![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who read Pasteur, then promoted antiseptic surgery and introduced carbolic acid and gloves?
|
Joseph Lister
|
|
|
What causes purpura?
|
Lack of clotting factors due to lack of Vit K leads to bleeding under the skin
|
|
|
Describe these Host-Parasite Relationships:
Symbiotic Commensal Saprophytic Parasitic |
Symbiotic - mutual benefit
Commensal - hitching a ride; doesn't harm or help host Saprophytic - lives off of dead material Parasitic - harmful to host - organisms can belong to more than one category |
|
|
Host resistance
|
an organism's ability to fight disease
infection ≠ disease |
|
|
What is the Iceberg concept of infection?
|
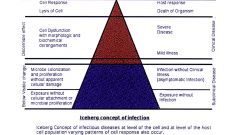
|
|
|
What are the five layers of skin?
|
Superficial Layer
Intermediate Layer Parabasal Layer Basal Layer Basement Membrane |
|
|
What are the five barriers to infection?
|
- Mechanical
- Secretions - Epithelial - Chemical - Microbial (the normal flora) |
|
|
What actions do host cells take to combat infection?
|
- Limit the spread of the agent
- Destroy the agent - Prepare the area of damage for later repair |
|
|
What is the neutrophil's role in infection?
|
- first responders among the leukocytes
- non-specific response - phagocytic |
|
|
What is the lymphocyte's role in infection?
|
- inflammation & immunity
- specific- remove or confine foreign substance - antibody immunity and cellular immunity |
|
|
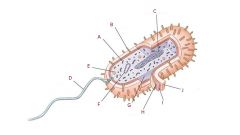
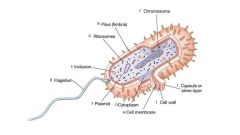
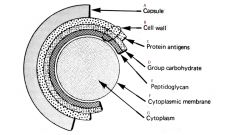
Candida Albicans
|
Causes oral candidiasis and thrush
- present in mouth, GI, skin & vagina of many normal individuals - in immune impaired host, it can invade and cause disease - some agents are always pathogenic, others only sometimes "opportunistic pathogens" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the organism classification strata?
|
King Philip can only grow strawberries
Kingdom Phylum Class Order Genus Species |
|
|
What is the process for gram staining?
|
1. Heat fix bacterial smear
2. Crystal violet & iodine 3. water rinse -> alcohol rinse -> water rinse 4. Safranin counterstain 5. Final water rinse |
|
|
What color will gram positive rods color when gram stained?
Gram negative? |
Gram pos - purple
Gram neg - red |
|
|
What occurs when Mycobacterium tuberculosis is gram stained?
|
Nothing, it does not respond to gram stain; must do Ziehl-Neilson
|
|
|
What is the process for the Ziehl-Neilson Acid Fast stain?
|
1. Heat fix bacterial smear
2. carbolfuschin -> heat 3. water rinse -> acid alcohol -> water rinse 4. Loeffer's Methylene blue counterstain 5. Final water rinse |
|
|
Describe the oxygen tolerance of Facultatively Aerobic organisms
|
can grow with or without oxygen
|
|
|
How may infectious organisms are aerobic?
|
very few
|
|
|
What are the four common typing properties for organisms?
|
1. Growth requirements
2. Biochemical properties (what they produce) 3. Immunotyping (antibodies directed at organism) 4. Generic typing (PCR, electrophoresis, other) |
|
|
What is the Kirby Bauer method?
|
antibiotic impregnated discs are set in the agar plate
- if the antibiotic has good inhibition, no growth around disc - if no inhibition, bacteria will grow right up to disc |
|
|
In the developed world, are most infectious organisms endogenous or exogenous?
|
endogenous
|
|
|
What are the three mechanisms of cellular injury by infectious organisms?
|
1. Direct tissue invasion
2. Toxin production 3. Immunologically mediated - strong immune reaction - TB - cross antigenicity - streptococcus - immune complex formation - streptococcus |
|
|
Bacteremia
Septicemia |
Bacteremia - the presence of viable bacteria w/in the blood
Septicemia - the presence of various pus forming organisms or their toxins in the blood |
|
|
Sepsis
|
A systemic disease caused by septic organisms or their toxins in the blood
- chills, fever, ↓ BP, impaired cardiac function, shock |
|
|
Shock
|
a condition where the supply of the circulation does not meet the demands of the body
|
|
|
What are the three Streptococcal Hemolytic Reactions?
|

|
|
|
What is the most dangerous type of strep?
|
Group A β hemolytic
- Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
|
What are some of the serious illnesses caused by strep?
|
- pharyngitis
- cellulitis - impetigo - endocarditis - rheumatic fever - scarlet fever - puerperal sepsis |
|
|
shigella
|
bacillary dysentary
(fecal oral) |
|
|
What accounted for the gradual decline in tuberculosis in the US in the first half of the 20th century?
For the steep incline in the 1950's? |
1st half - better living conditions
50's - antibiotics |
|
|
How does the body respond to TB in healthy individuals?
In the immunocompromised? |
Healthy people form a granuloma around TB
Immunocompromised or weak, the body is unable to encapsulate the TB |
|
|
Treponema palladium
|
syphilis
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
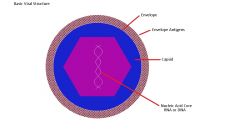
What are three ways viruses replicate and survive?
|
1. Lysing the host cell and producing numerous progeny
2. Budding 3. Incorporate into host's DNA (long term survival) |
|
|
What are the steps of the viral multiplication cycle?
|
1. Attachment to cell surface
2. Penetration 3. Uncoating 4. Transcription of mRNA 5. Translation of early proteins 6. Replication of viral DNA 7. Transcription of mRNA 8. Translation of late proteins 9. Assembly of virons 10. Release |
|
|
Fungal disease
|
Plantlike, but lack pigments to generate sugar from sunlight
- live by saprophytic or parasitic means - two types: yeast, molds |
|
|
Trichophyton tonsurans
|
ringworm
|
|
|
What is the pathophysiology of Entamoeba histolytica?
Where is it endemic? |
Flask shaped ulcer in colon wall
Mexico & South America (fecal oral) |

