![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
20 y.o. sexually active female, c/o dysuria, for 3-4 d, denies fever, started on bactrim for 3 days. returned with the same symptoms UA shows no bacteruria, increased wbc, urine culture is negative
|
Chlamydia infection
|
|
|
What next test will you use to confirm diagnosis?
|
PCR of the urine for chlamdia
|
|
|
20 y.o. sexually active female, c/o dysuria, for 3-4 d, denies fever, started on bactrim for 3 days. returned with the same symptoms UA shows no bacteruria, increased wbc, urine culture is negative
|
Chlamydia infection
|
|
|
How do you treat the patient is she's not pregnant or not allergic
|
doxycycline
|
|
|
What next test will you use to confirm diagnosis?
|
PCR of the urine for chlamdia
|
|
|
if she's pregnant
|
amoxicillin, azithromycin, or erythromycin
|
|
|
How do you treat the patient is she's not pregnant or not allergic
|
doxycycline
|
|
|
what if the above patient is pregnant and allergic
|
Spectinomycin, azithromycin, or cephalosporin desensitization
|
|
|
if she's pregnant
|
amoxicillin, azithromycin, or erythromycin
|
|
|
20 y.o. F came w/ fever, pain on movement of wrist joint, swollen right knee joint, single pustular lesion over dorsal surface of the hand, joint aspiration shows increased cell count, gram negative cocci, what's the diagnosis
|
Disseminated gonococcal infection, due to arthritis, swollen joints, fever, age of patient, and has one pustular lesion (maximum amount is 10)
|
|
|
what if the above patient is pregnant and allergic
|
Spectinomycin, azithromycin, or cephalosporin desensitization
|
|
|
What's the next step?
|
Culture all of the orifices vaginal, rectal, and oral.
|
|
|
20 y.o. F came w/ fever, pain on movement of wrist joint, swollen right knee joint, single pustular lesion over dorsal surface of the hand, joint aspiration shows increased cell count, gram negative cocci, what's the diagnosis
|
Disseminated gonococcal infection, due to arthritis, swollen joints, fever, age of patient, and has one pustular lesion (maximum amount is 10)
|
|
|
How do you treat?
|
ceftriaxone and doxycycline
|
|
|
What's the next step?
|
Culture all of the orifices vaginal, rectal, and oral.
|
|
|
Patient is having recurrent gonococal bacteremia, what do you do next?
|
order CH50 level for complement deficiency
|
|
|
How do you treat?
|
ceftriaxone and doxycycline
|
|
|
What do you do if the CH50 level is low
|
order c5-C9 levels,
|
|
|
Patient is having recurrent gonococal bacteremia, what do you do next?
|
order CH50 level for complement deficiency
|
|
|
What do you do if the CH50 level is low
|
order c5-C9 levels,
|
|
|
patient worked up for dementia and is now VDRL positive, what do you do?
|
Do a CSF examination and send it for VDRL to rule out neurosyphilis
|
|
|
young female comes with neck stiffness, fever, headache, has painful erythematous lesion on genitalia, large tender inguinal lymphadenopathy, CSF examination shows increase lymphocytes, mildly elevated proteins, and normal glucose.
|
Asceptic meningitis secondary to genital herpes. (patient is having fever, neck stiffness, lymphocytes, and normal glucose is the sign of
|
|
|
74 y.o. F c/o watery, yellowish vaginal discharge, has dyspareunia, thin and pale vagina, wet mount shows numerous WBC, no bacteria, KOH is negative, what's diagnosis and what do you treat it with.
|
atrophic vaginitis due to estrogen deficiency. treat with estrogen.
|
|
|
mother has hiv and hep C, in newborn baby what test would you like to order,
|
PCR for HIV and Hepatitis C
|
|
|
IV drug abuser came with complaint of fever, maculopapular rash, cervical lymphadenopathy, lymphopenia, HIV test is negative, heterophile antibody test is negative, what's the most diagnosis?
|
Acute retroviral syndrome that occurs 10-21 days before seroconversion.
|
|
|
How can you confirm this finding?
