![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
From where do naive T cells receive their survival signals?
|
From encounters with self-peptied:selfMHC complexes and also via their IL-7 receptors
|
|
|
T-cells that are prepped to remove an antigen are called ____; these act on _____
|
armed effector T cells
target cells |
|
|
The most important antigen presenting cells are the _____.
|
dendritic cells
|
|
|
Which system initially induces tissue dendiritic cells the innate or the adaptive?
|
Innate - see page 319
|
|
|
What distinguishes mature dendiritic cells from one another?
|
Their surface molecules, the co-stimulatory molecules
|
|
|
List the professinal antigen presenting cells
|
Dendritic Cells
B cells Macrophages |
|
|
Pathogens that accumulate in large numbers inside macrophage and dendriditic cell vesicles tend to stimulate the differentioation of ___ cells
|
Th1
|
|
|
Extracellular antigens stimulate the production of Th__ cells
|
Th2
|
|
|
Th1 induce b cells to make ____ antibodies- why?
|
IgG - because they are effective at opsonizing extracellular pathogens for ingestion by phagocytic cells
ALSO - IgM - to initiate the humoral immune response via activation of niave antigen specific B cells |
|
|
Th2 induces b cells to make ____ antibodies
|
IgA and IgE and some weakly neutralizing and/or weakly opsonizing subtypes of IgG
|
|
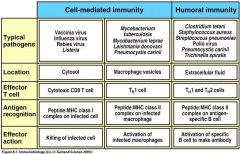
Fill in the Blanks
|
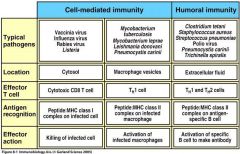
Figure 8.1-page 320
|
|
|
True or False
Both Th1 and Th2 cells can also contribute to humoral immunity by the production of antibodies |
True
|
|
|
The major components of cell mediated immunity are ____.
|
armed effector t cells
|
|
|
The activation and clonal expansion of a naive T cell on initial encounter with antigen on the surface of an antigen-presenting cell is often called ____.
|
Priming
|
|
|
Where are adaptive immune responses initiated in regards to the t-cell response?
|
In the peripheral lymphoid tissues
|
|
|
Pathogens infecting mucosal tissues accumulate where?
|
In Peyer's patches of the gut or tonsils
|
|
|
Pathogens in the blood are trapped where?
|
Spleen
|
|
|
In what ways does the innate immune response play a role in antigen delivery to naive T cells?
|
Inflammation- increases entry of plasma into infected tissue and therefore drainage of tissue into lymph
Induces maturation of tissue dendritic cells via non antigen specific receptors or cytokine signaling (also activates macrophage) |
|
|
True or False
Once in the lymph nodes, dendritic cells can no longer phagocytose antigens |
True
|
|
|
In what part of the lymph nodes are macrophages most likely to be found?
|
Marginal Sinus
|
|
|
Why aren't b-cells very efficient at mounting an adaptive immune response?
|
Antigen specificity (and scarcity) limits the likliehood of encountering a niave t cell specific for the same antigen
|
|
|
Where do naive t cells enter lymphoid tissues
|
HEV
|
|
|
The main classes of adhesion molecules involved in lymphocyte interactions are ____.
|
The selectins, integrins, members of the immunoglobin superfamily, and some mucin-like molecules.
|
|
|
____: the selectin expressed on leukocytes
|
L-selectin-CD26L
|
|
|
____: the selectin expressed on vascular epithelium
|
P-selectin - Cd62P
AND E-selectrin - Cd62E |
|
|
L selectin binds to the carbohydrate moiety ____ which bind to the following vasucal addressins: ___
|
sulfated sialyl-Lewis^x of the vascular addressins CD34 and GlyCAM-1 and in mucosa - MAdCAM-1 (gut)
|
|
|
What proteins are required fir t-cells to cross the endothelial barrier in lymphoid tissue?
|
integrins and the immunoglobin superfamily.
|
|
|
What is responsible for signaling integrines?
|
Chemokines
|
|
|
Migration of naive T cells into lymphoid tissues is mediated by ____.
|
CCL21 AKA SLC (secondary Lymphoid Tissue Checmokine)
|
|
|
CCL21 (aka SLC) is expressed by _____.
|
High vascular endothelial cells, stromal cells, and dendritic cells in lymphoid tissues.
|
|
|
All t cells exoress a B2 integrin known as ____.
|
LFA-1 (lymphocyte function associated antigen)
|
|
|
LFA-1 plays a role in ______.
|
Migration of both naive and effector T cells out the blood. It is also thought to be one of the most important adhesion molecules for T cell activation because antibodies against them inhibit activation of niave and armed effector T Cells.
