![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an Arrhenius Acid? |
Increases the amount of hydrogen and water ions in an aq solution |
|
|
What is an Arrhenius Base? |
an arrhenius base increases the number of hydronium (OH-) ions in an aqueous solution |
|
|
A species that donates a proton (H+) is referred to as.... A) Arrhenius acid B) Bronsted lowry acid C) Arrhenius base D) Brownsted lowry base |
Answer: (B) a bronsted lowry acid which donates or losses a proton |
|
|
With bronsted lowry acid-bases, equilibrium will favor.... A) the formation of weaker acid and bases B) the formation of stronger acids and bases C) Both a and b |
Answer: (A) equillibrium will favor the formation of weaker acids and bases |
|
|
Which is NOT a amphoteric solvent? A) HF B) H3O+ C) Acetic acid D) HCl E) NH4+ |
Answer: (D) HCl |
|
|
Which completely dissociates in aqueous solutions ...... strong baes or strong acids? |
Answer: Strong acids because all of its protons are donated |
|
|
A weak acid will have A) a large ka value B) a small ka value C) a small pka value D) a large pka value E) both b and d F) both a and c |
Answer: (E) a weak acid will have a large pka value and a small ka value |
|
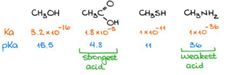
Rank according to acid strength from weakest to strongest
|
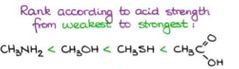
Answer: notice that a large ka value and small pka values hints at a strong acid |
|
|
Acidity increases: A) with increasing atomic number B) electron withdrawing groups C) with electronegativity D) with size E) All of the above |
Answer: (E) All of the above are ways in which acidity increases |
|
|
Basicity increases with increasing negative charges True or False |

Answer: True, the more negatively charged the greater the stability as a base |
|
|
If a molecule is a weak acid, it is a strong base or weak base? |
Answer: a molecule that is a weak acid is considered a strong base and vice versa |
|
|
A binary hydrogen compund contains A) two hdrogens and 1 other element B) One hydrogen and a single element C) None of the above |
Answer: (B) one hydrogen with one other element is present in an binary hydrogen compound. |
|
|
Which molecule has no acid-base properties.... A) HI B) NH3 C) HCl D) CH4 E) HBr F) None of the above |
Answer: (D) CH4 has no acid-base properties |
|
|
What is an Oxyacid? |
Answer: an oxyacid is an acid that contains an oxygen. Ex: HOCl |
|
|
An increase in the amount of oxygen atoms result in... A) a decrease in acidity B) an increase in acidity C) a neutral molecule |
Answer: (B) an increase in acidity |
|
|
What happens to electron density as the number of oxygen atoms increase? |
Answer: the electron density supporting the O-H bond decreases |
|
|
A resonance structure is less stable with an increased number of oxygen atoms True of false |
Answer: False, a resonance structure is more stable as the number of oxygen atoms increase |
|
|
Transitional metal cations are A) Acidic B) Basic C) both a and b |
Answer: (A) transitional metals are acidic |
|
|
Metal Ions are strong acids when... A) The radii is small in size B) The cation charge increases C) None of the above D) Both a and b |
Answer: (D) Metal ions are strong acids when the atoms radii is small and the cation charge increases |
|
|
An electron pair acceptor is... A) A lewis acid B) An electrophile C) A lewis base D) A nucleophile E) Both a and b F) Both c and d |
Answer: (E) an electron pair acceptor is a lewis acid and electrophile |
|
|
What links a lew base and acid? |
Answer : A coordinative or dative bond |
|
|
A nonpolarizable acid and base are considered Hard: True or False |
Answer: True, a nonpolarizable acid-base is considered hard |
|
|
Does softness increase down a group based on mass? |
Answer: Yes, down a coulun on a periodic table the softness of an element increases. |
|
|
Will Ag+ react more favorably with NH3 or PH3? note: soft binds to sodt while hard binds to hard. |
Answer: The silver ion will react more readily with NH# since it is a soft acid |
|
|
Name the two type of solids: |
Answer: Amorphous and Crystalline |
|
|
Which is NOT a characteristic of a crystalline solid: A) Has a unit cell B) Minimizes free energy C) Lacks a 3D arrangment of atoms D) Possesses long range periodicity E) Atoms, ions, and molecules are tightly packed geometric arrays F) All of the above |
Answer: (C) a cystalline solid does not lack a 3D arrangement |
|
|
