All of the above ***
|
|
|
Physicians may be at an increased risk for Unipolar Disorder and suicidal ideation secondary to:
Constant family discord and emotional neglect emanating from extended work hours Discomfort with admitting errors Discomfort with asking for mental health treatment Stigmatization of mental difficulties to licensure boards Fear of disclosure of mental difficulties to licensure boards All of the above |
All of the above***
|
|
|
The standard of care for panic disorders and agoraphobia includes:
SSRIs, BNZs, TCAs Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Respiratory Training Systematic Desensitization All of the above ALL of the above except “A” and “C” |
All of the above***
|
|
|
Executive functions include:
Multi-tasking, task attack, time management Visual-spatial processing, concentration, control of emotions Organizational skill, delay of gratification, abstract thinking Receptive and functional language skills, symbol recognition A and C, only B and D, only |
A and C, only***
|
|
|
The tests that comprise the Halstead-Reitan Battery of Neuropsychological Tests include:
Category Test and Rhythm Test Tactual Performance test Trail-making test and critical flicker frequency test Finger-Oscillation test Time sense test ALL of the above A, B, and C, only |
aLL of the above***
|

