![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Immunosuppressive agents? |
Glucocorticoids, Calcineurin inhibitors, Proliferation signal inhibitors, Micophenolate mofetil, Thalidomide, Cytotoxic agents, Monoclonal antibodies, Immunosuppressive antibodies |
|
|
MOA of glucocorticoids? |
Diminish the circulating lymphocytes T&B. Interfere with the function of antigen. presenting cells. Inhibit the production of cytokines, chemokines,INF γ, interleukins2, circulating antibodies Diminution of cell mediated immunity (CMI) |
|
|
What are the uses of glucocorticoids? |
ITP, rheumatoid arthritis, bronchial asthma, allergy. |
|
|
What is calcineurin involved in |
necessary for the T cell activation involved in graft rejection. |
|
|
Who activates calcineurin? |
It is activated by cyclophylin, FKBP, mammalian target of rapamycin |
|
|
MOA of cyclosporin? |
Preferentially suppresses cell mediated immune reactions. Diffuses in T-cell & binds to cyclophili, This complex binds with calcineurin. Inhibits dephosphorylation of NFAT& Decrease in IL-2. No stimulus for increase in number of T-cells |
|
|
Metabolism of cyclosporin? |
Hepatic CYP3A4 |
|
|
Cyclosporin |

|
|
|
Whats Tacrolimus and the MOA and uses? |
a macrolide antibiotic• Mechanism of action: suppresses cell mediated immune reactions. Diffuses in T-cell & binds to FKBP. This complex inhibits calcineurin. Inhibits the gene transcription of IL2inhibits the T cell activation. Uses1. Prevent graft rejection2. Psoriasis |
|
|
Difference between cyclosporins and tacrolimus |
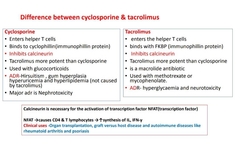
|
|
|
Proliferation signal inhibitor |
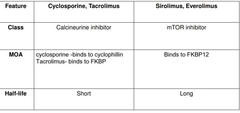
Eg- Sirolimus, Everolimus • MOA enters T lymphocytes &binds with FKBP12 Sirolimus +FKBP 12 →↓mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) blocks the progression of activated T cells from G1 to S phase of cell cycle and thus their proliferation. • Oral, metabolized by hepatic CYP3A4 • Used with corticosteroids/cyclosporins • Everolimus shorter half life • Clinical uses-Prevents graft rejection, Coronory stents, Stem cell transplantation • Uses- bone marrow depression, hepatotoxicity, hyperlipidemia |
|
|
Purine synthesis inhibitor MOA and uses |
Mechanism of action: Preferentially suppresses cell mediated immune reactions Mycophenolate mofetil inhibits ionisine monophosphate dehydrogenase This enzyme is necessary for de novo synthesis of purine. Inhibits both T and B lymphocytes 1. GI disturbance and myelosuppression are adverse effects 2. It does not cause nephrotoxicity |
|
|
Thalidomide MOA and uses |
MOA- Thalidomide inhibits TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor α), interleukins, NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor cells • Antiangiogenic , immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects • Sedative drug withdrawn due to teratogenic effects • Clinical -erythema nodosum leprosum, multiple myeloma, SLE Adverse effects • Teratogenic, peripheral neuropathy, constipation, hypothyroidism, ↑thrombosis |
|
|
Cytotoxic agents |
Cyclophosphamide, methatrexate |
|
|
Cyclophosphamide MOA and uses and toxicity |
Alkylating agent ,Cyclophosphomide, • MOA, destroys lymphocytes while they are in proliferative phase Effective against both B and T lymphocytes Clinical uses: • High doses to prevent bone marrow transplant • Low doses used in auto immune disorders like bleeding disorders Childhood nephrotic syndrome, SLE systemic lupus erythematous Toxicity • Pancytopenia • Heamorrhagic cystitis • cardiotoxicity |
|
|
Methatrexate uses and adverse effect |
Antineoplastic agent.Dihydrofolate reductase inhibito r • Immuno suppressant • Uses, rheumatoid arthritis • Adverse effect, hepatotoxicity |
|
|
Antimetabolite |
Azathioprine. are purine metabolism inhibitor • Prodrug and activated to 6 mercarptopurine • It is metabolized by xanthine oxidase • Cannot be given along with allopurinol(xanthine oxidase inhibitor) • Clinical uses: Prevention of organ transplant rejection, glomerular nephritisSLE,Rheumatoid arthritis • ADR – Bone marrow suppression, increased susceptibility to infections |
|
|
Axathioprine MOA |
MOA 6 Mercaptopurine blocks purine metabolism inhibition of neuclic acid synthesis(DNA nad RNA) inhibits T and B lymphocytes ↓immunological responses |
|
|
Pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor |
Leflunomide |
|
|
Leflunomide MOA |
MOA, Active metabolite inhibits dihydroorate dehydrogenase inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis ↓ T lymphocyte proliferation( ↓CMI)+ ↓ B lymphocytes( ↓autoantibodies) • Rheumatoid arthritis, graft rejection |
|
|
Monoclonal antobodies |
Alemtuzumab Monoclonal antibody attack antigen expressed in lymphocytes. Antibody being IgG1. Inactivates T&B lymphocytes Infliximab IgG1 antibody having TNF α (antiinflammtory activity) expressed in inflammatory cells Clinically - • alemtuzumab (antibodies on lymphocytes)-Chronic lymphocytic leukemia • Infliximab (Anti TNF antibody)- Indicated in Rheumatoid arthritis & Crohn’s disease |
|
|
Immunostimulants |
Roferon. Interleukin-adesleukin. Recombinant GCSF (fligrastim). Recombinant GM CSF (sargramostatim). Levamisole. BCG,bacillus calmette Guer. ADR - Agranulocytosis |
|
|
Uses of roferon? Uses of Interleukins , Aldesleukin? |
Interferons (INF α, INF β) Antiviral agents , Roferon • Clinical use , Hepatitis B, • Adr, flu like symptom, rashes Interleukins , Aldesleukin (IL,2) • Cellular immunity is stimulated used to treat skin and kidney cancer • Adr, weight gain, low BP • Clinical use , is malignant melanoma and renal carcinom a |
|
|
Uses of colony stimulating factors |
colony stimulating factor • Recombinant GCSF , Filgrastim • Recombinant GM CSF – sargramostatim • useful for chemotherapy and myelosuppression |
|
|
Uses of levamisole |
Levamisole( Antihelmenthic drug) • Restores depressed immune function of B, T cells, Monocytes, Macrophages • Clinical use , along with 5FU for treatment of colorectal carcinoma after surgery |
|
|
Uses of ADR -Agranulocytosis? Uses of BCG,bacillus calmette Guerin? |
ADR , Agranulocytosis • Clinical uses 1)Treatment of pediculosis • BCG,bacillus calmette Guerin is a viable stain of Mycobacterium bovis • Clinically used, intravesical therapy of superficial bladder cancer • Adverse Effects –Hypersensitivity, Shock, Chills |

