![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Systematize body of knowledge |
Science |
|
|
|
Deals with living organism |
Biological Science |
|
|
|
Deals with non-living organism |
Physical Science |
|
|
|
Changes that matter undergoes in terms of properties, structure, and composition |
Chemistry |
|
|
|
Does not contain carbon |
Inorganic chemistry |
|
|
|
Contains carbon |
Organic chemistry |
|
|
|
Study of mechanism, rate and energy transfer a matter undergoes |
Physical Chemistry |
|
|
|
Study of chemical in living organisms |
Biochemistry |
|
|
|
Study of chemical composition of matter which are measurable and identified |
Analytical Chemistry |
|
|
|
Anything that occupies space and has mass |
Matter |
|
|
|
Qualities or attributes that can be used to distinguish sample of matter from another |
Properties |
|
|
|
Readily ovservable properties, can be measured without affecting the substance |
Physical Properties |
|
|
|
Dependent -mass and volume -length and weight |
Extrisic or Extensive |
|
|
|
Independent -melting and freezing point -density and durability |
Intrisic or Intensive |
|
|

Classification of matter |
🤔 |
|
|
|
-Most common state of matter in the universe -Consist of highly charged particle, with extremely high kinetic energy |
Plasma |
|
|
|
Solid to Liquid |
Melting |
|
|
|
Liquid to Gas |
Evaporation |
|
|
|
Gas to Liquid |
Condensation |
|
|
|
Liquid to Solid |
Freezing |
|
|
|
Solid to Gas |
Sublimation |
|
|
|
Gas to Solid |
Deposition |
|
|
|
Two types of pure substance |
Elements and Compounds |
Constant composition-pure |
|
|
Two types of mixture substance |
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous |
Variable composition-Mixture |
|
|
-pure chemical substance -contains one type of atom -building blocks of substance -represented by symbol |
Elements |
|
|
|
Has intermediate properties |
Metalloids or semi-metals |
|
|
|
-good conductor of heat and electricity -form basic oxides -lustrous, malleable, ductile -high density and melting point -tend to lose electrons |
Metal |
|
|
|
-poor conductor of heat and electricity -form acidic -dull, brittle if solid -low density and melting point -tends to accept electrons |
Non metals |
|
|
|
Enumerate all metalloids |
Silicon, Germanium, Polonium, Antimony, Arsenic, Tellurium, Boron |
|
|
|
Pure substance made up of 2 or more elements Can be decomposed or broken down |
Compounds |
|
|
|
All ___ are ___ but not all ___ are ___. |
Compound:Molecule :: Molecule:Compound |
|
|
|
2 Types of Compound |
Molecular and Ionic Compounds |
|
|

Classification of Compounds |
😁 |
|
|
|
2 or more substances combined ind varying proportions |
Mixtures |
|
|
|
Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous |
Homogeneous- one phase, uniform composition Heterogeneous- distinct physical phase |
|
|
|
Special type of homogeneous mixture Contains solute which are distributed throughout a solvent system |
Solution |
|
|
|
Heterogeneous mixtures of 2 substances of different phases |
Colloids |
|
|
|
Give all the properties of colloids |
»Tindal Effect- scatter light »Brownian Movement- zigzag or random motion of particles »Adsorption- adhere to surface »Charge of Electricity |
|
|
|
Heterogeneous fluid containing solid particles Internal- solid External- fluid |
Suspension |
|
|
|
Basic unit of matter |
Atom |
|
|
|
Atomos means _____. |
Indivisible |
|
|
|
Found in nucleus and collectively called nucleons |
Proton (+) Neutron (no charge) |
|
|
|
Negative charged particles |
Electron |
|
|
|
Matter is made up of little units called atom |
Atomic Theory |
|
|
|
Said that atoms (atomos) are uncuttable |
Democritus |
|
|
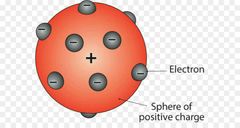
»Discovered first subatomic particle »Plum Pudding Model or Raisin Bread Model |
J.J Thompson or John Joseph Thompson |
|
|
|
Coined the term electron |
George Stoney |
|
|
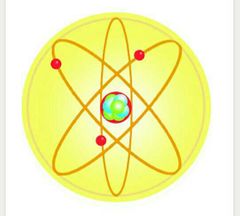
The Billiard Ball Model |
John Dalton |
|
|
|
Daltons Assumptions |

