![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
____ proved that infectious agents that cause disease are by microorganisms.
|
Robert Koch
|
|
|
List the four categories of disease causing microorganisms.
|
1. Viruses
2. Bacteria 3. Pathogenic Fungi 4. Parasites (eukaryotic) |
|
|
True or False
The adaptive immune response is specific and has "memory" |
True
|
|
|
____ & ____ discovered the crude properties of antibodies.
|
Behring and Kitasato
|
|
|
Antigen ---> _____ ______
|
Antibody Generation
|
|
|
Both innate and adaptive immune responses depend upon the activity of what cells?
a. RBC's b. macrophages c. leukocytes d. none of the above |
c. leukocytes (aka WBC)
|
|
|
Innate immunity largely involves ____ & ____.
|
granulocytes and macrophages
|
|
|
Granulocytes are AKA
|
polymorphonuclear leukocytes
|
|
|
Adaptive immune system depends on ____.
a. polymorphonuclear leukocytes b. erythrocytes c. macrophages d. none of the above |
d - none of the above- they depend on lymphocytes
|
|
|
The cells of the immune system originate in the ____.
|
Bone marrow
|
|
|
_____ gives rise to stem cells of limited potential.
|
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
|
|
|
Flowchart the different types of blood cells and their relationship lineages.
|
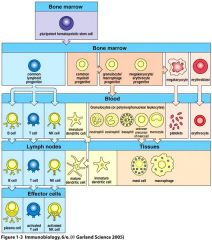
Figure 1.3
|
|
|
The myeloid progenitor is the precursor of which cells?
|
granulocytes
macrophages dendritic cells mast cells (of innate system) My GranMa DenMas |
|
|
Macrophages are the mature form of _____.
|
Monocytes
|
|
|
______ cells are specialized to take up antigen, process it, and display it for recognition by T lymphocytes.
a. Dendritic Cells b. Granulocytes c. Mast Cells d. Macrophages |
a. Dendritic Cells
|
|
|
Immature dendritic cells migrate to areas that both ____ and ____.
|
Phagocytic and macropinocytic
|
|
|
Mature denditic cells migrate to _______.
|
The lymph nodes
|
|
|
What are the function of mast cells?
|
Although mostly involved with allergy responses, they also play a role in protecting mucosal sufaces against pathogens. Also- plays a role in vasuclar permeability.
|
|
|
Which of the three granulocytes are the most numerous?
|
Neutrophils
|
|
|
Lack of neutrophils can lead to ____ infections.
|
Bacterial
|
|
|
Eosinophils are important against ____ infections.
|
Parasitic
|
|
|
Basophils function similarily to _______.
|
Mast Cells
|
|
|
The ____ gives rise to the lymphocytes and NK cells of the innate immunity - and to some extent dendritic cells
|
Common lymphoid progenitor
|
|
|
Which are greater in number: myeloid progenitor cells or lymphoid progenitor cells?
|
Myeloid
|
|
|
Draw a macrophage, and give the activated function.
|
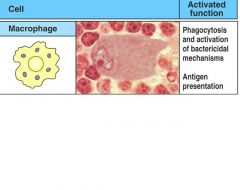
Figure 1-4
|
|
|
Draw a dendritic cell and give its activated function
|
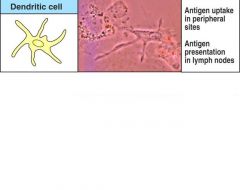
Figure 1-4
|
|
|
Draw a Neutrophil and give its activated function
|
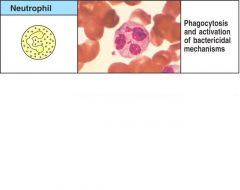
Figure 1-4
|
|
|
Draw an eosinophil and give its activated function
|
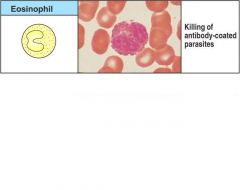
Figure 1-4
|
|
|
Draw a basophil and give its activated function
|
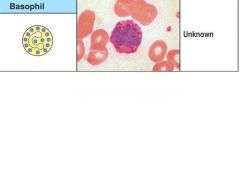
Figure 1-4
|
|
|
Draw a mast cell and give its activated function
|
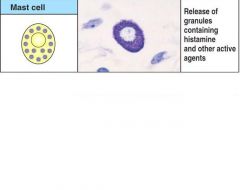
Figure 1-4
|
|
|
In order for small lymphocytes to become functional they require both an encounter with an antigen and with _____.
|
co-stimulatory molecules
|
|
|
What are the antigen receptors of B-lymphocytes called?