Which is NOT a type of crystalline solid? A) molecular crystals B) ionic crystals C) covalent crystals D) metallic crystals E) group VIII crystals F) none of the above G) all of the above |
Answer: (F) none of the above. All are diffrent types of crystalline solids |
|
|
How many crystal systems are there? |
Answer: 7 |
|
|
Name the 7 crystal system |
Answer: 1. Cubic 2. Tetragonal 3. Orthorhomic 4. Monoclinic 5. Triclinic 6. Rhomobohedral 7. Hexagonal |
|
|
Which below does NOT have all of its angles at 90 degrees? A) Hexagonal B) Cubic C) Tetragonal D) Orthorhomic |
Answer: (A) hexagonal, which has 90 degree angles at the alpha and beta angle but a 120 degree angle at the gamma angle |
|
|
What is Bravais lattice? |
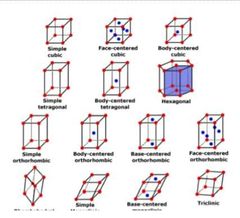
Answer: It's an infinite array of points with an arrangement and orientation that looks exacly the same from any lacttice point |
|
|
How many cubic bravais lattices are there? A) 2 B) 5 C) 3 D) 8 |

Answer: (C) 3 |
|
|
In a cubic crystal, a = b= c, meaning theres only one lattice constant (a) True of False |
Answer: True |
|
|
What is usually located at lattice points? A) ions B) molecules C) atoms D) all of the above |
Answer: All of the above |
|
|
Summary of three cubic lattices |
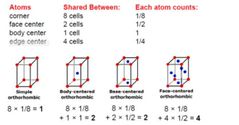
|
|
|
Which has a closed packed structure? A) Fcc B) hexagonal (ABABAB) C) cubic (ABCABC) D) All of the above |
Answer: (D) All of the Above are examples of closely packed structures |
|
|
Most metals crystallize into ccp, hcp, or bcc structure will the exception of ..... |
Answer: Actinides |
|
|
Which bond is the strongest when dealing with metallic solids? A) covalent B) ionic C) metallic bonding D london dispersion |
Answer: (A) covalent bonding is the strongest type of interaction |
|
|
Metals have a low conductivity and electricity: True or false |
Answer: False |
|
|
For every anion, there's one site with Oh symmetry and two td sites True or False |
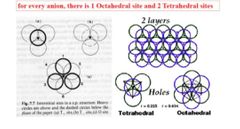
Answer: True |
|
|
What is a band gap? |
Answer: the energy difference between the highest valence and lowest conduction band |
|
|
Increasing temperature results in increasing conductivity True or False |
Answer: True, more heat results in more conductivity |
|
|
Which has a partially filled orbital? A) conductor B) p orbital C) insulator |
Answer: (A) a conductor has a partially filled orbital |
|
|
Which is a characteristic of an Insulator? A) delocalization occurs within bands B) electron vacancies C) restricts electron movement D) electron are free to move around E) All of the above |
Answer: (C) an Insulator restricts the movement of an electron. The rest are characteristics of a conductor |
|
|
Tends to occur to the right and in the middle of band gap... A) insulator B) semi conductor C) metals |
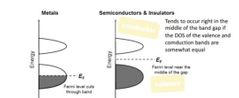
Answer: (B) a semi conductor occurs to the right |
|
|
Electrons are located in the conduction band if.... A) at 298 degrees Kelvin B) at 0 degrees Kelvin C) none of the above |
Answer: (A) 298 Kelvin because the valence band is partially filled |
|
|
What is doping? |
Answer: the modification of materials by replacing a few atoms in original with electrons of more or less electronics |
|
|
Which is NOT a characteristic of Doping? A) allows control of conductivity in semiconductor B) can add impurity like phosphorus C) none above; all are characteristics of Doping |
Answer: (C) All are characteristics of doping |
|
|
Which is NOT a Semiconductor? A) N type B) M type C) P type D) O type F) Both B and D |
Answer: (F) M type and O type aren't known semiconductors |
|
|
What is Plancks Equation? |

|
|
|
A coordination compound contains one or metal metal atoms as well as one or more ligands True or False |
Answer: True |
|
|
Which is a lewis base in M-L? |
Answer: the metal is a lewis base meaning it donates a pair of electrons |
|
|
Complex ions that have ligands coordinated directly to the metal are... A) the secondary coordination sphere B) the primary coordination sphere C) the tertiary coordination sphere |
Answer: (B) the primary coordination sphere |
|
|
Which is NOT a ligand? A) anions B) complex cations C) complex ions D) counterions |
Answer: (D) counterions |
|
|
The Ewing Bassett Sytem is give in parentheses as A) a roman numeral (VI) B) a normal number (3+) |
Answer: a normal number (3+) |
|
|
Metal ion in complex cations change their name by ending in -ate. True or false |
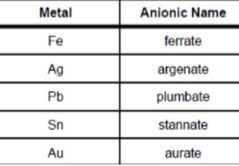
Answer: false, metal ions in a complex anion changes its name by an -ate ending |
|
|
What is a chelating ligand? |
