![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Law Of Demand |
As goods price falls, more is demanded (and vice versa( |
|
|
Contraction/Extension in demand curve |
Movement along the demand curve due to change in price, Extension=price fall, Contraction=price rise |
|
|
Conditions of Demand |
Non-price factors influencing demand, E.g. Income, Quality, Substitutes, Advertising |
|
|
Rational Behaviour |
Acting in pursuit of self-interest, for consumers, this means attempting to maximise their utility, welfare or satisfaction gained from good and services consumed |
|
|
Utility |
The satisfaction or welfare an individual gains from consuming a good or service. |
|
|
Marginal utility |
The addition utility gained from consuming one extra unit of goods or services. |
|
|
Relationship between total utility and marginal utility |
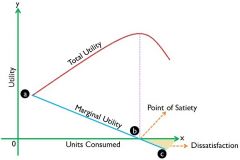
|
|
|
Adam Smiths diamond and water paradox |
"Nothing is more useful than water: but; scarce any thing that can be exchanged for it. A diamond, on the contrary, has scarce any value in use; but a very great quantity of goods may frequently be exchanged for it"- Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations. |
|
|
Utility Maximisation constraints |
-Limited income, there are limits on the wealth and income. To truly maximise utility you need to buy it all. -A given set of prices, consumers are price takers and must accept the market ruling prices. -Budget constraint, the opportunity cost of choosing where to spend your income. -Limited time, consumers can rarely consume more than one good at a time, limited room to store all goods for future consumption. |
|
|
Asymmetric Information |
When one party to a market transaction possesses less information relevant to the transaction. |
|
|
Adverse selection |
The seller knows more about the faults of the good for sale than the buyer, therefore the market ruling price is lowered to protect buyers from overpaying for defected goods. Very similar to George Akerlof's second-hand car market. "if he wants to sell, do I really want to buy?" |
|
|
Behavioural Economics |
A method of economic analysis that applies psychological insights into human behaviour to explain how individuals make choices and decisions. |
|
|
Bounded rationality |
When making decisions individual's rationality is bounded by the information available to them, the limitations of their minds and the finite time available to make decisions. |
|
|
Bounded self-control |
Limited self-control in which individuals lack the self-control to act in what they see as their self-interest. |
|
|
Cognitive biases |
A mistake in reasoning or some other mental thought process occurring as a result of, for example, using rules-of-thumb or holding onto one's preferences or beliefs regardless of contrary information. |
|
|
10 Cognitive Biases |
-Status Quo Bias -Memory Bias -Ingroup Bias -Observational selection Bias -Positive selection Bias -Post-purchase Rationalisation -Neglecting probability -Bandwagon effect Bias -Current moment Bias |
|
|
Status Quo Bias |
People prefer things to remain the same so are biased against change. |
|
|
Memory Bias |
People remember emotional events more vividly and it affects what and how people remember. |
|
|
Ingroup Bias |
Doing similar things to people in your group, suspicious of things people not in your group do. |
|
|
Observational Bias |
Noticing something once and wrongly assuming it happens much more frequently. |
|
|
Positive expectation bias |
The sense that luck will eventually change for the better, e.g. gambling addictions. "Bad luck must change eventually right?" |
|
|
Post-purchase rationalisation |
Believing that the purchase of a bad, expensive or faulty good was a good idea. Trying to justify bad ideas. |
|
|
Neglecting probability |
The inability to grasp a proper sense of risk leading to and overstating or understating of risks. e.g air travel vs car vs bike |
|
|
Negativity bias |
People tend to pay more attention to bad news rather than good news. Perceive negative news as being more important or profound. |
|
|
Bandwagon effect bias |
Succumbing to group think or herd behaviour. |
|
|
Current moment bias |
Preferring pleasure or satisfaction now rather than later. Pain can be left for later. |
|
|
Availability Bias |
Make judgements based on how easily you can remember examples of similar events. |
|
|
Anchoring |
People rely heavily on the first piece of information they find, the "anchor". Individuals use this piece of information when making subsequent decisions. |
|
|
Altruism |
Concern for the wellness of others.Not acting in your own self-interest. |
|
|
Choice Architecture |
A framework setting out different ways in which choices can be presented to consumers, and the impact on the consumers decision making. |
|
|
Framing |
How something is presented influences the choices people make. |
|
|
Mandated choice |
People are required to make a choice by law. |
|
|
Restricted choice |
Offering a limited number of options so that people are not overwhelmed by the complexity of the situation. If there are too many choices people make a poorly thought-out decision. |
|
|
Nudge |
Seek to lead people by providing them with information. Allows them to make their own choices. |
|
|
Shove |
Instruct people to behave in a certain way, often by offering a financial incentive to reward and a disincentive to punish. |