|
membraine immunoglobulin (mIg)
|
|
|
Lymphoid organs are divided broadly into
a. ventral and secondary organs b. peripheral and primary lymphoid organs c. central and primary lymphoid organs d. more than one of the above |
b. peripheral and primary lymphoid organs
|
|
|
Draw a lymph node and its parts
|
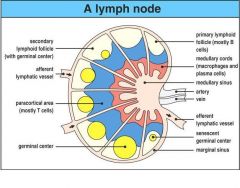
Figure 1-8
|
|
|
What is the function of peripheral lymphoid organs
|
To trap antigen-bearing dendritic cells to allow initiaiton of adaptive immune responses, and to provide signals that ustain recirculating lymphocytes
|
|
|
3 types of lympoid tissues?
|
GALT
BALT MALT |
|
|
Draw and label the transverse and longitudinal section of the white pulp
|
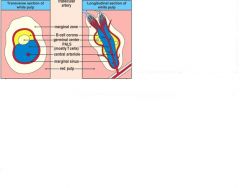
Figure 1-9
|
|
|
GALT contains which of the following?
a. tonsils b. adenoids c. appendix d. peyer's patches e. all of the above |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Peyer's patches contain what kind of specialized cells?
|
M cells (multi-fenestrated)
|
|
|
Lymphocytes are able to enter peripheral lymphoid organs via ____?
|
HEV (high endothelial venules)
|
|
|
What are the three major types of peripheral lymphoid tissues and their functions?
|
spleen--> collects antigen from blood
lymph nodes--> collect antigens from sites of infection in the tissues mucosal associated lymphoid tissues --> collects antigens from epithelial surfaces |
|
|
T cells pro and diff into what?
|
antigen specific effector cells
|
|
|
B cells pro and diff into what?
|
antibody-secreting cells
|
|
|
Cytokines secreted from macrophages function to ___?
|
increase permeability of blood vessels
|
|
|
Chemokines secreted from macrophages function to___?
|
Call for help- neutrophils come first followed by monocytes that mature into macrophages
|
|
|
Briefly describe how adaptive immune system is booted up.
|
Immature dendritic cell in peripheral tissues ingest pathogens either by RME or macropinocytosis- migrate to regional lymph nodes via afferent lymphatics-arrive as a mature dendrite presenting its angtigen to stimulate clonal expansion and activate specific naive t lymphocytes
|
|
|
True or False
The immature dendritic cell performs phagocytosis |
True (page 13)
|
|
|
B cells pro and diff into what?
|
antibody-secreting cells
|
|
|
Cytokines secreted from macrophages function to ___?
|
increase permeability of blood vessels
|
|
|
Chemokines secreted from macrophages function to___?
|
Call for help- neutrophils come first followed by monocytes that mature into macrophages
|
|
|
Briefly describe how adaptive immune system is booted up.
|
Immature dendritic cell in peripheral tissues ingest pathogens either by RME or macropinocytosis- migrate to regional lymph nodes via afferent lymphatics-arrive as a mature dendrite presenting its angtigen to stimulate clonal expansion and activate specific naive t lymphocytes
|
|
|
True or False
The immature dendritic cell performs phagocytosis |
True (page 13)
|
|
|
Additional material that is added to increase a response to an immunizing antigen is called a ____
|
adjuvent
|
|
|
Lymphocyte _____ _____ ensures that billions of lymphocytes in the body collectively carry millions of differetn antigen receptor specicifities.
|
receptor repertoire
|
|
|
Clones secrete _____ antibodies.
|
clonotypic
|
|
|
List the four basic principles of the clonal selection hypothesis
|

Figure 1.15
|
|
|
What is the central principle of adaptive immunity?
|
Clonal selection of lymphocytes
|
|
|
Define clonal deletion
|
The removal of deveoping lymphocytes that are potentially self reactive
|
|
|
Approximately how many different biochemically disitnct forms of the constant portion of an antibody achieve?
|
Four to five
|
|
|
What is the function of the constant region in an antibody?
|
It determines how the antibody disposes of the pathogen once it is bound
|
|
|
True or False
Only heavy chains have constant and variable regions; light chains have only variable regions |
False-
Both heavy and light chains have both constant and variable regions |
|
|
Draw the basic schematic structure of an antibody
|
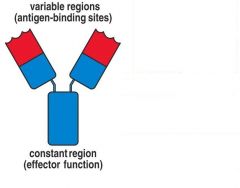
Figure 1.16
|
|
|
Draw a more complicated antibody
|
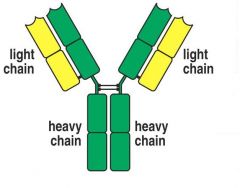
Figure 1.17
|
|
|
How do developing lymphocytes create antigen diversity and uniqueness?
|
By rearranging its receptor gene segments
|
|
|
Aside from rearrangements of receptor gene segments, how else is diversity of antigen receptors produced?
|
junctional diversity and combinatorial diversity
|
|
|
How are B cell and T cell maturation regulated?
|
Through survival signals from the antigen receptore
|