|
|
|
In an integrin, the B chain defines the ____ of the integrin and the alpha chain defines the _____.
|
class
different integrins within a class |
|
|
A_B_ integrin = LPAM-1
|
A4B7=lymphocyte peyer's patches
|
|
|
LFA:___ (all T cells)
LPAM-1:___(subset of naive cells) VLA:___ (activated effector T cells) |
LFA-1:ICAM-1
LPAM-1:MAdCAM-1 VLA:VCAM-1 |
|
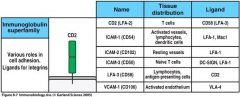
Fill in the Blanks
|
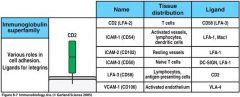
Figure 8.7 page 326
|
|
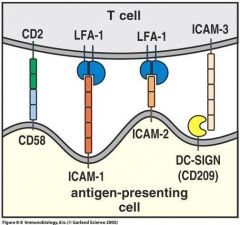
Fill in the Blanks
|
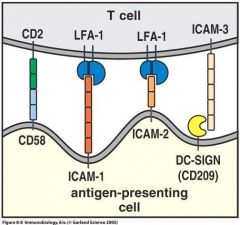
Figure 8.8 page 327
|
|
|
True or False
Naive CD8 T cells seem to require a stronger co-stimulatory signal than CD4 T cells. |
True
|
|
|
List the two co-stimulary molecules.
|
B7.1 (CD80)
B7.2 (CD86) |
|
|
What is the receptor for B7 molecules on the T cell?
|
CD28
|
|
|
Ligation of CD28 and B7 molecules is required for what process?
|
Clonal Expansion of naive T cells
|
|
|
True or False
Both B7 molecules and CD28 are members of the immunoglobuline superfamily |
True
|
|
|
CD40 and CD40 ligand belong to the ____ family of receptors and ligans
|
Tumor necrosis
|
|
|
CD40 helps to do what?
|
Sustain or modify the co-stimulatory signal
|
|
|
What other TNF molecules (besides CD40 and CD40L)contribute to co-stimulation of T cells?
|
4-1BB (CD137)
4-1BBL ( |
|
|
What is T-cell:antigen-presenting cell dialogue?
|
The bidirectional stimulation of both APC and T-cells via the receipt of activating signals
|
|
|
What is the finction of CTLA-4?
|
It's a B molecule that delivers an inhibitory signal to the activated T cell
|
|
|
Lack of CTLA-4 in mice leads to what?
|
massive overgrowth of lymphocytes
|
|
|
Define anergy.
|
The state of a T-cell whereby activation by a specific antigen cannot be achieved, even when presented by a professional APC.
|
|
|
Whys is it necessary for only one cell to deliver both the antigen specific signal and co-stiulatory signal?
|
To prevent immune responses to self antigens.
|
|
|
True or False
Leukocytes only adhere to arteries, they do not adhere to veins. |
False
Leukocytes adhere to veins only, NOT arteries |
|
|
What receptor does a dendritic cell commonly use to take up antigens?
|
DEC205
|
|
|
Give an example of a typical immature dendritic cell.
|
Langerhans' cells of the skin
|
|
|
Langerhans' cells contain ___ granules.
|
Birbeck
|
|
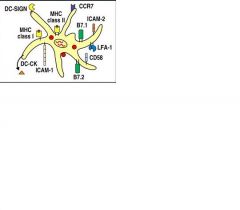
Is this an immature or mature dendritic cell, and how do you know?
|
It is a mature dendritic cell because it has B molecules and lots of adhesion molecules
|
|
|
Once in the lynphoid tissues, dendritic cells secretes the chemokine _____ that attracts naive t cells
|
DC-CK (CCL18)
|
|
|
LPS receptors are found on ___ and ___ and associate with _____ (receptor) which then activates the transcription factor ____.
|
macrophages and dendritic cells
TLR-4 NFkB |
|
|
How do pathogens that have evolved to esacape phagocytic receptors eventually get taken up by dendritic cells?
|
Via macropinocytosis
|
|
|
In evasive bacteria- what causes recognition after ingestion by dendritic cells?
|
unmethylated CpG dinucleotide motifs by TLR-9
-exposure to this DNA actovates NFkB (a transcription factor) and MAP kinase signaling pathways which leads to cytokine production. ALSO HSP |
|
|
True or False
Viral peptides are only presented on class 1 MHC on dendritic cells |
False- They are presented on both MHC 1 and MHC 2
(page 333) |
|
|
Dendritic cells can present ____ which are associated with graft rejections.
|
Alloantigens
|
|
|
B cells can easily uptake ___ antigens via receptor mediated endocytyosis.
|
soluble
|