|
|
|
|
Made the first cathode ray |
Michael Faraday |
|
|
|
Determined the change of an electron through a series of 'oil-drop' experiment |
Robert Millikan |
|
|
|
Discovered X-Rays |
Wilhelm Roentgen |
|
|
|
Discovered radioactivity |
Antoine Henry Becquerel |
|
|
|
Discovered Gamma Radiation |
Paul Villard |
|
|
|
Discovered transmutation |
Frederick Soddy and Ernest Rutherford |
|
|
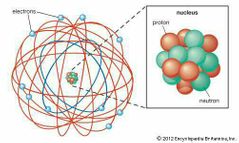
Discovered Alpha and Beta Particles, "Gold Foil Experiment", and "Nuclear Planetary Model". |
Ernest Rutherford |
|
|
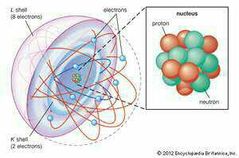
Shell model |
Neils Bohr |
|
|
Electron Cloud Model |
Erwin Schrodinger |
|
|
|
Changes in matter *does not produce a new substance |
Physical Change |
|
|
|
Takes place on the molecular model wherein a new substance is produced |
Chemical Change |
|
|
|
Enumerate evidences of chemical change |
»Evolution of Heat and Light »Evolution of Gas »Formation of a Precipitate »Production of Mechanical and Electrical Energies |
|
|
|
Change in nucleus |
Nuclear Change |
|
|
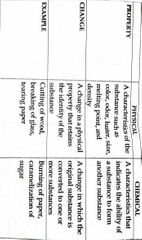
Summary of Physical and Chemical Change |
😇 |
|
|
|
State if it is true or false. If false write the correct equation: 1. Atomic Number = Number of Protons + Number of Electrons + Number of Neutrons 2. Mass Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons 3. Neutron= mass # + proton |
1. Atomic Number= # of Protons= # of Electrons 2. True 3. Neutron= mass no. - proton |
|
|
|
Isotope vs. Isobar vs. Isotones |
Isotope- same no. of protons, but differ in mass no. Isabase- same mass number Isotone- same number of neutrons |
|
|
|
»Developed by Russian Scientist named Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869 »Complete list of all the elements |
Periodic Table of Elements |
|
|
|
Group or Family Consist of 18 |
Vertical Column |
|
|
|
Period or Series Consists of 7 |
Horizontal Row |
|
|
|
First to set up the table (33 elements) |
Antoine Lavoiser |
|
|
|
First to consider the idea of trends among properties of elements 'Triads' 10-12 |
Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner |
|
|
|
First person to device a periodic table of chemical elements arranged in their relative atomic masses. "Law of Octaves" |
John Newlands |
|
|
|
First periodic law, properties are periodic |
Julius Lothen Meyer and Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev |
|
|
|
First modern periodic table |
Henry Mosely |
|
|
|
Specific abbreviation used to denote the name of the elements |
Symbol |
|
|
|
Significance of a Symbol |
-represent short form of elements -represents one atom of the element -indicates the atomic weight of the element |
|
|
|
Tried to name various elements based on pictorial symbol, 1807 |
John Dalton |
|
|
|
A Swedish Chemist who devised a system using the letter of the element, 1814 |
Jon Jacob Berzelius |
|
|
|
Significance of Chemical Formula |
-shorthand notation for compounds -combination of symbol of elements -represents the number and kind of atoms present in the compound. |
|
|
|
Electrons gained, lose or shared by an atom |
Valence electrons or oxidation number/state. |
|
|
|
Cations vs. Anions |
Cations- loses electrons Anions- gains electron |
|
|
|
Illustrate Isotope Symbol |
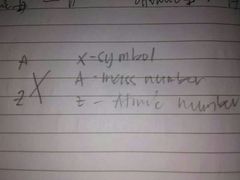
|
|
|
|
Rules in writing symbols |
1. First letter of the element as the symbol for that elemeny and written in capitals. 2. In some cases, the initial name in capital alomg with its second letter in small is used 3. Symbol of the element were derived from their latin names |
|
|
|
State the English and latin name of the following symbols. |
😇 |
|
|
|
Na |
Sodium-Natrium |
|
|
|
W |
Tungsten-Wolfram |
|
|
|
Ag |
Silver-Argentum |
|
|
|
K |
Potassium-Kalium |
|
|
|
Au |
Gold-Aurum |
|
|
|
Sn |
Tin-Stann |
|
|
|
Sb |
Antimony-Stibium |
|
|
|
Hg |
Mercury-Hydrargyrum |
|
|
|
Pb |
Lead-Plumbum |
|
|
|
Fe |
Iron-Ferrum |
|
|
|
Cu |
Copper-Cuprum |
|
|
|
Rules in Writing Formula |
1. Write the formula side by side 2. Above each symbol, write the valence electron 3. Crisscross the valence 4. Omit subscript whenever it's equal to one, common factors should be canceled 5. When the radicals need subscript, enclose it with parentheses 6. Reduce subscript to small whole number 7. When a radical already contains a parentheses, enclose it with a bracket |
|

