![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
_________ are longer than _________ and there are only a few per cell. They are used for gene transfer between cells (found only in gram-_________ bacteria and not restriced to species), while _________ are mainly for attachment to surfaces such as the epithelial cells of the mucosa. |
Pili fimbriae negative fimbriae |
|
|
_________ involves a process called conjugation where a "sex" pilus (or F-pilus) extends from a donor bacterium (F+) to a recepient (F-). A copy of part of the donor bacterium's genome then passes along the pilus into the recipient cell. The passed DNA may code for _________ which explains the abundance of _________ bacteria. |
Gene transfer drug resistance drug-resistant |
|
|
Pili are also involved in _________ motility. |
twitching |
|
|
Located as a shell of the cell envelope, the glycocalyx is a coat of either _________ or _________. |
slime layer capsule |
|
|
The _________ is loosely bound to the cell and serves to protect the cell against dehydration and also as a food source (composed of polysaccharide matter with or without proteins). |
slime layer |
|
|
A _________ is composed of polysaccharide matter with or without proteins BUT it tends to be strongly bound to the cell. Colonies of cells possessing _________ are characteristically mucoid in nature. |
capsule capsules |
|
|
The capsule protects the organism against _________ by white blood cells, an important immune defence mechanism without which we would become vulnerable to infection. Therefore, the presence of a capsule is often an indicator of virulence and the capsule itself is considered to be a _________. |
phagocytosis virulence factor |
|
|
The slime layer and capsule are in contrast to _________, which is secreted and makes up the matrix. |
exopolysaccharide |
|
|
_________ is a gram-negative anaerobic bacterium that inhabits the oral cavity and is linked to severe periodontal disease. It is non-motile. |
Porphyromonas gingivalis |
|
|
_________ (a surfactant) synthesis is required for normal Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm architecture. |
Rhamnolipid |
|
|
Both _________ and _________ cell systems are used to study biofilm formation. |
static flow |
|
|
_________ strains can be used to identify pathways for biofilm development. |
Mutant |
|
|
As bacteria grow on surfaces in the oral cavity, they _________ the environment around them. |
modify |
|
|
_________ between genetically distinct species (co-aggregation) is the foundation of plaque formation. |
Direct contact |
|
|
_________ and _________ are two key mechanisms involved in plaque development. |
Co-aggregation succession |
|
|
In order for target genes to turn on and quorum sensing to occur, the bacteria must be in high _________. |
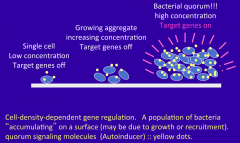
density |
|
|
The autoinducers ________ are produced by gram-negative bacteria. These are ________ cell-density dependent signals important for biofilm development. |
acyl-homoserine lactones (AHL) diffusible |
|
|
Gram-positive bacteria have a different system for cell-dependent signaling which consists of ________ that are processed and transported to turn certain genes on. |
peptides |
|
|
During the early stages of plaque development, Streptococci constitute up to ________% of supragingival plaque. |
70 |
|
|
________ associated with extracellular DNA in the matrix of a biofilm are being targeted to combat biofilm based infections. |
DNA binding proteins (DBPs) |
|
|
The process of successive biofilm formation involves ________ inhibition, ________ inhibition, ________ pathways, action on the ________, and fighting ________. |
non-specific specific signaling matrix persisters |

