![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two listed benefits and two listed detriments of the immune system?
|
Beneficial:
Protection from Invaders Elimination of Altered Self Detrimental: Discomfort (inflammation) Damage to self (autoimmunity) |
|
|
What are the three general tiers agains invading organisms?
|
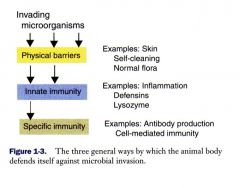
Physical barriers may be considered to be a type of innate immunity
|
|
|
What are examples of physical barriers against invading microorganisms?
|
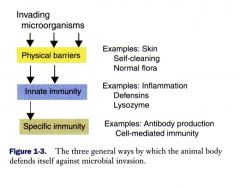
Skin, self-cleaning, normal flora, gut villi, lung cilia
|
|
|
What are examples of innate immune defense against invading organisms?
|
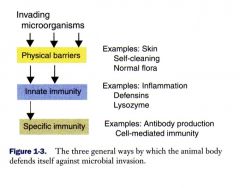
Inflammatory responses: defensins, macrophages), lysozymes, neutrophils, dendritic cells, NK cells, mast cells, eosinophils
|
|
|
What are examples of specific immune system responses against invading organisms?
|
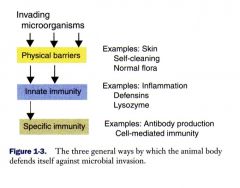
Antibody production (B cells)
Cell-mediated immunity (T cells) |
|
|
How long does specific immunity take versus innate immunity?
|
Innate takes 2-6 hours, specific takes 5-7 days.
|
|
|
What are the components of the humoral response of the innate system?
|
cytokines: Complement, interferon, TNF, stuff like that
|
|
|
What are the components of the cellular response of the innate system?
|
dendritic cells, NK cells, mast cells, eosinophils, macrophages and neutrophils
|
|
|
What are the components of the humoral response of the acquired system?
|
antibodies (immunoglobulins)
|
|
|
What are the components of the cellular response of the acquired system?
|
T-cells, B-cells and other effector cells
|
|
|
Is innate immunity or acquired immunity antigen dependent?
|
Acquired immunity
|
|
|
Is innate immunity or acquired immunity antigen specific?
|
Acquired immunity
|
|
|
Does innate immunity or acquired immunity have an immunologic memory?
|
Acquired immunity
|
|
|
Does innate immunity or acquired immunity have a time lag?
|
Acquired immunity
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of innate immunity of the skin?
|
The squamous cells secrete sweat for flushing and the cells themselves desquamate;
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of innate immunity of the GI tract?
|
peristalsis, low pH, bile salts, and fatty acids
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of innate immunity of the lungs?
|
There are surfactants and the tracheal cilia act as a mucociliary elevator
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of innate immunity of the nasopharynx and eye?
|
Flushing with tears, mucus, and saliva, and lysozymes
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of innate immunity of the blood and lymphoid organs?
|
phagocytes and NK cells kill through phagocytosis and direct and antibody dependent cytololysis
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of innate immunity of the serum and other serous fluids?
|
Iron deprivation through lactoferrin and transferrin.
Antivral proteins and phagocytic action of the interferons and TNFa Peptidoglycan hydrolysis of the lysozymes opsonization, enhanced phagocytosis and inflammation of by fibronection and complement. |
|
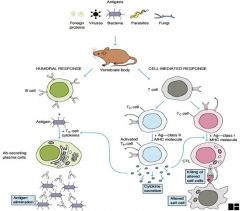
How much of this can you explain/understand?
|
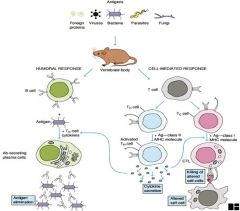
Pastey says that if you get this, you get 25% of immunology.
Here's some help: The B-Cells are producing antibodies. The Cell-mediated response is always T-Cells. There are two kinds of T-Cells – helper cells, Th, and Cytotoxic T-Cells, Tc. The T-Cell receptors recognize segments of amino acids. On the Tc cells, the molecule binds to it and the CD8 process next to the binding site, binds to the MHC (major histocompatibility complex I or II). The Tc cells are very important in killing virus-infected cells and tumor cells. The Th help either B-Cells (Th2) or T-Cells (Th1). Without the Th, neither B- or T-Cells can work. These guys have the CD4 |
|
|
When do T-cells differentiate into Th or Tc cells?
|
After they leave the thymus.
|
|
|
What type of cell do B-cells become?
|
plasma cells that release antibodies
|
|
|
What type of cells do RBCs, platelets, granulocytes and macrophages come from?
|
Myeloid cells.
|
|
|
What type of cells to T and B-cells come from?
|
Lymphoid cells
|

