![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which are the upregulated and downregulated acute phase reactants |
Unregulated: -C-reactive protein, opsonin, fixes complement and facilitates phagocytosis, marker of inflammation -ferritin, binds and sequesters iron to inhibit microbial iron scavenging -fibrinogen, coagulation factor and promotes endothelial repair -hepcidin prevents release of iron bound by ferritin - serum amiloyd a, prolonged elevation can lead to amyloidosis Downregulated: -Albumin, reduction conserves amino acids for positive reactants -transferrin internalized by macrophages to sequester iron |
|
|
Types of complement activation pathways |
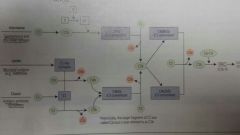
Classical pathway, ig G or ig M mediated Alternative pathway, microbes surface molecules Lectin pathway, mannose or other sugars on microbes surface |
|
|
Chemotactic factors for neutrophils |
C5a, il-8, leukotriene b4, formyl-methionyl-peptides and fibrinopeptides |
|
|
Function of C3b |
Opsonization and clear immune complexes |
|
|
Anaphylaxis related complement |
C3a, c4a and c5a |
|
|
Inhibitors of complement |
Decay accelerating factor and C1 esterase inhibitor prevent complement on self cells |
|
|
Complement disorders |
-C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency, cause angioedema, ace inhibitors are contraindicated -c3 deficiency, increase risk of severe, recurrent piogenic sinus and respiratory tract infections, increase risk to hs type III -C5-C9 deficiency, increase susceptibility to neisseria bacteremia - DAF deficiency, complement mediated rbc lysis and paroxymal nocturnal hemoglobinuria |