Answer: a chelating ligand is bound to more than one atom |
|
|
What happens when a chelating ligand is bound to a metal? A) it forms a chelate ring B) a straight chain is formed C) None of the above |
Answer: (A) a chelate ring forms when bound to a metal |
|
|
Which of the polydentate ligands has 4 donor sites: A) tetradentate B) pentadentate C) bidentate D) monodentate E) tridenate |
Answer: (A) a tetradentate has 4 donor sites |
|
|
What is an ambidentate ligand? |
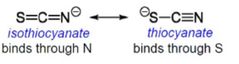
Answer: an ambidente ligand can bind to a metal using either of several atoms |
|
|
In a CN molecule, hard acids bind to nitrogen while for soft acids they bind to sulfur True or False |
Answer: True |
|
|
Is the Nitrogen or Sulfur in CN- favored to bind to a metal? |
Answer: The sulfur bonded to a metal is more favored |
|
|
The softer The element The more soluble it is... True or False |
Answer: True |
|
|
What is an isomer? |
Answer: an isomer has the same number of molecules with different arrangements |
|
|
Which is NOT a structural isomer found in coordination complexes... A) hydrate B) ionization C) coordination D) linkage E) all of the above |
Answer: (E) all of the above isomers are found in coordination complexes |
|
|
Which isomer occurs when water binds within the primary and secondary coordination sphere of a metal ion? A) coordination isomer B) ionization isomer C) hydrate isomer D) linkage isomer |
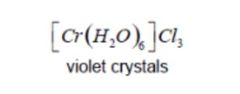
Answer: (C) hydrate isomer |
|
|
What is a type of stereo isomer? A) optical B) geometrical C) both a and b |
Answer: (C) Both a and b, optical and geometrical |
|
|
Geometrical isomers occur for A) trigonal planar B) tetrahedron C) octahedral D) square planar E) Both a and b F) Both c and d |
Answer: (F) occurs in both for an octahedral and square planar |
|
|
An optical isomer is chiral and can form a pair of enantiomers. True or False |
Answer: True |
|
|
If a mirror plane is present, the molecule is chiral True or false |
Answer: False, if a mirror plane is present the molecule is not chiral |
|
|
Optical activity does not occur in square planar complexes True or false |
Answer: True |
|
|
What can impact coordination geometries? A) solubility B) coordination geometry C) steric hindrance D) a large number of bonds which results in more stability E) all of the above |
Answer: (E) all of the above can impact coordination geometry |
|
|
Which coordination is the MOST common? A) 5 B) 7 C) 3 D) 6 |
Answer: (D) coordination 6 is the most common |
|
|
Which coordination is RARE? A) 1 B) 8 C) 4 D) 3 |
Answer: (A) coordination 1 is the rarest |
|
|
Which is NOT a coordinate geometry found in coordination 4? A) see saw B) trigonal planar C) tetrahedral D) square planar |
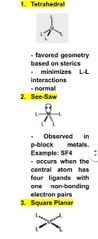
Answer: (B) trigonal planar is not a coordinate geometry seen in coordination 4 |
|
|
Coordination 4 is commonly found in d^0, d^5, and d^10 orbitals True or False |
Answer: True |
|
|
Which coordination is uncommon for transitional metals? A) 8 B) 5 C) 7 D) 1 E) 2 |
Answer: (A) coordination 8 is uncommon for transitional metals |
|
|
Coordination where all angles are 90 degrees A) 4 B) 1 C) 7 D) 6 |
Answer: (D) coordination 6 has angles where there degree is 90 |
|
|
Coordination where all of its axial and equatorial sites are equal? A) 8 B) 3 C) 5 |
Answer: (C) coordination 5 |
|
|
Can be prepared in the absence of coordinating solvents... A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 |
Answer: (A) coordination 1 can be prepared in the absence of coordinating solvents such as NH3, THF, and so on |
|
|
Which is NOT a coordinate geometry of coordination 5? A) square pyramidal B) trigonal bipyramidal C) trigonal distortion |
Answer: (C) trigonal distortion, is not a geometry of coordinate 5 but of coordinate 6 |
|
|
A high homo is a base or acid |
Answer: it is base |
|
|
A low lumo is an acid or base |
Answer: an acid |
|
|
A lumo receives a pair of electrons (lewis acid) while a homo donates a pair of electrons (lewis base)
True or False |
True |
|
|
Which semiconductor donates a pair of electrons? A) p type B) m type C) n type |
Answer: (C) n type donates a pair of electrons Note: the p type is an acceptor |
|
|
The semiconductor is A) medium B) larger C) small |
Answer: (B) the semiconductor band is relatively large in size |
|
|
What is the band theory? |
Answer: when the number of atoms are large, the orbitals are large, results in MO forms developing continuous bands |