|
Order p24 antigen or HIV RNA PCR
|
|
|
The patient had unprotected sex two weeks ago. he came to know that his partner is HIV positive. which test will be helpful?
|
HIV RNA PCR
|
|
|
HIV patient with anemia, what type of anemia would it be?
|
normocytic normochromic anemia.
|
|
|
How do you treat this anemia??
|
erythropoietin.
|
|
|
HIV patient with a CD4 count of 30, is on 3 antiretroviral drugs, and bactrim, what else does the patient need?
|
MAI prophylaxis, azithromycin, or clarithromycin
|
|
|
An HIV patient on AZT, 3TC, and Indinavir is found to have hemoglobin 7, hematocrit 20, and an MCV of 120, what is causing the anemia
|
AZT
|
|
|
HIV patient with CMV Immunoglobulin G negative, needs blood transfusion, what do you do?
|
Transfuse with CMV negative blood.
|
|
|
HIV patient comes in with fever, cough, and shortness of breath, R. lower lung crackles, CXR-right lower lobe infiltrate is present. CD4 count is 350. what's the most likely diagnosis???
|
community acquired pneumonia.
|
|
|
HIV patient presents with fever, cough, SOB, on examinaiton has bilateral diffuse crackles, CXR has bilateral diffuse inflitrate, CD4 count is 150. what's the most likely diagnosis?
|
PCR/ Pneuomcystis Jiroveci PNA. Increased LDH, ABG will have hypoxia. AA gradient could be elevated.
|
|
|
How do you confirm PCP?
|
Send sputum for methylamine silver spain or Giemsa stain
|
|
|
How do you treat a patient with PCP who has a sulfa allergy
|
Give them IV pentamadine, cannot use Bactrim.
|
|
|
If a patient with PCP and PaO2 is less than 70 or the A-a gradient is more than 35, what other management is important.
|
add steroids treatment to standard PCP treatment.
|
|
|
What are side effects of Bactrim
|
Can cause fever skin rash, bone marrow suppression, hyperkalemia, increased serum creatinine (trimethoprim intefers with creatinine secretion)
|
|
|
A patient with HIV is being treated for PCP with IV Bactrim suddenly developed left sided chest pain, and shortness of breath. Has decreased breath sounds on left upper chest, has tracheal deviation towards the right. cardiac enzymes and troponin are pending. CXR is shown.
|
Pneumothorax. Patients with PCP are at increased risk of developing pneumothorax.
|
|
|
HIV patient, w/ fever, night sweats, weight loss, cough, cervical, and axillary lymphadenopathy. CXR shows r. upper lope infiltrate. What's the diagnosis?
|
tuberculosis
|
|
|
HIV patient with fever, night sweats, weakness,severe weight loss. on exam no obvious source of fever. CXR is negative. CD4 count is 30.
|
Mycobacterium Avium Intracellulaire
|
|
|
How do you treat Mycobacterium Avium?
|
clarithromycin + ethambutol +/- rifampin
|
|
|
HIV patient or neutropenic patient comes with fever, cough, hemoptysis, CXR has bilateral nodular densities. what is the most likely diagnosis?
|
Aspergillosis
|
|
|
How you confirm the diagnosis of aspergillosis?
|
Have to confirm bronchoscopic biopsy which will show regularly branched septate hyphae
|
|
|
What is the treatment of aspergillosis?
|
amphotericin B or voricanozole
|
|
|
If treatment of aspergillosis is ineffective, what is the next step?
|
call surgical consult, the patient needs a resection of the lung
|
|
|
HIV patient with symptoms of pneumonia, has oral ulcer, hepatosplenomegaly, coming from Ohio, what is the diagnosis?
