![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What conditions are under the heading of IBD?
|
Crohn's
Ulcerative colitis |
|
|
What age of people get IBD?
|
20's
|
|
|
How should you manage someone with IBD?
|
Eradicate early.
|
|
|
What gene is closely linked to crohn's?
|
NOD2
Involved with pathogen tolerance: can't recognize what's bad and what's not --> chronically inflamed |
|
|
What is the effect of smoking on crohns? Ulcerative colitis?
|
Crohns: makes worse
Ulcerative: protective |
|
|
What dietary factors are involved with IBD?
|
Omega 3 vs. omega 6 ingestion
Omega 3: protective Omega 6: causing problems |
|
|
What are the components in mucosal innate immunity?
|
Barrier function
Macs Dendritic cells |
|
|
What are the components of mucosal adaptive immunity?
|
T lymphocytes
B lymphocytes |
|
|
What is the major effector cell in IBD?
|
T lymphocytes: IL23
|
|
|
Where are peyers patches located? Why?
|
Terminal ileum
It's where large concentrations of bacteria start to show up |
|
|
What process takes place at the peyers patches?
|
Endocytosis
|
|
|
What type of immunity is implicated in IBD?
|
Adaptive immunity/T cells
|
|
|
What are the presenting symptoms of IBD?
|
Diarrhea
Abdominal pain Rectal bleeding Weight loss |
|
|
What are some of the extraintestinal manifestations of IBD?
|
Joint
Skin Eye |
|
|
What should increase your index of suspicion for IBD?
|
Onset in 2nd-3rd decade
FH Bloody stool Anemia Weight loss E. nodosum, arthritis, fever, uveitis |
|
|
What organs are involved in ulcerative colitis? Crohns?
|
Ulcerative colitis: colon (usually starts in rectum)
Crohns: anywhere in the bowel |
|
|
What are the symptoms of proctisis?
|
Tinismus (think you have to poop but can't)
Bleeding Urgency |
|
|
What are the conditions that mimic ulcerative colitis on a scope?
|
Infection
ABs |
|
|
What are some skin conditions that occur in IBD? When do these occur/
|
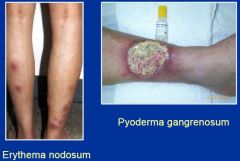
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Erythema nodosum They happen when the whole colon is involved, often. |
|
|
What are some complications in the eye of IBD?
|
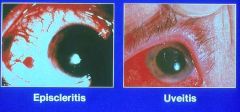
Episcleritis
Uveitis |
|
|
What are the chronic complications of ulcerative colitis?
|
Bleeding
Perforation Cancer Strictures |
|
|
What's the most common location for Crohns?
|
Distal small intestine: ileocolonic
|
|
|
What findings on a scope lead you more towards a diagnosis of Crohns?
|
Deep, punched out ulcers
Strictures are more common in Chrons (esp. in the ileum) |
|
|
What parts of the bowel does crohns involve? Ulcerative colitis?
|
Crohns: full thickness (transmural thickness)
Ulcerative colitis: just the upper layer |
|
|
What are common complications from Crohns?
|
Strictures
Fistulas Abscesses |
|
|
What are findings on CT for Crohns?
|
Fat stranding
Wall enhancement Hypervascularity |
|
|
What complication is seen in ulcerative colitis but not Crohns?
|
Toxic megacolon
|
|
|
What are common intestinal complications from Crohn's?
|
Cancer
Fistulas Abscess Perforation Strictures |
|
|
What are findings in a history that favor Crohns?
|
Pain > diarrhea
Perianal disease |
|
|
What are findings in a blood test that favor Crohns?
|
ASCA + /ANCA -
|
|
|
What are findings in imaging that favor Crohns?
|
Small bowel involvement
Rectal sparing Deep ulcerations Fistulas |
|
|
What are findings histologically that favor Crohns?
|
Granulomas
Transmural inflammation |
|
|
What are the modalities of treatment for IBD?
|
Surgery
Medications Emotional support Nutrition |
|
|
What are the kinds of immunomodulation we do for IBD?
|
Suppress t helper cells
Inhibit cytokines (TNF-alpha) Support the epithelia |
|
|
What condition do we treat with sulfasalazine?
|
UC
Colonic crohns WE DON'T GIVE IT FOR SMALL BOWEL DISEASE! |
|
|
What are ways that we get drugs selectively to the colon?
|
pH dependent
Time release Bacterial cleavage. |
|
|
What's the mechanism for sulfasalazine?
|
Inhibits lipoxygenase pathywahy
O2 scavenger Inhibition of IL-2 |
|
|
What are the indications for corticosteroids in IBD?
|
Bridge to AZA/anti TNF-alpha
|
|
|
What's the mechanism of azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine?
|
Inhibit nucleotide biosynthesis
Inhibit T cell activation |
|
|
What are the indications for azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine?
|
Active UC, CD
Inhibits Abs to anti-TNF-alpha |
|
|
What are the side effects of azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine
|
Pancreatitis
Neutropenia Teratogenic! Malignancies |
|
|
What is infliximab active against?
|
Anti-TNF
|
|
|
What are the complications of anti-TNF-alpha drugs?
|
Cancers
Fungal infections |

