![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Shapes of the bones? Examples of each |
Long bones- femur, humerous, short bones- Carpals, flat bones- Parietal, irregular bones- Vertebrae |
|
|
Function of bones? |
Support, storage of Calcium phosphate, Blood cell production, protection, leverage |
|
|
Cells in bones? (3), and function |
Osteoblasts: Produce bone matrix, builds around itself until it is trapped Osteoclasts: Destroy bone cells (Giant cells) Osteocytes: Mature bone cell, most abundent |
|
|
Bone marrow? |
Loose connective tissue |
|
|
Compact bone? Location? |
Solid, stress in limited direction, osteons. Located in the diaphysis and layers covering bone surfaces |
|
|
Spongy bone? Location? |
Has alot of air spaces; lightens. Allows for stress in many directions. Red marrow is present. Located in the epiphysis |
|
|
Periosteum? |
Covers bones. Isolates bone from other tissue, route for vessels and nerves |
|
|
Endosteum? |
Cellular, lines marrow cavity and inner surfaces |
|
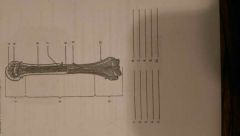
Macro Structure: Name 1-10 |
1: Proximal Epiphysis 2: Diaphysis 3: Distal Epiphysis 4: Spongy bone 5: Articular cartilage 6: Compact bone 7: Marrow cavity 8: Endosteum 9: Periosteum 10: Blood vessel |
|
|
Osseous Tissue? (Micro) |
Suportive connective tissue with calcium phosphate matrix and collagen fibers |
|
|
Lamellae? (Micro) |
Sheets of calcified matrix (rings) |
|
|
Canaliculi? (Micro) |
Channels interconnect lacunae and blood; contains cytoplasmix extensions |
|
|
Osteon? (Micro) |
Basic functional unit of compact bone |
|
|
Central and Perforating canals? (Micro) |
Central: Blood vessels Perforating: Connect vessels of central canals |
|
|
Trabecuale? (Micro) |
Rods or plates in spongy bone |
|
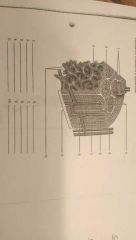
Microscopic Structure: Name of 1-10 |
1: Lamellae 2: Central Canal 3: Endosteum 4: Osteons 5: Artery 6: Vein 7: Periosteum 8: Perforating canal 9: Compact bone 10: Trabeculae |
|
|
Intramembranous Ossification: Ossification? Intramembranous? Ossification center? Examples? |
Ossification: Process of replacing other tissue with bone Intramembranous: Osteoblasts differentiate within embryonic or fetal fibrous connective tissue (skull, clavicle) Ossification Center: Place where ossification occurs Ex. Flat bones of skull, mandible, clavicle. |
|
|
Endochondral Ossification: Appositional growth? Example? Steps in the process? |
Appositional Growth: In diameter; periosteum turns into osteoblasts. Ex. Most bones in the body, femur, humerous etc |
|
|
Similarities between Endochondral Ossification and Intramembranous Ossification |
Stem cells turn into blasts, spongy bone and an increase of blood vessels, remodeling of the bone |
|
|
Differences between Endochondral Ossification and Intramembranous Ossification |
Intra: Dense connective tissue to bone, stem cells turn into blasts, connective tissue. Endo: Hyaline cartilage to bone, stem cells turn into blasts, perochondrium |
|
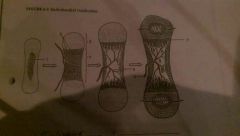
Endochondral Ossification. Label and list steps |
Steps: 1: Enlarging chondrocytes, die as matrix calcifies 2: Newly devoloped osteoblasts cover the shaft on the cartilage in a thin layer of bone 3: Blood vessels penetrate the cartilage. New osteoblasts form a primary ossification center 4: The bone of the shaft thickens and cartilage near each epiphysis is replaced by shafts of the bone 5: Blood vessels invade the epiphysis and osteoblasts for a secondary center for ossification 1: Enlarging chondrocytes 2: Disintergrating chondrocytes 3: Epiphysis 4: Diaphysis 5: Marrow cavity 6: Blood vessel 7: Epiphyseal cartilage |