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
Patient with symptom like pneumonia, has severe joint pain, recently traveled to Arizona. what's the diagnosis?
|
Coccidiodomycosis
|
|
|
Patient with bloody nasal discharge, has black necrotic lesion of the nose. what's the diagnosis?
|
Mucormycosis
|
|
|
What's the next step
|
CT or MRI
|
|
|
A patient in the ICU, on TPN via a central catheter, complains of ocular discomfort, leading to visual loss in the right eye, what's the diagnosis?
|
candida enophthalmitis
|
|
|
Patient is in the hospital, blood culture is growing candida, patient is asymptomatic, what do you do?
|
Start treatment with fluconazole
|
|
|
Patient is in the hospital, has central line, developed fever, central line removed, patient is afebrile. after 24 hours the blood culture is growing staph aureus, what do you do next?
|
Must begin treatment because Staph aureus can cause acute endocarditis. In staph epidermidis you can repeat the culture before treatment.
|
|
|
Blood culture is growing staph aureus, besides starting antibiotics, what else can you do?
|
Order a Transesophageal Echocardiogram to rule out endocarditis
|
|
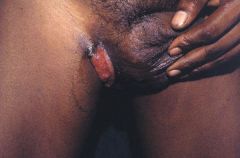
What are laboratories findings associated with this condition?
|
Donavan bodies
|
|
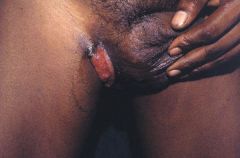
What are some treatment options for this lesion?
|
Tetracycline or erythromycin
|
|
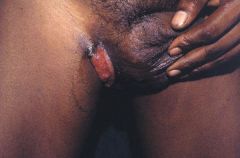
What are some treatment options for this lesion?
|
Tetracycline or erythromycin
|
|
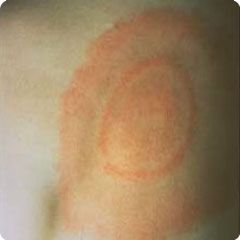
What are some late symtpoms associated with this rash
|
1st degree AV block, 2nd or 3rd degree AV block, bells palsy or foot drop, symptoms of meningitis, arthritis (after several year)
|
|
|
Patient in New Jersey c/o rash on thigh, on examination see erythematous rash, slightly raised with central clearing, patient says that the lesion is slowly growing, what do you do next?
|
No further test required. patient has lyme disease. start doxycycline.
|
|
|
A young female comes with fever, HA, after returning from vacation in long island new york. on examination has right facial palsy.
|
Lyme disease
|
|
|
Young male c/o weakness of right foot, he recently traveled to CT for hiking, he had developed an axillary rash, which has since resolved. he denied history of tick bite. on examination has weakness of dorsiflexion of foot. what's the most likely diagnosis?
|
Lyme disease
|
|
|
A newborn with machinery heart murmur, absence of red reflex in eye, microcephaly.What's the diagnosis?
|
congenital rubella syndrome
|
|
|
A 5 y.o. boy, brought by his mother, since he got up this morning has been having visual difficulty, and falling down, on examination has ataxia, and nystagmus. Has a h/o chicken pox about two weeks prior. what's the diagnosis.
|
Post infectious cerebellar ataxia, can develop after measles also.
|
|
|
A patient w/ fever, sore throat, plus cervical lymphadenopathy. what do you do next?
|
Rapid antigen test to diagnosis steptococcal throat infection.
|
|
|
If the rapid antigen test is positive, what do you do?
|
Start penicillin or erythromycin. no need for culture.
|
|
|
If rapid antigen test is negative, what do you do?
|
Send a throat culture and start antibiotic.
|
|
|
Patient comes in with fever, plus sore throat, and lymphadenopathy, plus splenomegaly, plus atypical lymphocytes. what to do next?
|
do a heterophil antibody test
|
|
|
If the heterophil antibody test is negative, what do you do next?
|
Order CMV immunoglobulin M, to rule out CMV. which can also cause atypical lymphocytes.
|
|
|
fever plus sore throat, plus gray membrane over tonsil and oropharynx. what's the diagnosis and how do you confirm?
|
Diptheria confirm with throat swab culture.
|
|
|
the patient has fever, plus sore throat, plus an enlarged tonsil, plus tender cervical lymphadenopathy, plus erythematous pharynx, with difficulty swallowing, voice has become muffled, on exam the tonsil is displace medially. what's the diagnosis?
|
Peritonsillar abscess?
|
|
|
What's the treatment for peritonsilar abscess?
|
Tonsillectomy plus penicillin or surgical drainage plus penicillin
|
|
|
patient has fever, plus sore throat, plus cough, plus nasal discharge, +/- conjunctivitis. what's the diagnosis?
|
Viral infection.
|
|
|
A patient has fever, respiratory distress in a child who is sitting, leaning forward w/ an open mouth and drooling of saliva. what's the diagnosis?
|
Acute epiglottis secondary to H. influenza B.
|
|
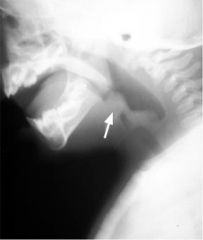
What's the treatment for the condition seen in this lateral next xray
|
Intubation and antibiotics (ceftriaxone or cefotaxime).
|
|
|
A child w/ fever, barking cough, inspiratory stridor. What's the diagnosis? How do you treat?
|
Croup-acute laryngeal tracheal bronchitis, caused by parainfluenza virus. Treatment is supportive (humidified oxygen, or nebulized epinephrine in serious cases, steroids can be used in moderate cases).
|
|
|
less than 2 y.o. child w/ cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, fever, on examination, expiratory wheeze is present. what's the diagnosis? how do you treat?
|
bronchiolitis caused by respiratory synctial virus, treat with oxygen and bronchodilators. ribavarin has been used but has not been that helpful.
|
|
|
A patient has fever, pain and swelling in one or both parotid glands. what's the diagnosis?
|
Mumps
|
|
|
Serious complication of mumps
|
can develop epididydorchitis which can lead to testicular atrophy, meningeal encephalitis, pancreatis
|
|
|
Patient with fever, sore throat, plus vesicular lesion on posterior pharynx and palate. what's the diagnosis and what causes it?
|
Herpangina caused by coxsackie virus
|
|
|
fever plus vesicular lesion on oral buccal mucosa, plus small tender cutaneous vesicular lesions on the hands, feet, and buttocks, what's the diagnosis? What causes it?
|
Hand, foot, mouth syndrome caused by coxsackie virus
|
|
|
A fish tank cleaner, presents with non-healing skin ulcer, biopsy of lesion is positive for AFP. what's the diagnosis? how do you treat it?
|
microbacterium marina. treat with doxycycline or bactrim
|
|
|
A pig raiser comes with seizure, MRI suggests a cystic lesion, what's the most likely diagnosis?
|
Neurocysticercosis
|
|
|
A sheep raiser comes with RUQ pain, U/S suggests a liver cyst, what's the most likely diagnosis?
|
Echinococcosis
|
|
|
A patient comes with RUQ, fever, chills, U/S shows bile duct dilatation, cystic lesion in the liver. the patient has immigrated from S. america to America ten years ago. Most likely diagnosis?
|
Hydatid cyst, echinococcus
|
|
|
yong child with perianal itching, worse at night, most likely diagnosis? Had do you confirm diagnosis?
|
Pinworm caused by enterobius vermaculis. clear tape on perianal area and look for eggs under the microscope.
|
|
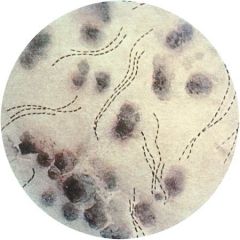
this organism seen on gram stain is associated w/ what disease.
|
hemophilus ducreyi, responsible for chancroid!
|
|
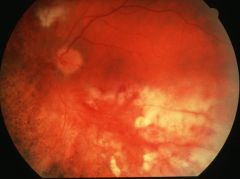
what is the ophalmoscopi findings indicative of?
|
fluffy exudates, perivascular hemorrhage. signs of CMV retinitis
|
|
|
fever, malaise, myalgias, w/ recent h/o of tick bite. what's the diagnosis? and what's the FIRST step?
|
ehrlichiosis, treat immediately w/ doxycycline. no need to confirm the diagnosis.
|

